The digestive system
advertisement

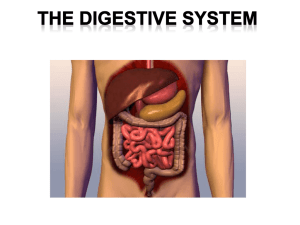
The digestive system “ The digestive system takes in food, breaks it down into nutrient molecules and absorbs them into the bloodstream, and then rids the body of the indigestible remains.” -E. Marieb PARTS 1. Gastrointestinal (GI) tract 2. Accessory organs Digestive processes (disassembly) 1. 2. Ingestion Propulsion a. swallowing b. peristalsis 3. 4. 5. 6. Mechanical digestion Chemical digestion Absorption Defecation 1. MOUTH (oral cavity) Mechanical digestion teeth/tongue Chemical digestion salivary glands: Contains enzymes 2. pharynx Skeletal muscle 3. esophagus Propels food using muscles (peristalsis) 4. stomach Mechanically and chemically digested into chyme Limited absorption Neural control Stretch receptors activated. Impulse to neurons in stomach wall. Continued gastric gland production and causes peristalsis Hormonal control: Food triggers release of gastrin (hormone). Goes in blood. Triggers: gastric gland juices constricts sphincter to prevent acidreflux, relaxes lower stomach sphincter. What food type is chemically digested in the mouth? What is the function of the esophagus? 5. Small Intestine Mechanical digestion Chemical digestion (all) Done with enzymes from pancreas and bile (formed in liver). Pancreatic duct and bile duct empty into superior small intestine Absorption (nutrients) 6. Large Intestine Mechanical digestion: Chemical digestion: Peristalsis Mass peristalsis Bacteria Absorption: Water Some vitamins Don’t write: What is bile? Bile is a yellow, brown, or green, watery solution containing bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, phospholipids and a variety of electrolytes. pH of 7.6 – 8.6 Liver Produces bile Bile: part waste product, part digestive secretion (mechanical digestion of lipids) Metabolism of carbs, lipids, and proteins Processing of drugs and hormones Excretion of bilirubin (from heme of old RBCs) liver summary… Blood from stomach and intestines passes through liver. When the liver has broken down harmful substances, they are excreted into the bile or blood. Bile by-products enter the intestine and ultimately leave the body in the feces. Blood by-products are filtered out by the kidneys and leave the body in the form of urine. gallbladder Stores bile releases in response to fatty food PANCREAS Releases enzymes into duodenum (s. intestine) has an endocrine function Summary questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What mainly happens in the small intestine? Where is bile made? What organ stores bile? In which organ is water mainly absorbed? What is the circular muscle contraction called that involuntarily moves food through the GI tract? Where is chyme produced?