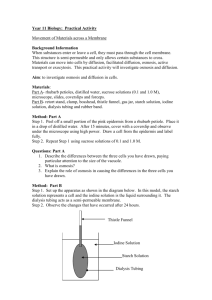
Diffusion, Semi-permeable Membrane, Osmosis
advertisement

Warm-Up Imagine if you had to live inside a sealed plastic bag. How long would you survive? What would be the three main issues with this? What is the function of the cell membrane? Predict what might happen if the cell membrane did not allow anything in or out. What is the term that refers to something that does not allow anything through it? Diffusion, Semipermeable Membrane, Osmosis Cell Membrane The cell needs nutrients for energy and raw materials (for growth). As well, the cell needs to get rid of waste products that are produced inside the cell. In order for the cell to do this , the cell membrane needs to allow some materials into the cell, but not others. For example: When you eat food, it goes into your stomach, then into your intestines. There are many cells that line the sides of your intestine. The digested (broken down) food passes through the cell membrane and into your cell. Semi-permeable Membranes The cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane. This means that it has many small openings that let some substances pass through it but not others. One way that substances can move through the cell membrane is by diffusion. When the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same, it is called equilibrium. Group Demo! Warm-up What is common between the three images? In your own words, define random. Diffusion Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Concentration is the amount of substance in a given space. The smell of fresh baked bread “spreading” throughout the room is an example of diffusion. The diffusion of dye in water. Randomness Diffusion Animation Osmosis Osmosis: the process by which water moves across the cell membrane from an area of high concentration to an are of low concentration. It’s actually a special case of diffusion (ie. Diffusion of water molecules) Water is moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration Problem Solving In your own words, state the problem that we are we have observed. We have a solution of starch solution in dialysis tubing. These are really big molecules. We submerge this “package” into a solution of KI (small molecules). We see that within the dialysis tubing, a colour change occurs and the contents turn blue. Why did the solution within the dialysis tubing turn blue and not the whole beaker of solution? Brainstorm Create a web to collect and record anything you think might possibly help your to come up with solutions to the problem. The solution within the tubing needed the temperature from the KI to activate KI was able to get into the tubing by the ends because they were not tied off correctly There are small pores within the tubing that allows the small KI to get in but not the big starch to get out The tubing began to be dissolve in the KI solution Solution Suggest solution(s) to the problem Propose a solution or solutions to the problem you stated and explain your reasons for choosing that solution. The KI molecules are small and diffuse through the pores and into the dialysis tubing. The KI molecules bind (stick) to the starch molecules causing them to turn blue. The starch molecules are too big to pass out of the membrane (tubing) so the blue colour stays inside. We know this because we understand the concepts of diffusion and semi-permeable membranes. The KI wants to move from high concentration in the beaker to low concentration in the tubing and it is small enough to move through the pores in the tubing, but the starch is too big to move out. Example: Dialysis Tubing with KI and Starch Solution Your cell membrane is like the dialysis tubing It looks like a bag It doesn’t seem like it is letting anything in and out, but it actually has pores! (eg. Tiny molecules can pass through) DEMO! – Practice Problem Solving Say that in the dialysis tubing, there’s a starch solution (really big molecules). You put it in KI solution (small molecules), and you see that colour seeps into the tubing (blue). Why does this happen?