Reconstruction

Reconstruction
Unit 4, Lesson 5
Essential Idea
Reconstruction was a time of political, economic, and social changes for both the
North and the South.
Initial Post-Civil War Issues
What will happen to the South?
Ex-Confederates/CSA states
Southern economy
Southern freedmen
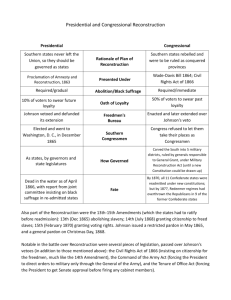
Lincoln’s Reconstruction Plan
Proclamation of
Amnesty and
Reconstruction/“10
% Plan” (1863)
Wade-Davis Bill
(1864)
Lincoln’s assassination
Freedmen
13 th Amendment (ratified 1865)
Black Reactions
White Reactions
Freedmen
Freedmen’s Bureau
Carpetbaggers
Scalawags
Andrew Johnson
Johnson’s background
“10% plus”
Southern governments by 1865
Black codes
Johnson’s Leniency
Johnson vs. Congress
Radical Republicans
Southern Congressmen barred
Civil Rights Act of 1866
Johnson’s veto
Congress overrides veto
Tension in Congress
Joint Committee Report on Reconstruction
The 14 th Amendment
14 th Amendment
(ratified 1868)
Terms
14 th Amendment
Radical Republicans Gain More Power
Midterm
Election of 1866
Johnson’s
“swing around the circle”
Radical
Republicans
Thaddeus
Stevens
Charles Sumner
Radical Republican Actions in 1867
Military Reconstruction Act
Command of Army Act
Tenure of Office Act
Andrew Johnson’s Impeachment
Edwin Stanton fired
Johnson impeached
Johnson’s Impeachment
Significance of verdict
Election of 1868
Ulysses S. Grant
“Waving the bloody shirt”
Impact of Freedmen
Results
The 15 th
Amendment
Fifteenth Amendment
(ratified 1870)
Black political participation
Hiram Revels
White reaction
Southern Reaction to Black Equality
Ku Klux Klan
“Invisible Empire”
Redeemers
The KKK
The “KKK Act”
(Force Acts of
1870/1871)
Grant vs. the Klan
What was Behind the Masks?
Civil Rights Limited
Civil Rights
Act of 1875
The Civil
Rights Cases
(1883)
What about Women?
Women before and during Civil War
Woman’s Loyal League
Reaction to 14 th and 15 th
Amendments
The North During Reconstruction
Political corruption
Spoils system
Democratic political machines
Boss Tweed vs.
Thomas Nast
Corruption in the Grant Administration
Jay Gould and James Fisk
Credit Mobilier scandal (1872)
Whiskey Ring scandal (1874-1875)
Indian Ring scandal (1876)
Corruptible?
Election of 1872
Liberal Republicans
Horace Greeley
“Waving the bloody shirt” again
Results
Panic of 1873
Causes
Create inflation?
Hard-money
Republicans
The “Crime of ’73”
Bimetallism
Coinage Act of
1873
“Crime of ’73”
Future implications
Republican support wanes
Panic of 1873
Corruption
(“Grantism”)
Monetary issues
Democratic Party grows
Samuel Tilden
(Democrat)
Rutherford B.
Hayes (Republican)
Initial results
Election of
1876
Compromise of 1877
Compromise of
1877
Terms
Impact
Reconstruction
Ends
Blacks Adjust to Freedom
Black communities
Churches and
Schools
The Old South is
“Redeemed”
Black disenfranchisement
Literacy tests
Poll taxes
Grandfather clause
Jim Crow is Born
Segregation
Jim Crow laws
Plessy v.
Ferguson (1896)
“Separate but equal”
Plessy and the
Rise of Jim Crow
A New From of Servitude
Sharecropping
Tenant farming
“Slavery without the chains”
“Exodusters”
The Exodusters
Redemption of the South
The South is
“redeemed”
Status for blacks?
Reconstruction:
Success or Failure?
A Failed Revolution?