Scapular Region
advertisement

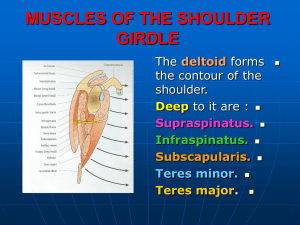
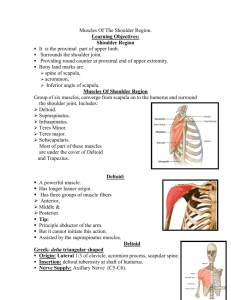
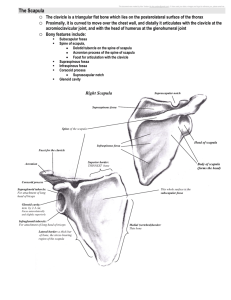
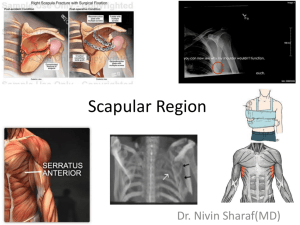
Scapular Region Dr. Sama-ul-Haque Dr. Rania Jabr Scapular Region Objectives Know the principal muscles of the scapular and scapulo-humeral regions. Understand the mechanism of scapular rotation in relation with shoulder movements. Bones of the shoulder region: The SCAPULA Anterior Posterior Muscles of The Shoulder Region These muscles connect scapula to humerus (move humerus through shoulder joint). 1. Deltoid. 2. Supraspinatus. 3. Infraspinatus. 4. Teres minor. 5. Teres major. 6. Subscapularis. Posterior view 1 2 3 4 5 Anterior view 6 Surface Anatomy Acromion (of scapula • Spine Trapezius muscle Infraspinatus muscle Teres minor muscle Triangle of ascultation Teres major muscle Deltoid Lateral third of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Nerve supply: Axillary nerve Action: Anterior fibers : Flexion, medial rotation Middle fibers: abduct arm from 15°- 90°. Posterior fibers : Extension, lateral rotation D Abductors of shoulders: 1. Supraspinatus 0-15 degree. 2. Deltoid 15-90 degree. 3. Trapezius & serratus anterior: abduction 90-180 degree. 4 Rotator cuff muscles: stabilize the shoulder joint. Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Subscapularis, Teres minor Rotator Cuff Muscles Supraspinatus Origin: supraspinous fossa. Insertion: greater tuberosity of humerus. Nerve supply: suprascapular nerve. Action: abduction of humerus from 0° - 15°. Infraspinatus: Origin: infraspinaous fossa. Insertion: greater tuberosity of humerus. Nerve supply: suprascapular nerve. Action: lateral rotation of humerus. Teres minor Origin: lateral border of scapula Insertion: greater tuberosity of humerus. Nerve supply: axillary nerve. Action: lateral rotation of humerus. Teres major: Origin: lateral border of scapula Insertion: bicipital groove of humerus (med lip) Nerve supply: lower subscapular nerve. Actions: extension, adduction & medial rotation of humerus (swimming). Subscapularis Origin: subscapular fossa. Insertion: lesser tuberosity of humerus. Nerve supply: upper & lower subscapular nerves. Action: medial rotation of humerus. Transverse scapular ligament • Attach to suprascapular notch • Subscapular nerve (C5,6) below it and Subscapular artery above it, Serratus anterior Front of the medial border of scapula. Nerve supply: • Long thoracic nerve. Action: • Depression & protraction of the scapula (boxing) • Raising the arm above 90 degree (climbing). • Accessory muscle of respiration Injury of long thoracic nerve Subscapularis Injury of long thoracic nerve: Winged Scapula: Cause; Paralysis of serratus anterior as it is "big swing muscle" or "boxer's muscle” Antagonist of Rhomboids Complete abduction at the shoulder joint requires superior rotation of the scapula so that the glenoid fossa faces superiorly. Glenoid fossa • Superior rotation of Glenoid fossa: trapezius serratus anterior Scapula rotates when we move our arms to allow more range of motion at the shoulder joint Posterior scapula