1 - Online Campus
advertisement

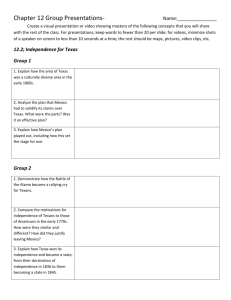
QUIT 9 Expanding Markets and Moving West CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE MAP GRAPH SECTION 1 The Market Revolution SECTION 2 Manifest Destiny SECTION 3 Expansion in Texas SECTION 4 The War with Mexico VISUAL SUMMARY HOME 9 Expanding Markets and Moving West CHAPTER OBJECTIVE To understand the causes and consequences of western settlement and to summarize the events surrounding the independence of Texas and the war with Mexico HOME 9 Expanding Markets and Moving West INTERACT WITH HISTORY In the 1820s and 1830s the country was energized by new inventions and new business. Now it is 1840, and an economic downturn dampens the hopes of workers and business owners alike. Newspaper ads urge Americans to pack up and move west. But many people and nations already inhabit the North American West. Mexico owns a large part of the area, and Native Americans have been living there for centuries. What are the ways that a nation increases its territory? Examine the Issues • What are some reasons countries expand their borders? • What might be benefits or drawbacks of expansion? HOME 9 Expanding Markets and Moving West TIME LINE The United States The World 1825 The Erie Canal connects the East to the West. 1828 Andrew Jackson is elected president. 1828 Uruguay becomes an independent republic. 1830 Joseph Smith establishes the Mormon Church. 1830 Revolutions occur in Belgium, France, and Poland. 1832 Chief Black Hawk leads Sauk rebellion. Andrew Jackson is reelected. 1833 Santa Anna is elected president of Mexico. 1835 Ferdinand I becomes emperor of Austria. 1836 Martin Van Buren is elected president. continued . . . HOME 9 Expanding Markets and Moving West TIME LINE The United States The World 1837 John Deere invents the steel plow. 1837 Constitutional revolts occur in Lower and Upper Canada. 1840 Benito Juárez begins liberal reform movement in Mexico. 1841 John Tyler becomes president when President William Henry Harrison dies. 1844 James K. Polk is elected president. 1847 U.S. wins Mexican-American War. 1848 Gold is discovered in California. Zachary Taylor is elected president. 1848 Marx and Engels issue the Communist Manifesto. HOME 1 The Market Revolution KEY IDEA Technological changes created greater interaction and more economic diversity among the regions of the nation. OVERVIEW ASSESSMENT HOME 1 The Market Revolution OVERVIEW MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW Technological changes created greater interaction and more economic diversity among the regions of the nation. The linking of markets continues today, as new technologies are opening the U.S. to globalized trade. TERMS & NAMES • specialization • capitalism • Samuel F. B. Morse • market revolution • telegraph • Cyrus McCormick • entrepreneur • John Deere ASSESSMENT HOME 1 The Market Revolution ASSESSMENT 1. Look at the time line below to help organize your thoughts. List the important innovations in transportation, communication, and manufacturing during the early 19th century. Erie Canal opens. Deere invents steel plow. Goodyear develops vulcanized rubber. 1825 1837 1839 Morse sends first telegraph message. 1844 Howe patents sewing machine. 1846 1850 continued . . . HOME 1 The Market Revolution ASSESSMENT 2. Compare economies of the different regions of the United States in the mid-1800s. ANSWER North—urban, industrial South—agrarian; dependent on slave labor Midwest—agricultural; important in supplying food to the East and to Europe continued . . . HOME 1 The Market Revolution ASSESSMENT 3. Why were the reaper and the steel plow important? ANSWER The two inventions allowed farmers to develop and farm their land more efficiently and cheaply. continued . . . 1 HOME The Market Revolution ASSESSMENT 4. During the 1830s and 1840s, transportation and communication linked the country more than ever before. How did these advances affect ordinary Americans? Think About: • the new kinds of transportation • specific changes in communications • the new industries of the time period ANSWER Expanded commuter lines; enabled cities to grow outward End of Section 1 MAP HOME GRAPH 2 Manifest Destiny KEY IDEA Americans moved west, energized by their belief in the rightful expansion of the United States from the Atlantic to the Pacific. OVERVIEW ASSESSMENT MAP HOME GRAPH 2 Manifest Destiny OVERVIEW MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW Americans moved west, energized by their belief in the rightful expansion of the United States from the Atlantic to the Pacific. The South and Southwest are now the fastest-growing regions of the United States. TERMS & NAMES • manifest destiny • Mormons • “Fifty-Four Forty or Fight!” • Joseph Smith • Oregon Trail • Treaty of Fort Laramie • Brigham Young • Santa Fe Trail ASSESSMENT MAP HOME GRAPH 2 Manifest Destiny ASSESSMENT 1. Look at the chart to help organize your thoughts. Compare the motivations of travelers on the Oregon, Santa Fe, and Mormon trails. Trail Motivations Oregon Trail New economic opportunities and new land New markets for goods and services Expanding trade with China and Japan Mormon Trail New economic opportunities and new land Missionaries wanted to convert Native Americans Freedom from religious persecution Santa Fe Trail New economic opportunities and new land New markets for goods and services continued . . . MAP GRAPH 2 HOME Manifest Destiny ASSESSMENT 2. What were the benefits and drawbacks of the belief in manifest destiny? Think About: • the various reasons for the move westward • the settlers’ point of view • the impact on Native Americans • the impact on the nation as a whole ANSWER Benefits: the wide range of new opportunities for settlers; westward expansion would result in a nation that stretched across the continent and that had vast resources. Drawbacks: treatment of Native Americans End of Section 2 HOME 3 Expansion in Texas KEY IDEA Mexico offered land grants to American settlers, but conflict developed over religion and other cultural differences, and the issue of slavery. OVERVIEW ASSESSMENT HOME 3 Expansion in Texas OVERVIEW MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW Mexico offered land grants to American settlers, but conflict developed over religion and other cultural differences, and the issue of slavery. Today, the state of Texas shares an important trading partnership with Mexico. TERMS & NAMES • Stephen F. Austin • Alamo • Antonio López de Santa Anna • Texas Revolution • land grant • Republic of Texas • Sam Houston • annex ASSESSMENT HOME 3 Expansion in Texas ASSESSMENT 1. Look at the chart to help organize your thoughts. Analyze the relationship between Mexican authorities and Anglos settling in Texas. Mexico Goals Actions Outcomes To protect northern provinces and bring in U. S. goods Offers land grants, closes borders, and institutes patrols Refuses purchase offers and loses Texas to the United States Settlers To use land grants to set up homesteads Ignore Mexican rules and border restrictions; try to negotiate with Mexico Win independence, form Republic of Texas continued . . . HOME 3 Expansion in Texas ASSESSMENT 2. Compare and contrast Santa Anna and Austin as leaders. Think About: • Santa Anna’s role as president of Mexico • Santa Anna’s qualities as a military leader • Austin’s settlement in Texas • Austin’s abilities as a negotiator ANSWER Santa Anna was ambitious, restless, and sometimes reckless. Austin was a successful land agent and was strict about the kinds of behavior tolerated in his settlements. continued . . . 3 HOME Expansion in Texas ASSESSMENT 3. Which group or country gained the most from the entry of Texas into the United States? Who lost the most? ANSWER The United States gained a huge portion of land but prompted war with Mexico; Mexico lost land. Southern states gained power in the Senate; Northern states lost control of the Senate. End of Section 3 HOME 4 The War with Mexico KEY IDEA Tensions over the U.S. annexation of Texas led to war with Mexico, resulting in huge territorial gains for the United States. OVERVIEW ASSESSMENT HOME 4 The War with Mexico OVERVIEW MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW Tensions over the U.S. annexation of Texas led to war with Mexico, resulting in huge territorial gains for the United States. The United States has achieved its goal of expanding across the continent from east to west. TERMS & NAMES • Zachary Taylor • James K. Polk • Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo • Stephen Kearny • forty-niners • Republic of California • Winfield Scott • gold rush • Gadsden Purchase ASSESSMENT HOME 4 The War with Mexico ASSESSMENT 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. List the events that formed the boundaries of the contiguous United States. Effect: Causes: Present-Day United States Borders 1846 Britain and the United States set Northwest boundary at 49th parallel. 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo includes Mexican cession. 1853 Gadsden Purchase established current borders. continued . . . 4 HOME The War with Mexico ASSESSMENT 2. How would you evaluate President Polk’s attitude and behavior toward Mexico? Think About: • Polk’s position on expansion • his actions once in office • his relationship with Santa Anna ANSWER POSSIBLE RESPONSE: Polk had expansionist beliefs and a strong conviction that the only way California, New Mexico, and Texas could be brought into the Union was through war. Polk’s secret agreement with Santa Anna not only failed but was unwise and illogical to begin with. continued . . . 4 HOME The War with Mexico ASSESSMENT 3. What were some of the effects of the California gold rush? ANSWER • diversity • population explosion • San Francisco became a major west-coast city. • scarce supplies continued . . . 4 HOME The War with Mexico ASSESSMENT 4. Would you have supported the controversial war with Mexico? Why or why not? ANSWER POSSIBLE RESPONSES: Proslavery forces supported the war and antislavery forces opposed it. From the Mexican perspective, the war was an unjust attempt by the United States to obtain a huge portion of land from a weaker country. End of Section 4