INFECTION CONTROL
advertisement

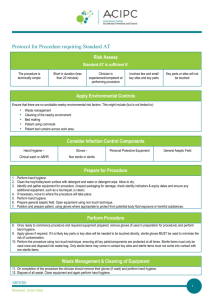
INFECTION CONTROL AND ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE Nosocomial Infections Infections patients receive while in an acute care hospital or any other healthcare facility. Urinary tract most common – catheters Wounds after surgery and respiratory tract infections also common CYCLE OF INFECTION Source (Infectious Agent) Reservoirs of Infection Portal of Exit Modes of Transmission Portal of Entry Host Infectious Agent Pathogenicity – ability to cause disease. Virulence – ability to grow and multiply with speed. Invasiveness – ability to enter tissues. Specificity – organism’s attraction to a particular host. Modes of Transmission Direct or Indirect contact (fomite) Droplet Vehicle Airborne Vector Microorganisms Algae Protozoa Fungi Bacteria Pathogens Parasites –Protozoa, Helminths Fungi – yeasts and molds Bacteria – colorless, minute, onecelled organisms with a typical nucleus Virus Viruses Influenza Common cold Mumps and measles Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E AIDS HIV and AIDS HIV enters the body after exposure through contact with blood or body fluids and attacks the immune system. Five phases (pg 57) Practice Standard Precautions and be cautious handling needles Needle sticks must be reported Viral Hepatitis Inflammation of the cells of the liver Hep A and Hep E are transmitted by the fecal-oral route Others by blood or body fluids Hep B , C and D can be chronic Acute demonstrated as flu-like symptoms then in 1-2 weeks becomes jaundiced, liver enlarges, liver cells die Can regenerate unless it turns chronic Tuberculosis Most commonly affects the lungs, but can affect any part of the body. It is a communicable (infectious) disease Pulmonary TB is treatable if caught early ASEPSIS A state of being free from germs Medical Asepsis - clean Surgical Asepsis – sterile GOALS OF HANDWASHING Reduce number of transient and resident bacteria on hands Prevent transmission of infection to: – Patients and family members – Health care workers – Yourself UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS Defined as the minimum standard for safety. Uniforms and Clothing Laundry UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS Gloves should be worn whenever contact with blood or other body fluids or tissue is expected. Gloves should be changed after each patient. Masks and eye shields worn to protect from droplets of blood or body fluids Gowns should be worn if blood/body fluids Hands and other skin washed immediately UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS Needles never recapped, bent or broken or removed from syringes. Needles disposed of in puncture resistant container. Mouthpieces, ambu bags and vent devices used rather than mouth-to-mouth Workers with oozing or open sores should refrain from direct contact with patients and equipment. ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS Protective Isolation Imaging Considerations Transporting Patients CATEGORY-SPECIFIC ISOLATION CATEGORY STRICT PROTECT NECESSARY AGAINST ITEMS Droplet/direct Gown,glove,mask CONTACT direct Gown,glove,mask Respiratory Droplets Mask ENTERIC Feces Gown, gloves TUBERCULOS TB Mask, gown(?) Drain/Secretion Direct Gown, gloves Inhibiting and destroying Microorganism growth Sanitization Disinfection Sterilization Sanitization Clean with detergent and brush Ultrasonic Disinfection Chemical germicides or boiling water Check dilution ratio of chemical Exposure to chemical may vary from 20 minutes to 3 hours Rinse Sterilization Sanitize first then dry Wrap or disposable packaging Hinged instruments should be left open (hemostats) Place in Autoclave (steam under pressure) Chemical Sterilization Indicators Special dyes change color with temperature, pressure or time Autoclave tape – used to tape package, diagonal stripes turn black Autoclave – 250 degrees F; 15 min to 30 min Surgery Suite Surgical Scrubs, booties, hat Mask when entering the room Portable in Surgery; if not, clean one before entering Sterile bags over tube if positioning over a patient SURGICAL ASEPSIS Sterile Attire Preparing A Sterile Field Sterile Field MAINTAINING A STERILE FIELD Area neat and uncluttered Organize supplies before procedure Avoid quick movements or rearrangement once opened Minimize people walking into areas Drop supplies w/out reaching over Close doors and windows MAINTAING A STERILE FIELD If clean item touches sterile, its contaminated Sterile objects >2.5cm from edge of field Avoid touching face or body with sterile gloves When pouring, pour small amount into trash then fill sterile container.