Document
advertisement

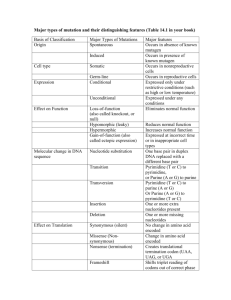
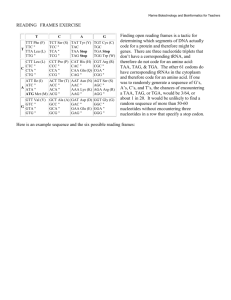
Institute of Molecular Biotechnology Jena Swetlana Nikolajewa, Andreas Beyer, Maik Friedel, Jens Hollunder, Thomas Wilhelm Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, Jena Germany Overview: Purine-Pyrimidine Patterns Part 1 New Classification Scheme of the Genetic code Part 2 Type II Restriction Enzyme Binding Sites Overview: Genetic Code Part 1. The purine-pyrimidine scheme of the genetic codes shows amino-acids patterns and regularities of codons symmetry characteristics possible predecessors of our contemporary quaternary triplet code explanation for the number (22) of tRNA genes in mammalian mitochondrial genome PuRines vs. PYrimidines A G C T Purine pairs with Pyrimidine 3 H Bonds 2 H Bonds The Common Genetic Code Table 2nd base 3 nucleobases (triplets) of A, G, C, U code for 20 AAs U C A G 64 possible codons (4x4x4=43) U UUU Phe UUC Phe UUA Leu UUG Leu UCU Ser UCC Ser UCA Ser UCG Ser UAU Tyr UAC Tyr UAA Stop UAG Stop UGU Cys UGC Cys UGA Stop UGG Trp U C A G C CUU Leu CUC Leu CUA Leu CUG Leu CCU Pro CCC Pro CCA Pro CCG Pro CAU His CAC His CAA Gln CAG Gln CGU Arg CGC Arg CGA Arg CGG Arg U C A G U C A G 3 termination codons: UGA, UAG, UAA Met (AUG) codon is also the start codon 1st base A AUU Ile AUC Ile AUA Ile AUG Met ACU Thr ACC Thr ACA Thr ACG Thr AAU Asn AAC Asn AAA Lys AAG Lys AGU Ser AGC Ser AGA Arg AGG Arg G GUU Val GUC Val GUA Val GUG Val GCU Ala GCC Ala GCA Ala GCG Ala GAU Asp GAC Asp GAA Glu GAG Glu GGU Gly GGC Gly GGA Gly GGG Gly The Common Genetic Code Table contains 64 fields… U C A G 3rd base Purine-Pyrimidine Classification Scheme of the Genetic Code C A binary representation of nucleobases purines : A, G → 1 pyrimidines: C, U → 0 23 = 8 different binary triplets 000 , 001, … ,111 each of these has again 8 possibilities, for instance: 000 stands for three pyrimidines: CCC, CCU, UUC, …, UUU 111 stands for three purines: GGG, GGA, GAA, …, AAA G binds via 3 hydrogen bonds in the complementary base pairing U binds via 2 hydrogen bonds in the complementary base pairing Purine-Pyrimidine Table of the Genetic Code Codon 000 Strong codons 6 H bonds Pro (C/U) Ser Proline 001 Pro 100 Ala 101 Ala 010 Arg CC GC (A/G) Ser (C/U) Thr (A/G) Thr (C/U) 110 Gly CG GG GG Glycine (A/G) Leu (A/G) AC (C/U) Val AC (A/G) AG Val (C/U) His Arg AG Arginine (A/G) Leu GU GU CA (A/G) Gln CA UU (A/G) Leucine (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) Isoleucine (A/G) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Isoleucine/Methionine (C/U) Tyr Histidine UA (C/U) Tyrosine (A/G) Stop (C/U) Asn UA (A/G) Glutamine (C/U) Asp Serine (A/G) CU (C/U) Phenylalanine Valine Stop/Trp UG Ser Phe UU Valine Tryptophan (C/U) (C/U) Leucine Cystein Glycine Gly UC Cys UG Arginine CU Weak codons 4 H bonds Leucine Threonine Arginine Arg Leu Threonine Alanine CG (C/U) Serine Alanine GC UC Mixed codons 5 H bonds Serine Proline 011 111 CC Mixed codons 5 H bonds GA (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Glutamatic acid AA (C/U) Asparagine Asparatic acid Lys AA (A/G) Lysine …the new scheme contains the same information in only 32 fields. Amino Acid Patterns: Polar Requirement of NCN and NUN Codons Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 hydrogen bonds 5 hydrogen bonds 5 hydrogen bonds 4 hydrogen bonds Codon 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser UC (C/U) Leu CU (C/U) Phe UU 001 Pro CC (A/G) Ser UC (A/G) Leu CU (A/G) Leu UU (A/G) 100 Ala GC (C/U) Thr AC (C/U) Val GU (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) 101 Ala GC (A/G) Thr AC (A/G) Val GU (A/G) 010 Arg CG (C/U) Cys UG (C/U) His CA (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) 011 Arg CG (A/G) Stop/Trp UG Gln CA (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) 110 Gly GG (C/U) GA (C/U) Asn Ser AG (A/G) (C/U) Asp Ile/Met AU Gly GG (A/G) Arg AG (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Glutamatic acid AA (A/G) (C/U) Asparagine Asparatic acid 111 (C/U) Lys AA (A/G) Lysine C. R. Woese, G. J. Olsen, M. Ibba, D. Söll Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases, the Genetic Code, and the Evolutionary Process. MMBR 2000(64) 202-236 Amino Acid Patterns: Hydrophobicity Codon Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 H-bonds 5 H-bonds 5 H-bonds 4 H- bonds 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser UC (C/U) Leu CU (C/U) Phe UU 001 Pro CC (A/G) Ser UC (A/G) Leu CU (A/G) Leu UU (A/G) 100 Ala GC (C/U) Thr AC (C/U) Val GU (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) 101 Ala GC (A/G) Thr AC (A/G) Val GU (A/G) 010 Arg CG (C/U) Cys UG (C/U) His CA (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) 011 Arg CG (A/G) Stop/Trp UG Gln CA (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) 110 Gly GG (C/U) Ser AG (C/U) Asp GA (C/U) Asn AA (C/U) 111 Gly GG (A/G) Arg AG (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Lys AA (A/G) (A/G) (C/U) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Kyte&Doolittle, 1982, http://biology-pages.info Codon-Anticodon Symmetry Codon Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 H-bonds 5 H-bonds 5 H-bonds 4 H-bonds 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser UC (C/U) Leu CU (C/U) Phe UU 001 Pro CC (A/G) Ser UC (A/G) Leu CU (A/G) Leu UU (A/G) 100 Ala GC (C/U) Thr AC (C/U) Val GU (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) 101 Ala GC (A/G) Thr AC (A/G) Val GU (A/G) 010 Arg CG (C/U) Cys UG (C/U) His CA (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) 011 Arg CG (A/G) Stop/Trp UG Gln CA (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) 110 Gly GG (C/U) Ser AG (C/U) Asp GA (C/U) Asn AA (C/U) 111 Gly GG (A/G) Arg AG (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Lys AA (A/G) (A/G) (C/U) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Point Symmetry Codon Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 H-bonds 5 H- bonds 5 H-bonds 4 H-bonds 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser UC (C/U) Leu CU (C/U) Phe UU 001 Pro CC (A/G) Ser UC (A/G) Leu CU (A/G) Leu UU (A/G) 100 Ala GC (C/U) Thr AC (C/U) Val GU (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) 101 Ala GC (A/G) Thr AC (A/G) Val GU (A/G) 010 Arg CG (C/U) Cys UG (C/U) His CA (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) 011 Arg CG (A/G) Stop/Trp UG Gln CA (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) 110 Gly GG (C/U) Ser AG (C/U) Asp GA (C/U) Asn AA (C/U) 111 Gly GG (A/G) Arg AG (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Lys AA (A/G) (A/G) (C/U) Ile/Met AU (A/G) D. Halitsky Extending the (Hexa-)Rhombic Dodecahedral Model of the Genetic Code: the Code's Four 6-fold Degeneracies and the Ten Orthogonal Projections of the 5-cube as 3-cube. Computer Systems Technology 2004 Codon-Reverse Codon (XYZ↔ZYX) Symmetry Codon Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 H-bonds 5 H- bonds 5 H-bonds 4 H-bonds 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser UC (C/U) Leu CU (C/U) Phe UU 001 Pro CC (A/G) Ser UC (A/G) Leu CU (A/G) Leu UU (A/G) 100 Ala GC (C/U) Thr AC (C/U) Val GU (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) 101 Ala GC (A/G) Thr AC (A/G) Val GU (A/G) 010 Arg CG (C/U) Cys UG (C/U) His CA (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) 011 Arg CG (A/G) Stop/Trp UG Gln CA (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) 110 Gly GG (C/U) Ser AG (C/U) Asp GA (C/U) Asn AA (C/U) 111 Gly GG (A/G) Arg AG (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Lys AA (A/G) (A/G) (C/U) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Codon-Reverse Codon (XYZ↔ZYX) Symmetry Stop AUC UAG STOP Asp AUC CUA GAU Asp Evolution of the Genetic Code our contemporary code is the quaternary triplet code: 43=64 fields 00* 00* 00* 00* 01* 01* 01* 01* 10* 10* 10* 10* 11* 11* 11* 11* CGU, UAC,… quaternary doublet code: 42=16 fields 00 00 00 00 01 01 01 01 10 10 10 10 11 11 11 11 CGU, UAC,… binary doublet: 41=4 fields 00 01 10 11 Evolution: Scenario 1 Codon 000 01 01 01 01 10 10 10 10 11 11 11 11 Mixed Mixed Weak 5 H bonds 4 H bonds Pro 100 Ala 101 Ala 111 00 5 H bonds Pro 110 00 6 H bonds 001 011 00 Strong CC (C/U) Ser Proline 010 00 CC (A/G) Ser (C/U) Thr (A/G) Thr Alanine Arg CG (C/U) CG Gly GG GG Glycine (A/G) Leu (A/G) AC (C/U) Val AC (A/G) Val His AG Arg AG (A/G) Leu GU GU CA (A/G) Gln (C/U) CA (C/U) Ile (A/G) (A/G) AU (C/U) Isoleucine (A/G) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Isoleucine/Methionine (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) Tyrosine (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) Glutamine Asp GA (C/U) Asn Glu GA (A/G) Glutamatic acid AA (C/U) Asparagine Asparatic acid Arginine UU Leucine Histidine Serine (A/G) CU (C/U) Phenylalanine Valine (C/U) Stop/Trp UG Ser Phe UU Valine Tryptophan (C/U) (C/U) Leucine Cystein Glycine Gly UC Cys UG Arginine CU Leucine Threonine Arginine Arg Leu Threonine Alanine GC (C/U) Serine Proline GC UC Serine Lys AA Lysine (A/G) Evolution: Scenario 2 Codon 000 Pro Pro 100 Ala 101 Ala 010 011 110 111 01 01 01 10 10 10 10 11 11 11 11 Mixed Weak 5 H bonds 4 H bonds CC (C/U) Ser CC GC GC CG CG (A/G) Ser (C/U) GG Leu Thr (A/G) Thr UC (A/G) Leu AC (C/U) Val AC (A/G) Val Cys UG (C/U) His (A/G) Gln AG Arg AG Leu GU GU CA (C/U) CA (C/U) Ile (A/G) (A/G) AU (C/U) Isoleucine (A/G) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Isoleucine/Methionine (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) Tyrosine (A/G) Stop Asp GA (C/U) Asn UA (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Glutamatic acid AA (C/U) Asparagine Asparatic acid Arginine UU Leucine Glutamine Serine (A/G) (A/G) Histidine Stop/Trp UG Ser CU (C/U) Phenylalanine Valine Tryptophan (C/U) Phe UU Valine Cystein (A/G) (C/U) Leucine Threonine (C/U) CU Leucine Threonine Glycine Glycine (C/U) Serine Arginine GG UC Serine Arginine Gly 01 Mixed Alanine Gly 00 5 H bonds Alanine Arg 00 Strong Proline Arg 00 6 H bonds Proline 001 00 Lys AA Lysine (A/G) Mitochondrial genomes have several surprising features genetic code of mitochondria ? only 22 tRNAs are required for mammalian mitochondrial protein synthesis The Mammalian Mitochondrial Genetic Code Codon Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 H bonds 5 H bonds 5 H bonds 4 H bonds 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser UC (C/U) Leu CU (C/U) Phe UU 001 Pro CC (A/G) Ser UC (A/G) Leu CU (A/G) Leu UU (A/G) 100 Ala GC (C/U) Thr AC (C/U) Val GU (C/U) Ile AU (C/U) 101 Ala GC (A/G) Thr AC (A/G) Val GU (A/G) 010 Arg CG (C/U) Cys UG (C/U) His CA (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) 011 Arg CG (A/G) Trp /Trp UG Gln CA (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) 110 Gly GG (C/U) Asp GA (C/U) Asn AA (C/U) 111 Gly GG (A/G) Glu GA (A/G) Lys AA (A/G) Ser STOP AG (A/G) (C/U) AG (A/G) (C/U) Met/Met AU (A/G) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Utils/wprintgc.cgi The Mammalian Mitochondrial Code 8 tRNAs for family codons + 14 tRNAs for non-family codons = 22 Codon Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 H bonds 5 H bonds 5 H bonds 4 H bonds tRNAPhe UU (C/U) 000 tRNAPro CC tRNASer1 UC tRNALeu1 CU 001 tRNALeu2 UU (A/G) 100 tRNAIle AU (C/U) tRNAAla GC tRNAThr AC tRNAVal GU tRNAMet AU (A/G) 101 tRNACys UG (C/U) tRNAHis CA (C/U) tRNATyr UA (C/U) 011 tRNATrp UG (A/G) tRNAGln CA (A/G) STOP 110 tRNASer2 AG (C/U) tRNAAsp GA (C/U) tRNAAsn AA (C/U) tRNAGlu GA (A/G) tRNALys AA (A/G) 010 tRNAArg tRNAGly 111 CG UA (A/G) GG STOP AG (A/G) http://mamit-trna.u-strasbg.fr/2DStructures.html Part 2. Common Patterns in Type II Restriction Enzyme Binding Sites Restriction Enzyme (Endonuclease) Restriction enzymes recognize short specific DNA sequences enable bacteria to destroy foreign DNA are useful tools in biotechnology The most well studied class of REs is type II, which cleave DNA within their recognition sequences Many recognition sequences are palindromic Are REase similar in the binding sites? Restriction Enzyme Source Recognition Sequence Pur (1)–pyr (0) pattern AluI Arthrobacter luteus AG↓CT 11↓00 HaeIII Haemophilus aegyptius GG↓CC 11↓00 BamHI Bacillus amyloliquefaciens G↓GA TCC 1↓11 000 HindIII Haemophilus influenzae A↓AG CTT 1↓11 000 EcoRI Escherichia coli G↓AA TTC 1↓11 000 Examples from Kimball‘s Biology Pages How significant is the Pattern RR/YY (11/00)? Asymmetrical (2%) recognition sequences Frequencies of dinucleotides trinucleotides tetranucleotides coded in three possible coding scheme: Type II 3726 R vs Y (G, A vs C, T) K vs M (G, T vs C, A) S vs W (G, C vs A, T) Symmetrical (98%) recognition sequences In the symmetrical set the most significant dinucleotides are RR (or 11) (p-value <10-63) and YY (or 00) (p-value <10-29) In the asymmetric set RRR, YYY and YYYY are even more significant, but RR and YY also stand out. Why is the Motif RR..YY preferred? Dinucleotides RR..YY are characterized by: stronger H-bond donor and acceptor clusters Figure 1 Example of an interaction between an H-bond donor cluster (resulting from two adjacent purines AA) and an H-bond acceptor. specific geometrical properties minimal slide values strong tilt in the negative direction positive roll low stacking energy Outlook Looking for binary patterns in the genomes Additional information http://www.imb-jena.de/tsb Thank you for your attention ! Purine-Pyrimidine Scheme of the Genetic Code Strong Mixed Mixed Weak 6 hydrogen bonds 5 hydrogen bonds 5 hydrogen bonds 4 hydrogen bonds Codon 000 Pro CC (C/U) Ser Proline 001 Pro 100 Ala 101 Ala 010 011 110 111 CC (A/G) Ser (C/U) Thr (A/G) Thr Alanine Arg CG (C/U) CG Gly GG GG Glycine (A/G) Leu (A/G) AC (C/U) Val AC (A/G) Val His AG Arg AG (A/G) Leu GU GU CA (A/G) Gln (C/U) CA (C/U) Ile (A/G) (A/G) AU (C/U) Isoleucine (A/G) Ile/Met AU (A/G) Isoleucine/Methionine (C/U) Tyr UA (C/U) Tyrosine (A/G) Stop UA (A/G) Glutamine Asp GA (C/U) Asn Glu GA (A/G) Glutamatic acid AA (C/U) Asparagine Asparatic acid Arginine UU Leucine Histidine Serine (A/G) CU (C/U) Phenylalanine Valine (C/U) Stop/Trp UG Ser Phe UU Valine Tryptophan (C/U) (C/U) Leucine Cystein Glycine Gly UC Cys UG Arginine CU Leucine Threonine Arginine Arg Leu Threonine Alanine GC (C/U) Serine Proline GC UC Serine Lys AA Lysine (A/G)