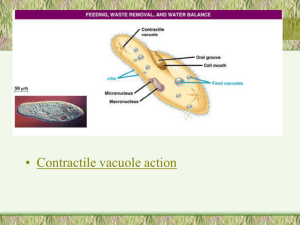
Biology 124 SI Chapter 31 answers
advertisement

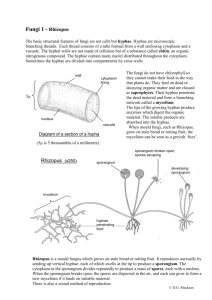
Biology 124 SI Chapter 31 1. What were the two body systems of fungi discussed in class? Hyphae – multicellular hair like projections surrounded by a cell wall. They spread out to form mycelium which maximizes the surface to volume ratio for nutrient absorption. The cell walls are strengthened by chitin, not cellulose. Yeast – single celled fungi that usually inhabit moist conditions. 2. What are the two different types of hyphae? Septate hypha – have cell divisions (septa) with pores that allow organelles to flow from cell to cell. Coenocytic hypha – no divisions, just thousands of nuclei. This allows for repeated division of nuclei without cytokinesis. 3. Beginning with mycelium, describe the general asexual and sexual reproductive cycles of fungi. During asexual, mycelium produce spores which germinate to form more mycelium. During sexual, mycelium undergo plsmogamy (fusion of the cytoplasm) with another mycelium usually of an opposite mating type. The fused pair is now heterokaryotic (meaning multiple nuclei). The pair then undergoes karyogamy (fusion of the nuclei) and the zygote quickly undergoes meiosis to give rise to 4 haploid spores which then germinate to form more mycelium. The mycelium can enter either the sexual or asexual portion of its lifecycle at any time depending on environmental ques. 4. How to the two opposite mating types find each other? Pheromones 5. What does it mean if an organism is a saprophyte? It obtains its nutrients from dead organisms. 6. What is a microsporidia? A single cellular parasite that infects eukaryotic cells (not plants) and propogates itself by way of spores (like a fungus). DNA suggests that this is a fungus, but it is under debate. 7. What are the different fungal types, and what are distinguishing characteristics of each? a. Chytrids-flagellated spores (zoospores). Freshwater and terrestrial, decomposers, parasites, and mutualists. b. Zygomycetes – resistant zygosporangium as sexual stage. Some are parasites, and some are commensal (have neutral relationships). Black bread mold. c. Glomeromycetes – arbuscular mycorrhizae formed with plants d. Ascomycetes – sexual spores (ascospores) born internally in sacs called asci. Vast numbers asexual spores (conidia) produced. Morel and truffle. They also have specialized hypha called conidiaphores. e. Basidiomycetes – Elaborate fruiting body (basidiocarp) containing many basidia that produce sexual spores (basidiospores). Club fungi (because bascidia look like clubs) 8. Describe the life cycle, both sexual and asexual, for black bread mold. See the diagram in your book.