Animal Structure and Function
advertisement

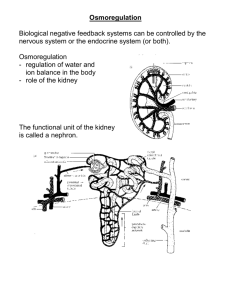
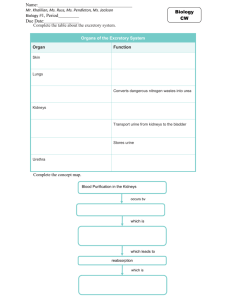
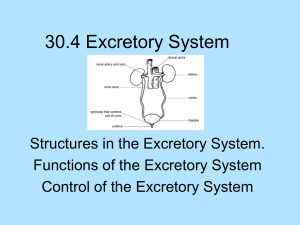
Controlling the Internal Environment Thermoregulation Osmoregulation Excretion Thermoregulation • Ectothermic • Endothermic • Poikilothermic • Homeothermic Heat Exchange Heat Exchange • Conduction - direct transfer of heat • Convection - transfer of heat by the movement of air or water across a surface • Radiation - emission of electromagnetic waves • Evaporation - loss of heat from changing a liquid into a gas Body Temp vs. Ambient Temp Thermoregulation Adjustments • Adjusting the rate of heat exchange – vasodilation/vasoconstiction – countercurrent heat exchange • Cooling by evaporation • Behavioral responses • Changing the rate of metabolic heat production Endothermic Animals • Invertebrates – Large flying insects – Honeybees Endothermic Animals • Fish – Bluefin tuna – Swordfish – Great white shark • Countercurrent heat exchange Amphibians and Reptiles • Most are ectothermic – regulate temperature by behavior Mammals and Birds • Contraction of muscles – moving – shivering • Nonshivering thermogenesis – triggered by hormones Feedback Mechanisms • High body temperature – hypothalamus activates skin blood vessels to dilate and the sweat glands to produce sweat • Low body temperature – hypothalamus activates skin blood vessels to constrict and the skeletal muscles to shiver Temperature Range Adjustments • Slow changes – acclimatization (enzymes and membranes) • Fast changes – heat-shock proteins Metabolic Cycles • Torpor • Hibernation • Aestivation Osmoregulation • Osmoconformers vs. Osmoregulators Osmoregulation • Marine Fish – – – – hypoosmotic lose water to environment must excrete salt small amounts of urine • Freshwater Fish – hyperosmotic – gain water from environment – must take in salt – large amounts of urine Functions of the Excretory System • • • • Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Excretion Excretion of Nitrogenous Waste • Ammonia • Urea • Uric Acid Invertebrate Structures • Protonephridia (flame cells) • network of closed tubules • used mostly for osmoregulation • found in platyhelminthes, some annelids, mollusk larvae Invertebrate Structures • Open tubules surrounded by a nephrostome • Osmoregulation and excretion • Found in annelids Invertebrate Structures • Malpighian Tubules • Open into the digestive tract • Osmoregulation and excretion • Insects and terrestrial arthropods Excretory Systems Origins in Vertebrates • Pronephros, Mesonephros, Metanephros Vertebrate Excretory Systems • Pronephros – adult hagfish, embryonic fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals • Mesonephros – adult lamprey, fish, amphibians, embryonic reptiles, birds, mammals • Metanephros – adult reptiles, birds, mammals The Human Excretory System • • • • Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra Blood Filtrate to Urine • Bowman’s Capsule and the Glomerulus – (filters the blood) • Proximal tubule – reabsorbed (NaCl, Potassium, Water, Nutrients) – secretes ( ammonia) – regulates (pH) Blood Filtrate to Urine • Loop of Henle – Descending loop • reabsorbed (water) – Ascending loop • reabsorbed (NaCl) Blood Filtrate to Urine • Distal tubule – reabsorbed (NaCl, Water) – secrete (potassium) – regulate (pH) • Collecting duct – reabsorbed (NaCl, Water, Urea) Control of the Kidney • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – water reabsorption • Renin-angiotensinaldosterone system (RAAS) – water reabsorption • Atrialnatiuretic Factor (ANF) – inhibits the release of renin