Shoulder Girdle/Joint Lab
advertisement

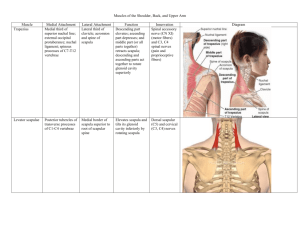
Shoulder Girdle/Joint Lab Josh Adetula Deborah Yang From Which joint is the shoulder connected to the spinal column? • The shoulder is connected to the spinal column via the scapulothoracic joint. Which of the following joints is NOT a part of the shoulder complex? • The Alatoaxial joint is not a part of the shoulder complex Where is the insertion of the Pectoralis minor? • It is inserted at the coracoid process of the scapula. Q: What is the function of the Levator Scapulae Muscle? A. The Levator Scapulae’s Function is to elevate the scapula. Flexion • Movement of humerus straight anteriorly from any point in the sagittal plane. Extension • Movement of the humerus straight posteriorly from any point in the sagittal plane Abduction • Upward lateral movement of the humerus in frontal plane out to the side, and away from the body. • Can be diagonal or horizontal Adduction • Downward movement of the humerus in the frontal plane medially toward the body. • Can be diagonal or horizontal Rotation • Lateral movment of the humerus in the tranverse plane along its long axis. • There are 2 types: Internal and External Sternoclavicular Joint • Distal (also is medial) to the most lateral edge of the deltoid. Q: Which Nerve innervates the rhomboid muscle? A. The rhomboid muscle is innervated by the dorsal scapula nerve • From which cord does the musclocutaneous nerve originate? The nerve originates from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. In which part of the scapula does the humeral head fit, to make the glenohumeral joint? • The humeral head fits into the glenoid cavity to make the glenohumeral joint. Scapula 1. Coracoid Process (A) 2. Scapular Notch (J) 3. Superior Margin (B) 4. Supraspinatus Fossa (L) 5. Superior Angle (K) 6. Scapular Spine (C) 7. Vertebral Margin (D) 8. Infraspinatus Fossa (H) 9. Inferior Angle (I) 10. Axillary Margin (E) 11. Glenoid Cavity Margin (F) 12. Acromion Process (G) The Deltoid musle is… • …the main adductor of the shoulder joint. If the long thoracic nerve gets injured, then which movement of the shoulder girdle will be affected? • Injury to the LTN would greatly affected abduction. Subclavius Muscle can be strengthened by… • The subclavius muscle can be strengthened by active depression. The origin of rhomboid muscle is the spineous process of… • Its origin is the spineous process of C7 to T5. Left Scapula (seen in lateral view) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Coracoid Process Glenoid Cavity Scapular Spine Acromion Process Infraspinatus Fossa Inferior Angle Clavicle injury results…. • When dealt a blow to the medial end of the clavicle, this will cause an AC separation (aka dislocated shoulder), which tears up the joint capsule. Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervations Pectoralis Minor Anterior Surfaces of the 3rd to 5th ribs Coracoid process of the scapula Abduction, Depression, & Downward Rotation Medial pectoral nerve (C8 & T1) Serratus Anterior Surface of the upper 9 ribs at the side of the chest Anterior side of the medial scapula Abduction & Upward Rotation Long Thoracic Nerve (C5 –C7) Trapezius – upper fibers Base of skull, occ. Protuberance, and posterior ligaments of the neck Posterior aspect of the lateral 3rd of the clavicle Elevation & Extension or Rotation at the head of the neck Spinal accessory nerve and branches of C3 & C4 Trapezius – middle fibers Spinous process of C7-T3 Medial border of the acromion process and upper border of scapular spine Elevation, Adduction, & Upward rotation Trapezius – lower fibers Spinous process of 4th-12th thoracic vertebrae Triangular space at the base of the scapular spine Adduction, Depression, & Upward rotation Rhomboids Spinous processes of C7-T5 Medial border of scapula, below scapula spine Adduction, downward rotation, & Elevation Dorsal Scapula Nerve (C5) Levator Scapulae Transverse processes of C1C4 Medial border of scapula Elevation Dorsal Scapula Nerve (C5) and branches of C3 & C4 Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervations Pectoralis major Upper Fibers – medial half of front of clavicle Lower Fibers- Anerior surface of first 6 ribs Flat tendon 2 or 3 inches wide to lateral lip of IT groove of humerus Rotation, Adduction, Flexion, Extension, & Abduction Lateral Pectoral Nerve (C5, C6, C7) Subscapularis Entire Anterior surface of subscapular fossa Lesser Tubercle of Humerus Rotation (Internal) Medial Pectoral Nerve (C8, T1) Coracobrachialis Coracoid process of scapula Middle of medial border or humeral shaft Adduction (Horizontal & Diagonal) Upper and lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6) Deltoid Anterior - Anterior lateral C3 Middle – Acromion (lateral) Posterior – Spine of Scapula (Inferior edge) Deltoid Tuberosity on the lateral humerus Abduction Flexion, Adduction Axillary Nerve (C5, C6) Supraspinatus Medial 2/3 of SSP Fossa Superiorly on Greater Tubercle of humerus Abduction Suprascapula nerve (C5) Latissimus Dorsi At Lumbar Vertebrae to Lower 6 Thoracic Vertebrae, back of Sacrum, and Posterior crest of ilium Medial side of IT groove of humerus, anterior to teres major insertion Extension, Adduction, and Rotation (internal) Thoracodorsal (C6, C7, C8) Teres Major Inferior 3rd of lateral border of scapula Medial lip of IT groove of humerus, posterior to latissimus dorsi insertion Extension, Adduction, and Internal Rotation Lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6) Infraspinatus Medial aspect of infraspinatus fossa, just below spine of scapula Posteriorly on greater tubercle of humerus External rotation, Horizontal/Diago nal abduction, Suprascapula nerve (C5, C6) Teres Minor Posteriorly on upper and middle aspect of lateral border of scapula Posteriorly on greater tubercle of humerus External rotation, Horizontal abduction, and diagonal adduction Axillary Nerve (C5, C6)