First Aid Vocabulary Packet
advertisement

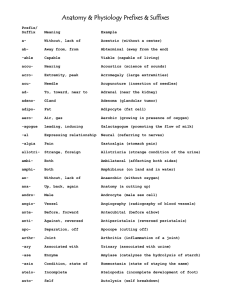
Athletic Medicine I First Aid Vocabulary For the next three Mondays, you will have a quiz on a grouping of vocabulary words. I will make a review assignment available each Friday before the quiz. Quiz Schedule 1. Monday, October 13: Group 1 (4th period); Tuesday, October 14 (3rd period) 2. Monday, October 20: Group 2 3. Monday, October 27: Group 3 Group 1 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Avulsion: Wound in which tissue is torn away from the body. Accident: Unforeseen or unplanned event or circumstance. Acute Injury: A sudden injury, usually associated with a traumatic event. Ambulation: To walk or move about from place to place. Anisocoria: Pupils of unequal sizes. Anoxia: Absence of oxygen to an organ or tissue. Atrophy: To waste away. Axilla: Armpit. Bandage: A strip of fabric used to dress and cover up wounds. Bilateral: Affecting both sides. Chronic Injury: Long-term injury usually related to overuse. Closed Fracture: Broken bone that does not penetrate the skin. Crepitus: A grating sound or sensation produced by friction between bone and cartilage, or the fractured parts of a bone. Cyanosis: A bluish discoloration to the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of blood. Debridement: The removal of lacerated, devitalized, or contaminated tissue. Diastolic Blood Pressure: The pressure in the arteries when the heart is between beats. Diplopia: Double vision. Dressing: A sterile pad or compress applied to a wound to promote healing and/or prevent further harm. Dyspnea: Difficult breathing; shortness of breath. Ecchymosis: Escape of blood into the tissues from ruptured blood vessels; marked by black-and-blue spot. Edema: Abnormal or excess accumulation of fluid in the tissues; swelling. Elevation: Act of raising something (body part). Epistaxis: Bloody nose. Etiology: The cause of disease or injury. Hematuria: The presence of blood in the urine. Hemorrhage: Abnormal discharge of blood. Hypertrophy: Excessive development of an organ or tissues. Hypertension: Abnormally high blood pressure. Group 2 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Hypermobility: Having joints that can move past the normal range of motion. Hyperventilation: Breathing deeper and more rapidly than normal. Hypoxia: Condition in which the body, or part of the body, is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Idiopathic: Relating to any disease or condition that arises spontaneously or for which the cause is unknown. Incision: Surgical cut made in the skin and/or flesh; usually has straight, even edges. Injury: Harm or damage done to the body. Joint: Place at which bones articulate (connect). ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Joint Capsule: Thin, fibrous sac containing fluid, which encloses a joint. Laceration: A cut or tear in flesh; edges are usually jagged. Luxation: Dislocation of an anatomical part. Microtrauma: Very slight injury or lesion. Muscle: A body tissue consisting of long cells that contract when stimulated and produce motion. Myositis: Muscle inflammation. Necrosis: Death of body tissue. Neuritis: Inflammation of a nerve(s). Neuroma: Tumor of nerve tissue. Nystagmus: Involuntary eye movement. Occlusion: Blockage or closing of a blood vessel or hollow organ. Open Fracture: Broken bone that penetrates the skin. Palpate: Examination of a body part by touch. Pathology: Structural and functional changes that result from injury. Point Tenderness: An area of tenderness limited to 2-3 centimeters in diameter. Primary Assessment: Assessment used to determine any life-threatening injuries. Puncture: Small hole caused by a pointy, sharp object. Quadriplegia: Inability to move and feel both arms and legs. Referred Pain: Pain located somewhere other than the site of injury/trauma. RICE; Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation. Rhinitis: Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose; usually caused by a cold. Secondary Assessment: Takes a closer look at the injury once life-threatening situations have been ruled out. Group 3 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Seizure: Convulsions resulting from abnormal electrical discharges in the brain. Sign: Indicator of disease that can be seen. Sprain: Overstretching or rupture of a ligament. Strain: Overstretching or rupture of a muscle. Subcutaneous: Under the skin. Subluxation: Partial dislocation; bone returns to normal position on its own. Symptom: A change in the body or mind which indicates that a disease or injury is present (cannot be seen). Syndrome: A disease or disorder that involves a particular group of signs and/or symptoms. Systolic Blood Pressure: Pressure in the arteries when the heart is beating. Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon. Tendon: Band of dense, fibrous connective tissue that connects a muscle to bone. Tinea: Fungal infection. Traumatic: An injury to living tissue caused by an extrinsic agent. Vasoconstriction: Narrowing of blood vessels. Vasodilation: Widening of blood vessels. Vasospasm: Spasm of the blood vessels that leads to vasoconstriction. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Volar: Palm of the hand. Xiphoid Process: Small cartilaginous extension of the lower part of the sternum. Abduction: Movement of a limb away from the midline. Adduction: Movement of a limb toward the midline. Jaundice: Yellowish pigment of the skin. Inversion: Movement of the ankle medially so the soles of the feet face each other. Eversion: Movement of the ankle laterally that turns the soles of the feet away from each other. Normal Blood Pressure: 100-120/70-80 Muscle: Soft tissue connected to bones to allow movement. Shock: Life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough oxygen.