The Digestive System
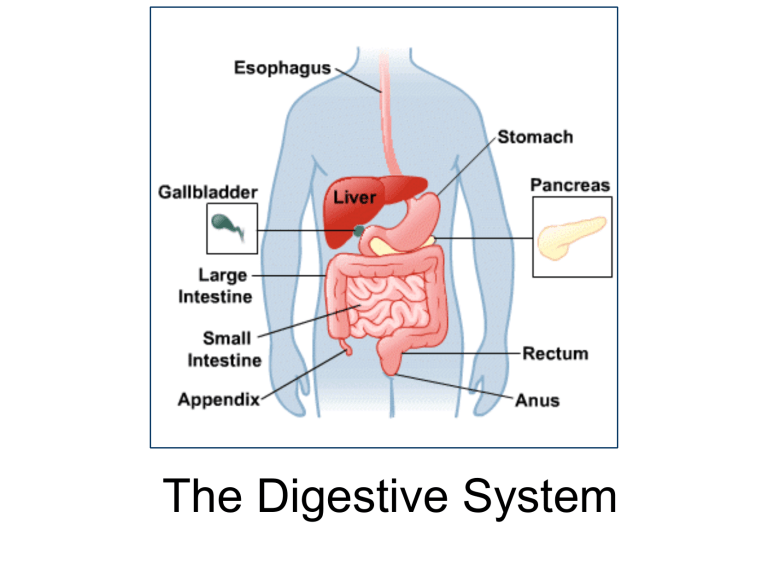
The Digestive System
Functions:
1. mechanical and chemical breakdown of food
2. absorption of nutrients
3.Getting rid of waste
Consists of:
1. alimentary canal
2. accessory organs
Alimentary Canal
Consists of : mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus
1. Mixing Movements
Rhythmic contractions mix food with digestive juices
2. Propelling Movements
Peristalsis - pushes food down the tube
A. Digestion Begins with the MOUTH
1.Mouth – begins digestion by
Chemical Digestion: mixing with saliva
Mechanical Digestion: reducing size of particles
(chewing)
a.Tongue – moves food during chewing, connects to the floor of the mouth via the frenulum, contains papillae (taste buds)
b. Teeth: help mechanically digest food
Tooth Decay
C. Salivary Glands i.Produce amylase – breaks up starch ii. Mucous cells produce mucus – lubrication during swallowing
B.Esophagus
Brings food from the mouth to the stomach
*10 inches long
C. Stomach
1. J-shaped pouch like organ that helps digest food even further
2. Stomach Muscles: are layered to promote a mixing of stomach juices a. Gastric Juices contain acids that break down food
• PEPSIN - most important digestive enzyme for breaking down food
Stomach Lining
3. is a mucous membrane that prevents the stomach from digesting itself
D. PANCREAS
1. Secretes Pancreatic Juice a. Pancreatic Juice breaks down fat, breaks down nucleic acid into nucleotides
E. Liver
1.Produces bile a. Bile aids in digestion, bile salts break down fat globules into smaller droplets – emulsification
F. Gall Bladder - under liver
1.
Stores Bile
G. Small Intestine
1.
*7 meters long (22 feet) a. absorbs nutrients from food and brings them to the blood.
Greater Omentum
a "curtain-like" membrane that covers the intestines, stores fat and lays like a drape
H. Intestinal villi increase surface area to absorb nutrients, connect to vessels
I. Large Intestine
1. re-absorbs water and passes along material that was not digested; contains intestinal flora
(bacteria to break down cellulose and produce intestinal gas)
Types 1 –2 indicate constipation .
with 3 and 4 being the ideal stools and 5, 6 and 7 tending towards diarrhea .
Which meal would take the longest to digest?
Disorders of the Digestive System
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Crampy abdominal pain
Fatigue
Loss of appetite
Pain with passing stool
(tenesmus); bloody stool
Persistent, watery diarrhea
Weight loss
Constipation
STOMACH ULCERS
Lactose
Intolerance
Inability to digest milk, can cause stomach upset
When people with celiac disease eat foods or use products containing gluten, their immune system responds by damaging or destroying villi
Without healthy villi, a person becomes malnourished, no matter how much food one eats.
Gallstones are made from cholesterol and other things found in the bile.