09 - SCAPULAR REGION
advertisement

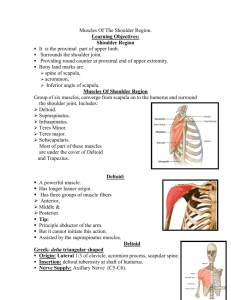
MUSCLES OF THE SHOULDER GIRDLE The deltoid forms the contour of the shoulder. Deep to it are : Supraspinatus. Infraspinatus. Subscapularis. Teres minor. Teres major. DELTOID It is triangular in shape. It is functionally divided into: anterior, middle and posterior parts. Origin : Anterior fibers: lateral 1/3 of the anterior border of the clavicle. DELTOID Middle fibers : lateral border of the acromion. Posterior fibers: lower border of the spine of the scapula. DELTOID Insertion : deltoid tuberosity (middle of the lateral surface of the humerus). DELTOID Nerve supply : Axillar nerve. DELTOID Action: 1. Middle fibers: abduction of the arm (helped by supraspinatus). 2. Anterior fibers: flexion and medial rotation. 3. Posterior fibers : extension and lateral rotation. AXILLARY NERVE Origin : Posterior cord of the brachial plexus (in the axilla). AXILLARY NERVE Course : Passes through the quadrangular space. It is closely related to the inferior part of the shoulder joint and the surgical neck of the humerus. AXILLARY NERVE Branches : 1. Articular : to the shoulder joint. 2. Anterior branch : deltoid muscle and the skin covering its lower half. 3. Posterior branch : Deltoid. Teres minor. Upper lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm. QUADRANGULAR SPACE It is an intermuscular space. Boundaries : Superior (posterior) :Teres minor. Superior (anterior): Subscapularis Inferior : Teres major. QUADRANGULAR SPACE Medially : Long head of triceps. Laterally : Surgical neck of the humerus. Contents : Axillary nerve. Posterior circumflex humeral vessels. ROTATOR CUFF It is formed of (4) muscles Supraspinatus. Infraspinatus. Teres minor. Subscapularis. It lies on the superior, posterior and anterior aspects of the shoulder joint. It is deficient inferiorly. ROTATOR CUFF Function : The tone of the muscles holds the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity. So they assist in stabilization of the shoulder joint. SUPRASPINATUS Origin : Supraspinous fossa of the scapula. SUPRASPINATUS Insertion : Upper facet of the greater tuberosity of the humerus and The capsule of • the shoulder joint. SUPRASPINATUS Action : 1. It initiates abduction of the shoulder joint. 2. Rotator cuff. INFRASPINATUS Origin : Infraspinous fossa. INFRASPINATUS Insertion : Middle facet of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. INFRASPINATUS Action : 1.Lateral rotation. 2. R.C. NERVE SUPPLY Suprascapular nerve. SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE Origin : Upper trunk of the brachial plexus in the posterior triangle. SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE Course : It descends behind the suprascapular ligament in company with the suprascapular vessels. Branches : Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus and Shoulder joint. TERES MINOR Origin : Upper 2/3 of the lateral border of the scapula. TERES MINOR Insertion : Lower facet of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. TERES MINOR Nerve supply : Axillary nerve. Action : 1. Lateral rotation. 2. R.C. SUBSCAPULARIS Origin : Subscapular fossa. SUBSCAPULARIS Insertion : Lesser tubercle of the humerus. SUBSCAPULARIS Nerve supply : Upper & lower subscapular Action : 1. Medial rotation. 2. R.C. ROTATOR CUFF TENDINITIS Manifestations : Spasm associated with pain in the middle range of abduction. It is a common cause of pain in the shoulder region. ROTATOR CUFF TENDINITIS Cause : Excessive overhead activity of the upper limb which can cause degenerative changes in the subacromial bursa. This is followed by degenerative changes in the supraspinatus tendon and extend to the other tendons of the rotator cuff. TERES MAJOR Origin : Inferior angle and lower third of lateral border of the scapula. TERES MAJOR Insertion : Medial lip of the bicipital groove of the humerus. TERES MAJOR Nerve supply : Lower subscapular Action : 1. Adduction. 2. Medial rotation.