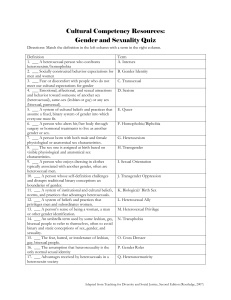
1
Lesson 16: Homophobia and
Heterosexism
Social Problems
Robert Wonser
Erotic Relations are Historical Relations
Sexuality has changed and
evolved historically
that it, is not universal and fixed
This removes bodies from the
biological realm and places them
firmly in the social realm.
2
Did you know?
Heterosexual and homosexual were invented in
the late nineteenth century by doctors and
scientists who created the science of sexology.
Before that time people engaged in homosexual
and heterosexual acts but their acts did not
adhere to them as identities.
Initially heterosexuals were defined as people only
interested in sex for pleasure. Term was used to
distinguish them from the time’s‘normals’ who
only engaged in sex for procreation.
The socioeconomic organization of society—not
3
genes, not brains—created the conditions for
living heterosexual and gay or lesbian lives.
Gendered sexualities
Like gender, sexualities are also expected
to be “opposite”, and gendered:
Compulsory heterosexuality – the
dominance of heterosexual values, and
the fact that both hetero- and nonheterosexuality are shaped by dominant
social scripts
Dichotomy between heterosexuality
and homosexuality only began in 19th
century
When is there an exception to this?
4
Lesbian or Bisexual Chic
Illustrates a mismatch between sexual
behavior and sexual identity
Paula Rust defines this phenomenon as
“same-sex behavior engaged in by
essentially heterosexual individuals under
certain extenuating circumstances, in
keeping with the cultural belief that there are
only two true forms of sexuality”
Behavior is most likely found “in a cultural
milieu favoring sexual experimentation.”
5
Lesbian or Bisexual Chic
Is this cultural acceptance of“girl-on-girl”
progressive?
Or are the images marketed for heterosexual
male audiences and focused on using women to
pleasure men (Luscombe 2004)?
Does this perpetuate the myth that bisexuality is
simply a phase and not a valid sexual identity?
On the other hand, is it subversive in that it
challenges compulsory heterosexuality?
6
Problem with term “Homophobia”
Problem with the term homophobia
because it literally means“fear of
homosexuals” – hatred, anger, and
aggression are stronger components than
fear.
Not just a mislabel but helps excuse hostile
behavior as the (understandable) result of
inescapable fear (Logan 1996).
7
Heterosexism
Homophobia refers to individual beliefs and
behaviors, not institutionalized discrimination.
Heterosexism is a system of attitudes, bias, and
discrimination in favor of opposite-sex sexuality
and relationships. It can include the
presumption that other people are
heterosexual or that opposite-sex attractions
and relationships are the only norm and
therefore superior.
8
9
Similar to“white privilege”; we’re not
taught to see how racism puts some in
a position of privilege but rather view it
as something that puts racial ethnic
minorities at a disadvantage.
Examples of Heterosexual Privilege
You can go wherever you want and know
that you will not be harassed, beaten, or
killed because of your sexuality
You do not have to worry about being
mistreated by the police or victimized by
the criminal justice system because of your
sexuality
You can express affection (kissing,
10
hugging, and holding hands) in most social
situations and not expect hostile or violent
reactions from others
Heterosexual Privilege
You are more likely to see sexually-
explicit images of people of your
sexuality without these images
provoking public consternation or
censorship
You can discuss your relationships and
publicly acknowledge your partner
(such as by having a picture of your
lover on your desk) without fearing that
people will automatically disapprove or
think that you are being“blatant”
11
12
You can legally marry the person whom
you love
You can receive tax breaks, health
insurance coverage, and spousal legal
rights through being in a long-term
relationship
You can express yourself sexually
without the fear of being prosecuted for
breaking the law
Heteronormativity
Heteronormativity is the belief
that people fall into distinct
and complementary genders
(man and woman) with
natural roles in life.
It asserts that heterosexuality is
13
the only sexual orientation or
only norm, and states that
sexual and marital relations
are most (or only) fitting
between people of opposite
sexes.
14
Heteronormativity
Consequently, a
"heteronormative" view is
one that involves
alignment of biological
sex, sexuality, gender
identity and gender roles.
Heteronormativity is often
linked to heterosexism and
homophobia.