Ch 31: Fungi
advertisement

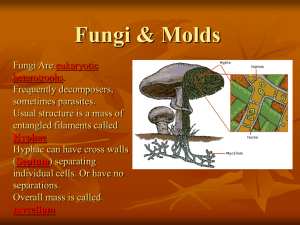
• Contractile vacuole action • Amoeboid movement • See it! • Chapter 31 ~ Fungi Humongous Fungus Honey Mushroom Blankets Forest, Kills Trees It is as large as 1,665 football fields combined. It is 3.4 square miles in size and covers 2,200 acres of land in the Blue Mountains of eastern Oregon. Fungi • Heterotrophic by absorption (exoenzymes) • Decomposers (saprobes), parasites, mutualistic symbionts (lichens) • Hyphae: body filaments •septate (cross walls) •coenocytic (no cross walls) • Mycelium: network of hyphae • Chitin cell walls (polysaccharide) Cell wall Nuclei Cell wall Pore Septum Septate hypha Nuclei Coenocytic hyph LE 31-2 Reproductive structure Hyphae Spore-producing structures 20 µm Mycelium Fungus Life Cycle Most have 3 distinct phases: 1. Haploid (n) 2. Heterokaryotic (n + n) (think of Sordaria) 3. Diploid (2n) Asexual phases: (n spores, n clones) Sexual Phases: (n spores, w/ genetic variety) Plasmogamy (cytoplamic fusion) Dikaryotic (n + n) Karyogamy (nuclei fusion) Diploid (2n) Meiosis (spores n) Bread Mold Life cycle Key Heterokaryotic stage Haploid (n) Heterokaryotic (n + n)) PLASMOGAMY (fusion of cytoplasm) Diploid (2n) KARYOGAMY (fusion of nuclei) Spore-producing structures Zygote Spores ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Mycelium SEXUAL REPRODUCTION MEIOSIS GERMINATION GERMINATION Spore-producing structures Spores Fungi Diversity, I • Phy: Chytridiomycota •aquatic fungi; chytrids •lineage closest to protists (flagella) • Phy: Zygomycota •Rhizopus (food mold) •mycorrhizae: mutualistic with plant roots •zygosporangia: resistant structure (freezing and drying) Fungi Diversity, II • Phy.: Ascomycota •sac fungi • yeasts, truffles, morels, Sordaria •asci: sexual spores •conidia: asexual spores • Phy.: Basidiomycota • club fungus •mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungus, rusts •basidiocarps: produce sexual spores Specialized Lifestyles, I • Molds •only the asexual stage (asexual spores) •Penicillium (antibiotic, cheese) • Yeasts •unicellular, asexual budding •Saccharomyces (bread, alcohol) Specialized Lifestyles, II • Lichens • symbiotic association held in a hyphae mesh •alga provides food, fungus provides physical environment •pioneer organisms •air pollution detection • Mycorrhizae •root and fungi mutualism •found in 95% of vascular plants •exchange of organic minerals •increases absorptive surface of roots