Chpt. 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion
advertisement

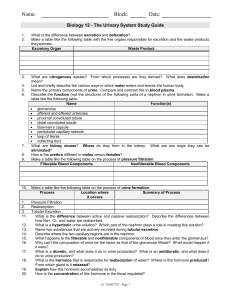
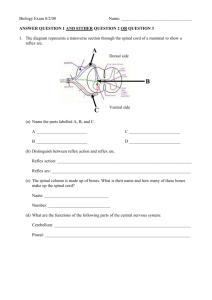
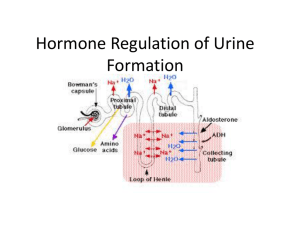
Chpt. 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Julianna Diddle Ethan Coombes • Where is homeostasis regulated in mamals vs. reptiles? –Regulated internally = MAMMALS --Regulated externally = REPTILES • What is an osmoconformer? -An animal that doesn’t actively adjust its internal osmolarity • What is an osmoregulator? –An animal that must control its internal osmolarity because its body fluids are not isoosmotic with the outside environment -hyperosmotic -saltwater -ioosmotic -hypoosmotic -freshwater • What special characteristics do anhydrobiotic animals have? –They can lose almost all body water & survive in a dormant state if their habitats dry up. • What are the three types of nitrogenous waste, what is different about them, and what is an animal that excretes each type? –Ammonia(NH3) -most toxic -Excreted by aquatic animals –Urea -low toxicity -Requires less water to dilute & can store large quantities -Mamals, adult amphibians, sharks, some bony fish, & turtles --Uric Acid -Least toxic -Insoluble -Can be excreted with little water loss but energetically expensive -Insects, land snails, many • What are the four main steps of the excretory process? 1. 2. 3. 4. Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Excretion Kidney Renal vein Renal Artery Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra • What is the functional unit of the kidney? (1,000,000/kidney in humans) –Nephron • What is the pathway of filtrate after leaving the glomerular capsule? –Proximal tubule, loop of Henle (descending & ascending loops), distal tubule, collecting duct, renal pelvis, ureter • What are the two types of nephrons? 1.) Juxtamedullary Extend into medulla, important for water conservation 2.) Cortical Loop of Henle stays in the cortex • What is the pathway for blood supplying each nephron? –Afferent arteriole, glomerular capillaries, Efferent arteriole, peritubular capillaries, vasa recta • Systems that expend energy to create concentration gradients are –. –Countercurrent multiplier systems • What is the hormone that regulates water balance & increases collecting duct permeability to water –Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) • What is the condition of increased urination called? -Diuresis • What does the RAAS do? (Renin-Angiostentin-Aldosterone System) -Works with the Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) to drop blood pressure & blood volume & triggers JGA to release renin -Angiostentin II & Aldosterone reduce renin secretion in response to JGA • What is the peptide hormone that opposes RAAS & is released by the atria of the heart in response to increased blood volume & pressure? –Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF) • What is osmoregulation? –Solute balance & gain or loss of water • What is excretion? -Elimination of nitrogenous wastes