Chapter Four - Myths of Creation
advertisement

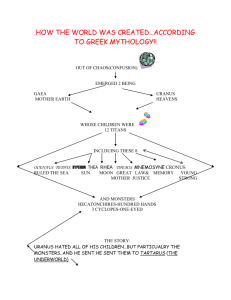
Divine Myth The Rise of Zeus “Sing all this to me, Muses, you who dwell on Olympus: from the beginning tell me, which of the gods first came to be.” Hesiod, Theogony (114–5) The cosmogony is the theogony. The Beginning of Creation • Classical mythology starts with the creation of the universe and the creation of the human race. • To the Greeks, the universe began with a mystery that sprang from the unknown, from Chaos. • Hesiod and Ovid had differing views of creation: - Hesiod conceived of Chaos as an enormous chasm born into darkness - Ovid viewed Chaos as shapeless, mutable matter The Children of Chaos • Is Gaia the mother of all things? Gaia • After Chaos came Gaia, the Earth; either born from Chaos or simply rising on its own. • Earth surrounded Chaos. From where they came is neither explained nor elaborated. - The Earth came into being to serve as a solid foundation - The emergence of Earth brought harmony and order to Chaos - Its birth separated heaven from Earth, water from land, and air from airless space • After Chaos and Gaia came Tartarus, located deep within the Earth’s depths and was the lowest level of the Underworld. • Then came Eros (love). The fairest of all the immortals, the driving force behind all creation. The Children of Chaos • Beings born through parthenogenesis (creation resulting from just one gender) 1. Chaos gave birth to a. Erebus - the darkness of the night b. Nyx (Night) 2. Gaia (in her sleep) gave birth to a. Uranus - Sky and the god of the sky,emerged as her equal b. Pontus - Sea and the god of the sea • From here on - virtually all of Creation came through mating • Uranus enveloped Gaia with love and showered her with fertile rain a. Gaia gave birth to the rest of the physical world (bodies of water, mountains, flora, fauna, etc.) b. 12 Titans (discussed later) 1. Two of them (Oceanus and Tethys) continued Creation themselves 2. Their mating produced a. 3,000 rivers of Earth all of which draw their waters from the mighty stream Oceanus b. 3,000 Oceanids, ocean goddesses all One of the 3,000 rivers An Oceanid or sea nymph Nyx mated with Erebus and produced *Hemera (Day) and Aether (upper air) -Night and Day dwell in the same house but never share that house together. *Moros - doom *Thanatos - death *Hypnos - sleep Nemesis - goddess of retribution Eris - goddess of strife, bred a host of woes ranging from famine and sorrow to lies and murder The Keres - female death spirits, would be charged with collecting and carrying off the bodies of the dead The Moirai - the fates, would be charged with determining the course of events in mortal lives a. Clotho - spun the thread of life b. Lachesis - measured it with a rod c. Atropos - snipped it with shears ending the life span The first children of Gaia and Uranus *Hecatonchires 1. Cottus, Briareus, and Gyges 2. Each had 50 heads and 100 arms/hands 3. The mightiest of all Gaia’s children 4. The later Titans and Olympians would quake with fear at the sight of them Cyclops, Hecatonchires • Also children of Gaea and Uranus • Cyclops –Not the Cyclops of Homer (Polyphemos) –Blacksmiths for the gods –Brontes (“Thunderer”), Steropes (“flasher”), Arges (“brightener”) Cyclops, Hecatonchires • Hecatonchires (“hundred-handers”) –Also fifty heads –Cottus, Briareus, Gyes Cyclopes (not the man-eating monsters of later myths) 1. Brontes, Steropes, and Arges 2. Had only one eye 3. Enormous stature 4. Almost godlike - they were smiths, builders, and the forgers of thunder and lightening 5. Also, arrogant, powerful, and unwilling to bow to authority 6. Uranus hurled them and their brothers down into Tartarus because he feared them so. The forge of the Cyclopes The Titans Thereafter Gaea was bedded with Uranus, lord of heaven, and bore deep-swirling (1) Oceanus, (2) Coeus, (3) Crius, (4) Hyperion, (5) Iapetus, (6) Theia and (7) Rhea, (8) Themis, (9) Mnemnosynê, (10) Phoebê, and fair-featured (11) Tethys. Last of all she gave birth to (12) Cronus, that scheming intriguer, cleverest child of her brood, who hated his lecherous father. Hesiod, Theogony (126–38) The 12 Titans - the first rulers of the universe (children of Gaia and Uranus) *The Daughters 1. Theia - early goddess of light 2. Rhea - earth goddess/mother of Olympian gods 3. Themis - earth goddess 4. Mnemosyne - personification of memory 5. Phoebe - early moon goddess 6. Tethys - most ancient goddess of the sea *The Sons 1. Oceanus - firstborn of the Titans; the god of the primordial river and the river itself, which flowed from the Underworld in a circular and never-ending stream around the edge of the world 2. Coeus - father of Leto 3. Crius - father of Astreus 4. Hyperion - early god of the sun 5. Iapetus - father of Prometheus 6. Cronus - the youngest but craftiest and most daring/father of the Olympian gods * All the Titans hated Uranus, and he hated them! 1. Once born, he thrust them all back into Gaia’s womb 2. He wanted to remain in power forever 3. He took great pleasure in Gaia’s pain 4. Finally, Gaia reached her breaking point and plotted revenge Gaia’s Revenge A. Gaia devised a scheme to avenge Uranus Cronus Against Uranus • Uranus stuffing newly born Titans back into Gaea • Cronus, the youngest, castrates Uranus with a sickle • Blood from the severed genitals becomes the Erinyes The Birth of Aphrodite, Monsters and Sea Deities • Aphrodite springs up from the “foam” at Cythera • Monsters • Altered Egyptian and Mesopotamian archetypes: –Harpies, Sirens, Sphinx More children produced from the blood of Uranus 1. The Eyrines (Furies) a. Alecto, Tisiphone, and Megara b. They avenge perjury and crime against one’s family 2. The Race of Giants born in full armor with spears in their hands 3. The “Ash Tree Nymphs” - inhabited the forests of Greece Uranus cursed them all with the name “Titans” which means “overreachers” and swore revenge The Furies Race of Giants Ash Tree Nymph The Birth of Aphrodite A Titanic Struggle A. The Titans gained their freedom and made Cronus their king and freed the Cyclopes and Hundred Handed Giants B. Cronus wasn’t much of an improvement and soon cast arrogant, authority hating brothers back into Tartarus C. The 12 Titans and Titanesses remained free and began breeding the second generation of Titans together 1. Theia & Hyperion (1 son and 2 daughters) a. Helios - the sun and god of the sun b. Selene - the moon and goddess of the moon c. Eos - the dawn and goddess of the dawn 2. Phoebe & Coeus (2 daughters) a. Leto (mother of Apollo and Artemis) b. Asteria 3. Oceanus & Tethys a. 3,000 male river gods b. 3,000 Oceanids 4. Cronus & Rhea (the most impressive union) a. Three sons 1. Zeus 2. Hades 3. Poseidon b. Three daughters 1. Hera 2. Hestia 3. Demeter c. All of whom would take their place on Mount Olympus Zeus Poseidon Hades Hera Hestia Demeter Zeus Against Cronus: The Battle with the Titans • Olympians win with the help of the Cyclopes and the Hecatonchires • Titans cast into Tartarus • Altas given special punishment –Forced to hold up the heaven at the edge of the earth Cronus’ Story *As lord of the immortals, Cronus became even more of a tyrant than Uranus *Zeus’ birth 1. Rhea pleaded with her mother to devise a plan to conceal his birth. 2. Rhea was sent to the island of Crete to give birth to Zeus 3. Gaia then hid Zeus in a cave on Mount Dicte and nourished him with food and love 4. Meanwhile, Rhea returned to Cronus and presented him with a rock wrapped in swaddling clothes 5. Cronus did not examine the package, he simply swallowed it 6. Zeus grew up on Crete in the care of the Ash Tree Nymphs, and he became invincibly strong and swift 7. Summarize Zeus’ plan to free his brothers and sisters Titanomachy -Clash of the Titans 1. Of the twelve original Titans, only five fought with Cronus a. None of the six original Titanesses got involved b. Oceanus and Tethys did not take sides and instead cared for Hera c. Hestia refused to take sides d. Prometheus and Epimetheus took Zeus’ side 2. Every day for 10 years both sides fought 3. Gaia foretold that the children of Cronus would triumph if joined by their allies in Tartarus a. Zeus heeded this oracle and went straight to Tartarus to free the Giants and Cyclopes b. The Cyclopes made special gifts for the gods 1. For Zeus - thunder and lightening 2. For Hades - the helmet of invisibilty 3. For Poseidon - the trident c. Briareus, Cottus and Gyges attacked the Titans by hurling boulders and the tops from mountains E. The battle ended with Poseidon and Hades distracting Cronus while Zeus hurled a lightening bolt at him F. Cronus finally conceded victory to his sons Zeus Against Cronus: The Battle with the Titans • Cronus swallows the newly born Olympians: – Demeter, Hera, Hestia, Hades, Poseidon, Zeus • Rhea delivers the youngest, Zeus, in Crete, hidden from Cronus • Zeus raised by nymphs – Alamlthea, Melissa, Corybantes, Curetes • Cronus fooled by rock in baby’s clothing Zeus Against Cronus: The Battle with the Titans • Zeus overthrows Cronus –The stone vomited out and became used as the omphalos in Delphi • Other Titans attack –The “Titanomachy” –Only the Titans Themis and her son Prometheus side with the Zeus and the Olympians Revenge A. Punishments 1. Zeus decreed all his enemies would remain in the lowest depths of Tartarus forever 2. The three Giants stood guard over them 3. Only one Titan avoided eternal punishment, Atlas, who had to lift up the sky and hold the weight of the heavens forevermore on his shoulders Rewards 1. Briareus - Zeus gave him a daughter 2. Any Titans who did not oppose him retained their places of honor 3. Zeus was assured that his reign would last forever Zeus’s Battle with the Giants • Will the succession continue after Zeus? • Metis, one of his consorts, is pregnant • Hears that the next child of Metis after this one will replace him • She is pregnant, so he ingests her • Athena, the warrior goddess among things, is born from his forehead (Prometheus or Hephaestus helps) Zeus’s Battle with the Giants • Much later: Battle of the Giants • Not in Hesiod • Giants spring from Uranus’s severed genitals • With the help of Hercules(!), are defeated • World divided among Zeus (Sky), Poseidon (Ocean), and Hades (Underworld) Zeus’s Battle with Typheous • Gaea with Tartarus produce Typhoeus • Defeated by Zeus’s thunderbolts • Apollodorus adds details – Olympians fled to Egypt disguised as animals – Zeus temporarily defeated and “deboned” – Hermes puts Zeus back together – Typhoeus defeated in a “bloody” battle at Mt. “Haemus” – Typhoeus buried under Mt. Etna Themes in Greek Creation Story • Divine Myth with folklore elements • Cosmos becoming increasingly complex, away from original unity Themes in Greek Creation Story • Female is ambiguous – creative and destructive • Creation is through sexual intercourse • Ascendancy of male over female • Based on contradictory tendencies in a family (folktale) Themes in Greek Creation Story • Zeus’s story on Crete from local religion on Crete – Zeus’s story there is pattern after a local vegetation god • Titans represent untamed forces of nature • Zeus overcomes them by righting old wrongs (against the Hecatonchires and the Cyclopes)