Midterm Review - TJ
advertisement

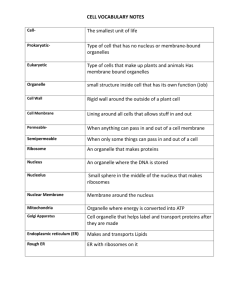
MIDTERM REVIEW Biology 9 Warm-Up (p. 2): Thursday Dec. 10 objective I can use my notes and textbook to review highest priority topics. warm-up 1. What is the difference between an autotrophic and heterotrophic organism? Give an example of each. (HINT: Use a book index!) 2. List TWO differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Thursday Dec. 10 hw Study for midterms!! Biology exam will be… agenda -6th: Binder Quiz -Do You Have A Study Guide? -Trivia: Intro/Method/Classify/Chemistry -Work on study guides -Exit Ticket Midterm Review, Day 1 Overview of Midterm Preparation Overview/ explanation of review process Steps For Mid-Term Review: 1. 2. 3. 4. Rank your understanding of each unit and prioritize studying (Course Content Meter, p. 69) Collect study guides and order by priority from Step 1- highest priority unit goes on top, second highest priority goes next.. Organize your binder! Begin filling out the study guide & reviewing for your highest priority unit 1) All organisms are composed of: A. B. C. D. diatoms. cells. cellulose. None of the above. 2) A hypothesis is: A. B. C. D. a definite answer to a given problem. a testable possible explanation of an observation. a proven statement. a concluding statement. 3) A neutral solution has a pH of: A. B. C. D. 1 5 7 10 4) Polar molecules such as water have: A. B. C. D. no negative or positive poles. both negative and positive poles. only a negative pole. only a positive pole. 5) All living things maintain a balance within their cells relative to the environment through the process of: A. B. C. D. growth. development. homeostasis. evolution. 6) Which of the following is an example of a quantitative observation? A. B. C. D. The chemical is 25 degrees Celsius. The chemical is liquid. The chemical is blue. The chemical has an odor. 7) When a molecule gains an electron, it has been A. B. C. D. oxidized. reduced. digested. inactivated. 8) The smallest particle of carbon that can retain the chemical properties of carbon is A. B. C. D. a carbon molecule. a carbon macromolecule. a carbon atom. the nucleus of a carbon atom. 9) The scientific name for the woodchuck is Marmota monax. What is its genus? A. B. C. D. Monax Eukarya Marmota Animalia 10) Which of the following is contained in eukaryotic cells but NOT prokaryotic cells? A. B. C. D. cell membrane cytoplasm ribosomes nucleus 11) The organism depicted to the right is a member of Kingdom.. A. B. C. D. Fungi. Animalia. Plantae. Protista. 12) _____________ is a bond formed by electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms. A. B. C. D. Hydrogen Covalent Divalent Ionic 13) Which of the eukaryotic kingdoms consists mostly of unicellular organisms? A. B. C. D. Plantae. Animalia. Fungi. Protista. 14) Humans and apes are both classified in the order Hominidae. Humans and apes are therefore also classified in the same: A. B. C. D. class. genus. family. species. 15) Compared to eukaryotes, prokaryotes… A. B. C. D. are less complex and have a nucleus. are more complex and have a nucleus. are less complex and don’t have a nucleus. are more complex and don’t have a nucleus. 16) The diagram on the right indicates that sodium’s _______________ is 11. A. B. C. D. atomic weight. molecular mass. atomic number. molecular stability. 17) List the hierarchical classifications in order from most general to most specific. A. B. C. D. kingdom, phylum, order, class, domain, genus, species, family species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain family, species, genus, domain, class, order, phylum, kingdom domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species 18) A _____________ is a substance that is formed when atoms of 2 or more elements join together. A. B. C. D. molecule. compound. solution. particulate matter. 19) These two particles make up the nucleus of an atom. A. B. C. D. protons & electrons electrons & neutrons protons & neutrons none of the above 20) This is the substance that dissolves a solute to form a solution. A. B. C. D. ice molecule particle solvent Warm-Up (p. 2): Friday Dec. 11 objective I can use my notes and textbook to review highest priority topics. warm-up 1. What is the function of enzymes? 2. How are enzymes affected in a) heat, and b) cold 3. Copy the table below and fill it in! k Macromolecule Monomer Function k 1) 2) k 3) 4) Friday December 11 hw Study for midterms!! Biology exam will be… -6th: Tues 12/15, 8:00-9:30 -7th: Tues 12/15, 9:35-11:05 -8th: Wed 12/16, 9:35-11:05 agenda -Individual: Unit 3/4 Questions -Small Groups: Key Questions/High Priority Units -Work on study guides -Exit Ticket 1) This organelle is a jelly-like fluid that fills all cells: 1. 2. 3. 4. Cytoskeleton Nuclear envelope Cytoplasm Centriole 2) This molecule stores genetic instructions in all cells: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribosome DNA Centriole Nuclear Envelope 3) This organelle make proteins: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Mitochondria 4) This structure controls what enters and leaves the cell: A. B. C. D. Cell Wall Nucleolus Cell Membrane Nucleus 5) All cells contain these three components: 1. 2. 3. 4. DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm DNA, cell membrane, ribosomes ribosomes, cell membrane, DNA cell membrane, DNA, cytoplasm 6) This organelle performs cell respiration to make ATP energy: A. B. C. D. Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum 7) This organelle helps to digest food, wastes, and dead organelles: 1. 2. 3. 4. Lysosome Vacuole Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus 8) This cell structure is made of thin protein rods and provides internal support and movement: 1. 2. 3. 4. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoskeleton 9) Plant cells have these 3 structures, which animal cells lack: 1. 2. 3. 4. Cell membrane, chloroplast, chlorophyll Cell wall, chloroplast, chlorophyll Cytoskeleton, chloroplast, centriole Cytoskeleton, centriole, cell membrane 10) This organelle modifies, packages, and ships proteins: 1. 2. 3. 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Chloroplast 11) This molecule carries genetic instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes: 1. 2. 3. 4. DNA RNA Protein Lipids 12) This organelle stores water (especially in plant cells): 1. 2. 3. 4. Centriole Lysosomes Vacuole Nucleolus 13) This organelle contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that collects sunlight for photosynthesis: 1. 2. 3. 4. Chloroplast Cell membrane Cell wall Centriole 14) Which of the following most likely happens to the cells of a person running the Boston Marathon? A. B. C. D. The respiration rate increases to produce more ATP The replication rate increases to produce more DNA The photosynthesis rate increases to produce more sugars The cell division rate increases to produce more muscle fibers 15) In red blood cells, the compound carbonic anhydrase increases the rate at which carbon dioxide is converted to bicarbonate ions for transport in the blood. In red blood cells, carbonic anhydrase acts as which of the following? 1. 2. 3. 4. A lipid A hormone An enzyme A sugar 16) Some bacteria live in hot springs. Their cells contain enzymes that function best at temperatures of about 70oC. At a temperature of 150oC, how will the enzymes in these bacterial cells most likely be affected? A. B. C. D. The enzymes will be destroyed by lysosomes. The enzyme will require less energy to function. The protein structure of the enzyme will be deformed. The enzyme will increase the rate of reactions than at 70oC. 17) Many plants have waxy coatings on some surfaces. This coating reduces water loss because it is not waterpermeable. This waxy coating is which of the following types of organic molecule? 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrate Lipid Nucleic Acid Protein 18) Passive transport is the movement of molecules from areas of _____ concentration to areas of _____ concentration. 1. 2. 3. 4. equal, low equal, high high, low low, high 19) When sodium ions rush into a cell during transmission of a nerve stimulus, this creates a very high concnetration of sodium molecules in the cell and a low concentration of sodium molecules outside of the cell. This is an example of: 1. 2. 3. 4. passive transport osmosis active transport facilitated diffusion 20) DNA and RNA are examples of which macromolecule? 1. 2. 3. 4. Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids BONUS: The drawing below represents an organism that a student observed when examining a sample of pond water with a light microscope. What is the organism? A. B. C. D. Prokaryote Plant Fungus Protist SURVEY… 1. 2. When you receive your square, write your name on top. On the same side as your name, write the unit that you need the MOST work on currently. REMINDER: -Unit 1: Classifications, Scientific Method -Unit 2: Chemistry -Unit 3: Biochemistry (Macromolecules, Enzymes) -Unit 4: Cells, Membranes, Transport Today’s Review: Key Questions These will help you be prepared to answer open response questions! Each person in your group should write out a paragraph or a list of bullet points to answer the key question for this unit. Work together but write your own answers! When finished, continue reviewing anything you want WITH YOUR GROUP. Exit Ticket Put a 1 next to the Unit that you still need the most work on Put a 2 next to the Unit you need the next most work on Put your name on the ticket and hand it in!