Hypersensitivity Reactions:
advertisement

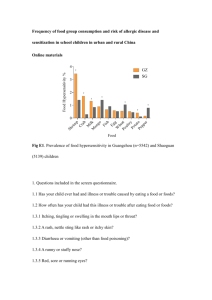
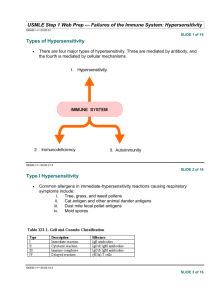
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Definitions: Hypersensitivity reactions: inflammatory immune responses induced by repeated antigen exposure resulting in host tissue damage. Allergen: is a nonparasitic antigen capable of stimulating hypersensitivity reactions. Types of Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions are divided according to mechanism of action into four groups: 1-Type I (Immediate hypersensitivity). 2-Type II (Cytotoxic hypersensitivity). 3-Type III (Immune complex hypersensitivity). 4-Type IV (Cell-mediated hypersensitivity). Types of Allergen: Exogenous: 1- Animal products. 2- Drugs ( penicillin) 3- Food : Egg albumen, Corn, legumes (peanuts, soybeans), milk, and seafood. 4- Insect venom. 5- Mold spores. 6- Plant pollens. Endogenous: -Self antigen. Type I Hypersensitivity: -Commonly known as allergic or immediate hypersensitivity. -Two types according to affected body sites: 1-Localized reaction: Skin, eye, Nasopharynx, Bronchopulmonary, and GIT. 2-Systemic reaction: In Bloodstream. -The reaction takes 15-30 minutes to appear as inflammatory response. -It could appear as a delayed response (10-12 hours later). -Examples: Eczema, Urticaria , Hay fever, Asthma. Mechanism of inflammation in Hypersensitivity Type I: Sensitization phase: 1-Exposure to allergen. 2-Isotype switching (IL-4, IL-13 activity). 3-Sensitization of Mast cell by IgE (FcεRI). Effector phase: 1-IgE Cross-linking. 2-Mast cell degranulation. 3-Release of vasoactive amines, Lipids, and cytokines. Type I Hypersensitivity (sensitization phase): N Type I Hypersensitivity (Effector phase): N Mast cell inflammatory mediators and their action: 1- Biogenic amines ( histamines): A-Bronchiole constriction, and mucus secretion from Goblet cell. B- Endothelial vasodilation ; increased vascular permeability, and vasoconstriction. 2- Lipid mediators: A-Leukotriene C4,and D4 ; similar to histamine effect. B-PAF (platelet aggregation: microthrombosis) C-Prostaglandins D2 : edema and pain. 3-Cytokines: TNF. Clinical examples on Type I Hypersensitivity: 1-Localized reaction in Skin: Urticaria Eczema 2-Systemic Anaphylaxis: In bloodstream. Lethal effect. Type II Hypersensitivity: -Known as Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity. -Allergen could be: 1-Endogenous: Cell surface protein. 2-Exogenous: Drug metabolite adsorbed onto cell membrane. -Sites of occurrence of Type II reactions: 1-On cell surface (Example: RBCs). 2-Within extracellular matrix (Example: Basement memb). Mechanism of inflammation in Hypersensitivity Type II: -IgG , IgM , Complement, and Cytotoxic cells are involved in this type of inflammation. Clinical Examples on Type II Hypersensitivity: 1-Immune Hemolytic Anemia: A-Alloimmune hemolytic anemia. :Erythroblastosis fetalis B-Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. : Blood transfusion anemia. 2-Goodpasture’s syndrome (nephritis). 3-Graves Disease. Type III Hypersensitivity: -Immune Complex hypersensitivity. -Soluble Immune complexes: (IgG- short peptide-IgG) or (IgG-Animal sera-IgG). -Two types: 1-Localized in skin: Example: Arthus reaction. Intradermal injection of antigen in skin; necrotizing vasculitis . 2-Systemic: Example: Serum sickness disease. -Types of Allergen: 1-Exogenous. 2-Endogenous: self antigen. Mechanism of Inflammation in Type III Hypersensitivity: -Immune complex (IgG), complement, and Neutrophils are involved. Clinical Examples on Type III Hypersensitivity: 1-Serum sickness disease that associated with: -Some types of Food allergy. -The prophylactic Vaccine. 2-Systemic lupus erythematosis. 3-Rheumatoid arthritis. Type IV Hypersensitivity: - known as cell mediated or delayed type hypersensitivity. - The classical example of this hypersensitivity is tuberculin (Montoux) reaction which peaks 48 hours after the injection of antigen (tuberculin). -Three types: 1-Contact dermatitis: toxic sensitizer or neoantigen. 2-Delayed type hypersensitivity(DTH): Granulomatous inf. 3-T cell mediated cytotoxicity. Mechanism of inflammation in type IV: -DTH cell,and toxin or neoantigen are involved. Clinical example: Tuberculin test: