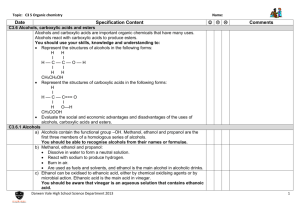
Equilibria - Calthorpe Park Moodle

Equilibria
⇌
Reversible Reactions
• In Reversible Reactions the products can react to form the original reactants
• Equilibrium reactions refer to the forward reaction (left to right) and the backwards reaction
• A reversible arrow is used
⇌
Reaction conditions
• An equilibrium only occurs if the reaction is in a closed system where nothing can get in or out.
• In a dynamic equilibrium the forward reaction and the backwards reaction occur at the same time and rate.
Industry
• Changing the reaction conditions, changes the equilibrium position and therefore the amount of reactants or products.
• This is important in industry where many products are made in equilibrium reactions.
The Haber Process
•
• Ammonia is made by the Haber Process
• Nitrogen + Hydrogen
⇌
Ammonia
N
2
+ 3 H
2
⇌
2 NH
3
• Nitrogen is from the fractional distillation of air and Hydrogen is obtained from methane.
Conditions for the Haber Process
• A high temperature increases the rate of reaction, but reduces the yield of Ammonia because the forward reaction to make ammonia is exothermic.
• A high pressure increases the rate of reaction, but is too expensive.
• Increasing the pressure favours the side of the equilibrium with the least number of gaseous molecules.
• Compromise temperature are used.
450 o C and 200 atm pressure
Economics of the Haber Process
• Using an Iron catalyst does not affect the position of the equilibrium, but it increases the rate of reaction and reduces the cost of the process. Iron is a cheap catalyst.
• Ammonia is cooled, liquefied and removed as soon as it is made to stop it decomposing.
• Unreacted Nitrogen and hydrogen are recycled.
• Ammonia is used to make fertilisers.
Organic
Chemistry
C
2
H
5
OH
Hydrocarbons
• Organic molecules contain carbon compounds
• Alkanes and Alkenes are hydrocarbons
• Ethane, C
2
H
6
Ethene, C
2
H
4
Functional Groups
• A functional group is the part of the molecule that is involved in chemical reactions.
• Replacing an H atom with a functional group makes other organic compounds:
• Alcohols, Carboxylic acids, Esters
-
OH
-
COOH
-
COO R
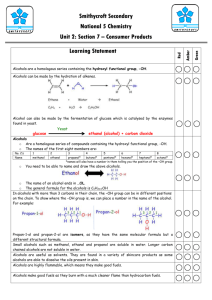
Alcohols
• Alcohols are a homologous series of compounds containing the
–
OH group.
• Ethanol, with a structural formula of C
2
H
5
OH.
• Displayed formula
• Ethanol is the alcohol found in drinks.
Properties of Alcohols
• They are Flammable and used as fuels
• Combustion of Ethanol :
C
2
H
5
OH + 3O
2
→ 2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
• They react with Sodium to produce
Hydrogen, but this is slower than sodium with water.
Oxidation of Alcohols
• They can be oxidised to Carboxylic acids by boiling with potassium dichromate
• E.g. Ethanol makes Ethanoic acid (Vinegar)
Carboxylic Acids
• These are weak acids with pH values higher than for strong acids.
• Strong acids are fully ionised, but weak acids are partially ionised.
CH
3
COOH
⇌
CH
3
COO
-
+ H
+
• Weak acids have a lower concentration of
Hydrogen ions, H
+
.
Esters
• Carboxylic acids and Alcohols react to make
Esters.
• Carboxylic acid + Alcohol → Ester + Water
Ethanoic acid + Ethanol → Ethyl ethanoate + Water
CH
3
COOH + CH
3
CH
2
OH →CH
3
COOCH
2
CH
3
+ H
2
O
Concentrated Sulphuric acid is the catalyst.
Properties of Esters
• Ethanoic acid + Methanol
⇌
Methyl ethanoate + Water
• Esters are volatile – evaporate easily.
• They are sweet smelling and fruity.
• Uses include as perfumes and food additives