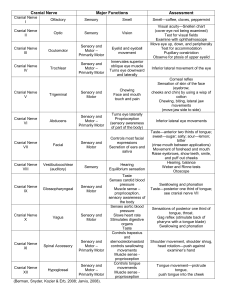
Sensory Function
advertisement

CONCEPT OVERVIEW Intracranial regulation: Mechanisms that facilitate or impair neurologic function. Interrelationships: Brain requires oxygenation. Respiratory and cardiovascular systems impacted by neurologic control. Extensions of neurologic function: Sensory perception. Tactile perception. 2 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Nervous system controls body functions through voluntary and autonomic responses to external and internal stimuli. Structural divisions of nervous system are: Central nervous system (CNS), which consists of brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system Autonomic nervous system 3 4 CRANIAL NERVE I – OLD FACTORY Not routinely tested Test with: Report of smell Head trauma Abnormal mental status Suspected intracranial lesion (tumor) Sensory function: With eyes closed occlude nares and present aromatic substance Patient able to correctly identify aromatic substance CRANIAL NERVE II – OPTIC NERVE Sensory Function-: Visual Acuity: Snellen Chart- L-20/20, R 20/15, B 20/15. Visual fields : intact, PERRLA Assess optic disc: color, shape: optic disc creamy yellow, round with distinct margins. CRANIAL NERVE III,IV,VI MOTOR FUNCTION •CNVI-abducens- innervates the lateral rectus muscle for lateral movement. Abducts the eye. •CNVI-trochlear- innervates the superior oblique muscles moving the eye down and in. •CNIII- ocular motor- innervates all the rest of the eye moving superior, inferior, medial, rectus and the inferior oblique muscles. CRANIAL NERVE V:TRIGEMINAL Motor Function: Palpate temporal and masseter muscles as patient clenches teeth. Try to separate jaw by pushing down on chin. Jaw strength equal bilaterally. Sensory Function Test light sensation with cotton ball over: forehead (ophthalmic); Cheeks (maxillary); Chin ( mandibular). Sensation intact and equal bilaterally. CRANIAL NERVE VII Motor Function: Smile, frown, puff cheeks, smile, show teeth. Facial muscles intact & symmetrical. Sensory Function: Not tested routinely- tested only is suspect facial nerve damage. Taste on anterior 2/3 tongue with cotton applicator with salt, sugar, and lemon Sweet, sour, bitter. Patient able to identify sweet, sour and bitter. CRANIAL NERVE VII Corneal Reflex: • Only perform if patient is unconscious or with abnormal facial sensation or movement. • Remove contact lenses if in place. • Lightly touch cornea with wisp of cotton from side, the lids of both eyes blink when the cornea is touched. This test the sensory of reception of the ophthalmic (afferent) branch CNV & the motor branch (efferent) of CNVII which creates the blink. Corneal Reflex intact. CRANIAL NERVE VII ACOUSTIC AKA: Vestibulocochlear Nerve Sensory function Assess hearing acuity: Ability to hear normal conversation o Whisper voice test – Whisper words heard bilaterally o Weber tuning fork test- tone heard midline equally in both ears o Rinne test is to assess hearing by comparing air conduction(AC) of sound to bone conduction(BC) of sound. AC>BC,\. CRANIAL NERVE IX AND X CN IX Glossopharyngeal CH X Vagus Motor function: Swallow- swallowing intact Depress with tongue blade & note pharyngeal movement as patient says, “ahhh”. Uvula rises and falls midline with phonation. Touch posterior wall to illicit gag reflex. Gag reflex intact. Note sound of voice. Sensory function Taste posterior 1/3 of tongue : not routinely tested. CRANIAL NERVE XI - SPINAL ACCESSORY Motor Function: Rotate head against resistance Shrug shoulders against resistance Shoulder shrug and head intact and equal bilaterally. CRANIAL NERVE XII – HYPOGLOSSAL Motor function Have patient protrude u\observe tongue for tremors and wasting Is tongue midline Tongue protrudes midline without tremors. Say light tight dynamite Note if the words are clear and distinct. Light, tight and dynamite are clear and distinct.