Human Development
advertisement

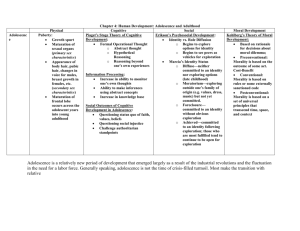
Human Development Developmental Psychology Definition: field of study in psychology that examines how people grow and change throughout the life span of a human Types of Development: - Cognitive Life Span: - Perceptual - Conception - Physical - Infancy - Social - Childhood - Adolescence - Adulthood - Aging - Death Why Study Human Development? • our experiences in one stage affects later stages • studying early stages helps us learn about developmental problems • can learn what types of experiences which foster well adjusted humans in later stages How Do We Study It? • Use Longitudinal & Cross-Sectional method* (interested in people across life span) Concerned with: - hereditary & environmental influences on behavior - discovering if development is gradual (inclined plane) or in stages (climbing stairs) Nature v. Nurture Nature = heredity/genetics • certain behaviors are “biologically programmed” based on nutrition & social experience • Maturation automatic & sequential process of development resulting from genetic signals • Critical Period point in development which a human is best suited to learn Nurture = environment • Mind is a “blank slate” and is written on by environment Nature v. Nurture Q What’s side of the debate are you on? Instructions • Get into Lab Groups • Nature on Left (near side chalkboard) • Nurture on Right (near windows) • Split a piece of paper in half and both sides state their case • Turn them into me and I will evaluate and declare a winner Birth through Childhood Physical Development So, what are you born with? • Physical characteristics (weight/height) • Reflexes (involuntary response) • Certain reflexes exist at birth: - Moro extension of arms when feel loss of support - Palmar hand grasping - Rooting turning to objects w/ check attempting to suck Physical Development Height & Weight: most dramatic gains happen prior to birth • Embryo Stage – 1st 8 weeks = tiny embryo develops fingers, toes, eyes, ears, nose, a heart, & circulatory system • Fetal (Fetus) Stage – lasts until birth & other vital organs form • Infancy (birth to 23 months) – double weight & height in 5 weeks (triple by 1 year) – grow 10 inches a year • Childhood (2 years to adolescence) – gain an avg. of 2-3 inches & 4-6 lbs each year until adolescence Perceptual Development • Definition: process by which infants make sense of the senses to which they are exposed • Five Senses are functional at birth – Newborns can utilize sight (prefer to focus on objects 9 inches or less away from them) – Focus on objects w/contour, contrast, complexity, and movement • Infants prefer new & interesting stimuli (take it all in and learn) • Sense of hearing & smell are better than eyesight at birth Social Development Focus on: the ways in which infants & children learn to relate to other people – Attachment: close emotional relationship between an infant & their caretakers • Secure Attachment: parent serves as a secure base from which to explore • Insecure Attachment: – Insecure tend to cling to parent & be angry when parent returns after separation – Avoidant seek little contact with parent – Contact Comfort: instinctual need to touch & be touched by something soft (i.e. skin) • Harry Harlow's experiment with Monkeys (1959) – Imprinting: process by which immediate attachments are formed by animals during critical period • In humans it does not happen: (takes months to form/no critical period in humans) Social Development – Temperament: characteristic of a child’s mood & activity level • Easy Infants: 40%; adaptable to new situations; predictable in schedule; positive in mood • Difficult Infants: 10%; intense reactions; not adaptable to new situations; negative mood • Slow-to-Warm Infants: 15%; initially withdraw when approached; may warm up later • Average Infants: 35%; do not fit into any of the above categories Social Development Parenting Styles are based on two dimensions: • Warm-Cold • Warm show lots of affection & enjoyment • Cold little affection & enjoyment shown; • Strict-Permissive • Strict impose rules & supervise closely • Permissive less rules & supervision Social Development Parenting Styles: Authoritative: affectionate & loving; sets limits; engages in verbal give-and-take Authoritarian: demands unquestioned obedience; less affection Permissive: few demands made; children allowed to make own decisions; inconsistent discipline Social Development Self-Esteem: value or worth that people attach to themselves Factors which affect: • Secure Attachment = High self-esteem • Ways in which parent react to their children • Love & Acceptance no matter what (Unconditional Positive Regard) • Love only shown when children behave as expected (Conditional Positive Regard) • Also…… Gender & Age Cognitive Development Definition: development of thought process Key Terms: • Schema: basic thought process/structure • Organization: combining & integrating simple schemas • Adaption: modifying existing schema to fit new experiences Theory & Theorist Jean • • • Piaget (1896-1980) Developmental Psychologist Focus how children think CreatedTheory of Cognitive Development Contributions & Focus: • developed a theory of intellectual development based on a stage oriented process of cognition • Belief children will not learn a skill through reinforcement or modeling unless they are cognitively ready to do so • Belief organized information through: • Assimilation: interpreting new info/stimuli based current knowledge known • Accommodation: changing thoughts/ideas through experiences Student Activity Task I • Read & Highlight Piaget’s “Stages of Intellectual Development” • Complete the “Piagetan Tasks” activity (Parts A,B,C) • Complete the “Application of the Stages of Cognitive Development” activity • See me for answers Theory & Theorist Lawrence Kholberg(1927-1987) • Developmental Psychologist • Focus Mental Processing & Moral Decisions • Created Theory of Moral Development Contributions & Focus: • Developed a six stage cognitive theory about the development of children’s moral reasoning • Belief a child’s stage of mental processing influences the way they make moral decisions • Belief child in a certain stage of development make moral judgments consistently • Stages follow a sequence that children do not skip or go backwards in Student Activity Task II • Read & Highlight Kohlberg’s “Stages of Moral Development” (Part A) • Complete Part B on the paper. • Complete the “Evaluation” activity. • Be ready to discuss, share, and turn in tomorrow. Adolescence Adulthood through Aging Young Adulthood Life Span: • age 20-40 Characteristics: • Physical Change: - height of strength & reaction time - signs of aging begin to show • Social Concern: - forming intimate relationships • Cognitive Skill: - intellectual abilities stable - processing skills stable Developmental Tasks: • Exploring adult roles • Becoming independent of parents • Developing intimate relationships • Adjustment to living with someone else • Starting a family • Maintaining/managing a home • Beginning a career • Involvement in “community” • Creation of “social network” Reassessment: • occurs in early 30’s • reevaluation of choices & decisions made while in 20’s • life changes occur (careers, divorce, move) • Biological factors are considered (women & childbirth) Settling Down: • occurs in late 30’s • “planting roots” • focus on career & life stability Middle Adulthood Life Span: • age 40-65 Characteristics: • Physical Change: - number of active brain cells decrease - vision decreases - menopause begins in women • Social Concern: - more aware of own mortality - caught between needs of their children & their own parents • Cognitive Skill: - intelligence remains stable - retrieval of long term memory slows Developmental Tasks: • Strengthening relationship w/spouse • Helping children adjust from home to real world • Assuming roles in community to improve overall world • Achieving mastery in career • Adjusting to physical changes • Making decisions about future • Pursuing Passions • Coping with aging parents Generality: • ability to influence the world around you • interest in guiding the next generation • Examples w/kids, w/co-workers, w/community Midlife Transition: • • • • occurs in age 40-45 realize “life is half over” realize “I’m not a kid anymore” Result perspectives change Midlife Crisis: • 2nd period of reassessment • Feeling of trapped in meaningless life roles • Result find new outlets (roles) • Middlescence: search for a new identity (similar to adolescence stage) Empty-Nest Syndrome: • occurs when children leave home & start own live • Result feelings of emptiness & depression (old research) • Result increase in freedom, focus on career/spouse, new things to focus on(new research) Late Adulthood Life Span: • age 65-older Characteristics: • Physical Change: - health problems begin to show - aging takes place • Social Concern: - acceptance & adjustment - opportunity for self-fulfillment • Cognitive Skill: - decrease in memory & cognitive ability Developmental Tasks: • Adjusting to physical changes • Maintain concern for others while balancing your own changes • Shift focus from work to retirement & leisure activities • Adjustment to financial changes • Adjustment to living with spouse in retirement (fulfilling living arrangement) • Adjustment to death of spouse Why Do People Age? 1. Theory #1 2. Theory #2 Cognitive Changes? • • • • Social Changes? • • • • Stage of Dying Kubler Ross Theory: • proposed by Elizabeth Kubler-Ross (1969) wrote “On Death & Dying” • worked with terminally ill people • Idea death happens in five stages in which dying people pass Stage of Dying Stage of Dying Stage 1 Denial • defense mechanism • deny the reality of the situation • block out the words & hide from reality Stage 2 Anger • intense emotion & guilt • possible resentment Stage 3 Bargaining • attempt to regain control of reality • thoughts of “if we only…” • try to postpone the inevitable Stage of Dying Stage 4 Depression • Two types: • 1 sadness & regret • 2 quiet preparation of actual death Stage 5 Acceptance • not all reach this stage • withdrawal and calm • limited social interaction