Powerpoint
advertisement

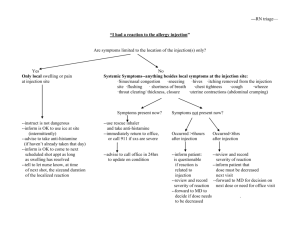
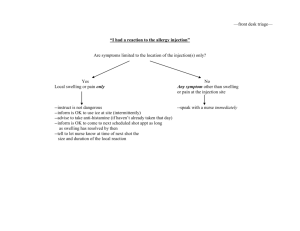
Cost-effectiveness of combined sexual and injection risk reduction interventions among Female Sex Workers who inject drugs in two very distinct Mexican-US border cities José L. Burgos, MD, MPH, AAHIVS Assistant Professor Division of Global Public Health School of Medicine University of California San Diego Funding: NIMH grant # K01 MH095680 NIDA grant # R01 DA023877 NIDA grant # R01 DA023877-S1 NIMH grant #R01 MH065849 Coauthors/Co-Investigators • • • • • • • • • Jose Luis Burgos, UC San Diego, USA Thomas L. Patterson, UC San Diego, USA Joshua S. Graff-Zivin, UC San Diego, USA James G. Kahn, UC San Francisco, USA Gudelia Rangel, COLEF, Mx. Victoria D. Ojeda, UC San Diego, USA M. Remedios Lozada, ISESALUD, Mx. Hugo Staines, UACJ, Mx. Steffanie A. Strathdee, UC San Diego, USA Clinical trial registration number: NCT00840658 About Mujer Mas Segura • A brief combined theory-based intervention to simultaneously reduce sexual and injection risks among IDU-FSWs ages 18+ • IDU-FSWs from Tijuana and Cd. Juarez were randomized to simultaneously examine two interventions – Interactive Vs. Lecture formats • Measures: questionnaires; biological samples to detect four STIs including HIV http://gph.ucsd.edu/research/contaminacion.shtml 2x2 Intervention Factorialeffects Designon to HIV/STI Simultaneously incidence Evaluate after 12 Injection months: and Sexual Risk Reduction Cd. Tijuana Juarez Intervention No Yes Risk intervention Interactive Sex Interactive Injection Risk Intervention (Adj RR; 95% CI*) No Yes Group A (control) Group B 1.15 Reference Group C 0.38 0.44 (0.16, 0.99) 0.89) (0.19, (0.58, 2.28) Group D 0.37 1.12 (0.16, (0.56, 0.89) 2.25) *Adjusted for # of unprotected sex acts with non-regular clients , and arrests prior to enrolment Strathdee, et al. 2012 Impact of Injection Risk Interventions on Injection Risk Index: Tijuana and Cd. Juarez Strathdee, et al. 2012 Goal of the CE analysis • To assess the cost-effectiveness of a behavioral intervention combining two interventions to increase safer sex and safer injection practices among FSW-IDUs in Ciudad Juarez and Tijuana, Mexico. • To inform evidenced based Sex work-harm reduction policies in the Mexico-U.S. border region in respect to access to sterile syringes and condoms among FSW-IDUs. Cost Effectiveness Model • Discrete transitional state mathematical model • Costs and outcomes for one-year and remainder of life of FSW-IDUs comparing a lecture format to each individual interactive components and the combined MMS intervention. • Societal perspective • Multivariate sensitivity analysis • Cost and outcomes discounted at an annual rate of 3% • Currency adjusted to 2012 U.S. Dollars Model Inputs Costs Administrative personnela Outreach workersa Counseling session (30 min) RN sample collection (15 min) Gc/CT RPR Rapid HIV test HIV confirmatory test Syringes, gloves, speculum, other Chlamydia (Azitrhromycin 1 gr.) Gc (Ceftriaxone 125 mg) Syphilis (Benzathine penicillin G) Three doses for HIV positive FSWs Participant’s time (hour) Space/Utilities/mileagea aAnnual Base Value $9,000 $9,600 $6.00 $3.00 $22.00 $5.00 $5.00 $56.00 $2.00 $20.00 $12.70 $ 10.00 $30.00 $6.29 $7,900 Source STPSb, CONASAMIc STPSb, ISESALUDd STPSb, ISESALUDd STPSb, ISESALUDd MMSe, CANf MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg MMSe, SEg STPSb, CONASAMIc MMSe costs; bSecretaría del Trabajo y Previsión Social ; cComisión Nacional de Salarios Mínimos; dInstituto de Servicios de Salud Pública; eMujer Mas Segura Project; fSecretaría de Economía Base value Range Among FSW-IDUs in Tijuanaa 64.3 (34.6, 93.9) Among FSW-IDUs in Cd. Juareza 66.1 (30.2, 102.0) Model Inputs HIV/STI combined incidence: Calculated HIV injection risk: Receptive contaminated syringe sharinga 0.669 Shared contaminated cotton/cooker/watera 0.0067 Contaminated syringe cleaned with bleacha 0 (0, 0.21) 0.005 7.5 (0.003, 0.089) (6, 11) Utilities QALYb lost per STI episode QALYb lost due to HIV infection aPer 100 person years adjusted life years bQuality Cost-Effectiveness on Averted STI Strategy Control sex groups (Lecture format) Intervention sex groups (Interactive format) Cost per averted episode of sexually transmitted infection Tijuana Cd. Juarez -- -- $42 $41 Reported Episodes of Receptive Syringe Sharing During the Previous Month Control injection group Intervention Injection group 81 79 52 15 Baseline 21 16 12 months Tijuana 55 Baseline 16 12 months Ciudad Juarez Cost-Effectiveness on Safer Injection Practices Strategy Control injection groups (Lecture format) Intervention Injection groups (Interactive format) Cost per averted episode of receptive syringe sharing Tijuana Cd. Juarez -- -- -- $5.00 Base case results for a cohort of 1,000 FSW-IDUs over a life-time Strategy Didactic control Interactive Safe Sex/ Lecture format Safe Injection Interactive Safe Injection/ Lecture format Safe Sex Combined interactive Safe Sex/Interactive Safe Injection Cost-Effectivenessa Tijuana Cd. Juarez -- -- $5,921 $4,710 Dominated Dominated $94,166,643 $7,162.74 aCost per QALY gained 180000 160000 Reported Numbers of Syringes Exchanged and Prevenkits* Distributed in Tijuana and Cd. Juarez 2007-2011 140000 120000 100000 Cd. Juarez Syringes 80000 Cd. Juarez Prevenkits 60000 Tijuana Syringes 40000 Tijuana Prevenkits 20000 *kits with sterile water, cooker, cotton & syringes 0 Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 Study Period 2011 Tijuana– Multivariate Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Interactive safer sex/ Interactive format safe sex intervention/ Lecture injection Lecture formasafer safe injection intervention Cd. Juarez– Multivariate Cost-Effectiveness Analysis For ciudad Juarez – Multivariate analysis Interactive safer sex/ Lecture safer injection Conclusions • In the absence of expanded NEP the combined Mujer Mas Segura intervention is likely to be cost-effective • Improved access to sterile injection equipment at the community level shows a larger impact in reducing unsafe injection practices among FSW-IDU, with no significant added benefit from the interactive safer-injection component of the Mujer Mas Segura Intervention. Acknowledgements • Our participants and the sex worker communities in Tijuana and Cd. Juarez • NIH Grants: R01 DA023877 DA023877-S1 K01 MH095680 • Staff from the Preven Casa, A. C., UCSD • San Diego County Public Health Laboratory References • Patterson TL, Mausbach B, Lozada R, Staines-Orozco H, Semple SJ, Fraga-Vallejo M, Orozovich P, Abramovitz DA, de la Torre A, Amaro H, Martinez G, MagisRodriguez C, Strathdee SA. Efficacy of a brief behavioral intervention to promote condom use among female sex workers in Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez, Mexico. Am J Public Health. 2008;98(11):2051-2057. • Burgos JL, Gaebler JA, Strathdee SA, Lozada R, Staines H, Patterson TL: Costeffectiveness of an intervention to reduce HIV/STI incidence and promote condom use among female sex workers in the Mexico-US border region. PLOS One 2010, 5(6):e11413. • Strathdee SA, Magis-Rodriguez C: Mexico's evolving HIV epidemic. JAMA 2008, 300(5):571-573. • Bell DC, Trevino RA: Modeling HIV risk. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1999, 22(3):280-287. • Sonnenberg FA, Beck JR: MARKOV-MODELS IN MEDICAL DECISION-MAKING A PRACTICAL GUIDE. Medical Decision Making 1993, 13(4):322-338. Extra Slides Prop. OR for reported easy access to sterile syringes