Nervous System - POLYTECH High School
advertisement

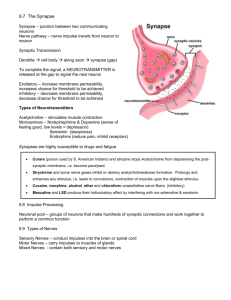
The CNS, PNS, SNS, and ANS A control and communications system ◦ Consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerve cells, and nerve fibers that run throughout the body Originates and coordinates physical reactions to the environment Controls involuntary muscles and organs Maintains homeostasis ◦ A balanced state within the body C.S. 24 Nerve cells are called neurons ◦ Star-shaped bodies with 2 long nerve fibers projecting from them ◦ Messages to the cell body are carried by nerve fibers called dendrites (part of the star) ◦ Messages that travel away from the cell body are carried by nerve fibers called axons (the tail) The axon is covered by a myelin sheath for protection – deterioration of this sheath is called MS The dendrite receives a message, transmits it to the cell body, and the cell body sends the message along to another neuron or to the organ that is to be affected (such as a muscle) The neurons and their fibers form a network that covers the entire inside of the body and all of the skin The long fibers of neurons are arranged in bundles called nerves ◦ The fibers of neurons within the nerves don’t actually touch ◦ They meet at a place called a synapse, which is a space where an electrical impulse is transmitted from an axon to a dendrite Classified according to the direction in which they transmit impulses Afferent neuron: sensory neurons – transmits impulses TO the brain and spinal cord from the sensory organs Efferent neuron: motor neurons – transmits impulses AWAY from the brain and spinal cord or other nerve centers ◦ Transmit only to muscles and organs Interneuron: transmits impulses from sensory to motor neurons ◦ Used in reflexes for defensive purposes C.S. 25 It is divided into categories depending upon function Central Nervous System (CNS) ◦ Brain ◦ Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) ◦ Somatic Nervous System (SNS) ◦ Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Sympathetic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System Made up of: ◦ The brain ◦ The spinal cord Control center for the movement and actions of the entire body ◦ Messages come to the CNS from throughout the body, where they are interpreted ◦ the CNS then sends out reaction impulses The most complex and specialized organ in the body 3 areas – forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain Divided into specialized sections ◦ Cerebrum ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 2 hemispheres – right and left 4 ventricles/lobes – frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital Cerebellum Corpus Callosum Pons Medulla 1. Frontal lobe of cerebrum (f) 2. Pituitary gland 3. Temporal lobe of cerebrum (f) 4. Pons (h) 5. Medulla oblongata 6. Parietal lobe of cerebrum (m) 7. Corpus callosum (f) 8. Occipital lobe of cerebrum (m) 9. Cerebellum (h) 10. Spinal cord 6 1 7 8 2 3 4 9 5 10 Main part of the brain Divided into hemispheres Outer surface is called the cortex ◦ Wrinkled with deep furrows to increase the surface area of the brain Consists of the forebrain and the midbrain Has 4 lobes (aka ventricles) Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Occipital lobe ◦ Top, front regions of each of the cerebral hemispheres. ◦ Used for reasoning, emotions, judgment, and voluntary movement ◦ Middle lobe of each cerebral hemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes ◦ Contains important sensory centers ◦ Region at the lower side of each cerebral hemisphere ◦ Contains centers of hearing and memory ◦ Region at the back of each cerebral hemisphere ◦ Contains the centers of vision and reading ability Part of the brain below the back of the cerebrum Regulates balance, posture, movement, and muscle coordination A large bundle of nerve fibers that connect the left and right cerebral hemispheres Allows for communication and coordination between the hemispheres In the lateral section, it looks a bit like a "C" on its side The part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum It is located just above the Medulla oblongata The lowest section of the brainstem (at the top end of the spinal cord) It controls automatic functions including heartbeat, breathing, etc C.S. 26 Descends from the medulla oblongata down into the canal formed by the vertebrae Made up of white (nerve tissue) and gray matter (same matter as brain tissue) Has 2 functions: ◦ Serves as the sensory-motor mechanism for reflex actions ◦ Is the 2-way transmitter of impulses, reactions, and stimuli triggered by various internal and external conditions Surround the brain and spinal cord for protection Dura mater – Outer layer Arachnoid – Middle layer Pia mater – Inner layer Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – between pia mater and arachnoid (sub-arachnoid space) Meningitis – an infection of the meninges ◦ Can be in any of the layers ◦ Can involve the CSF as well Made up of the nerves of the body that connect the CNS to the other parts of the body Includes the cranial and spinal nerves Cranial nerves link the brain with sensory receptors and muscles There are 12 cranial nerves Designated by Roman numerals I-XII and names I Olfactory Smell II Optic Vision III Oculomotor Eye/eyeball movements IV Trochlear Eyeball movements V Trigeminal Chewing; facial sensation VI Abducens Eyeball movements VII Facial Taste; facial expression VIII Auditory/Vestibulocochlear Hearing; balance IX Glossopharangeal Taste; swallowing; saliva secretion X Vagus Swallowing; voice; gag reflex; slowing of heartbeat (parasympathetic) XI Spinal accessory Muscles of neck/shoulder XII Hypoglossal Tongue movements Mnemonic device: “On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Fin And German Viewed Some Hops” - OR – “Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel A Girl’s V……. So Happy” Olfactory (I) – Identify smells Optic (II) – Eye chart; reading Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens (III, IV, VI) – With head still, follow a finger up/down/left/right; pupillary response (III) Trigeminal (V) – Bite down; Light touch on face Facial (VII) – Smile, frown; Taste on tip of tongue Vestibulocochlear (VIII) – Check hearing; stand on one leg with eyes closed, then the other leg Glossopharangeal and Vagus (IX, X) – Swallow; taste on back of tongue Spinal Accessory (XI) – Resisted shrug Hypoglossal (XII) – Stick out tongue and move it side to side Spinal nerves link the spinal cord with various structures Conduct impulses between the spine and the parts of the body not supplied by the cranial nerves ◦ Transmit sensory info to the spinal cord through afferent neurons and transmit motor signals to muscles and organs through efferent neurons Make sensation and movement possible 31 pairs ◦ One root of each pair goes to each side of the body 31 pairs come from the spinal cord as follows: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 8 cervical nerve roots 12 thoracic nerve roots 5 lumbar nerve roots 5 sacral nerve roots 1 coccygeal nerve root Each nerve divides to form several branches called rami ◦ Dorsal rami – control muscles and skin of the back ◦ Ventral rami – innervate all structures of the limbs and torso Ventral rami and adjacent nerves form networks called plexuses that go to general areas ◦ Cervical plexus – serves neck, upper shoulders, and diaphragm ◦ Brachial plexus – serves upper limbs, neck, and shoulder muscles ◦ Lumbar plexus – serves abdominal area and part of the legs ◦ Sacral plexus – serves buttocks area and lower legs Dermatome – Area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve root Myotome – Specific muscle supplied by a single nerve root Sclerotome – Area of bone supplied by a single nerve root C.S. 27 Subdivision of the PNS Made up of motor nerves that control the voluntary actions of skeletal muscles Subdivision of the PNS Made up of certain motor neurons of the PNS that conduct impulses from the spinal cord/brain stem to ◦ Cardiac muscle tissue ◦ Smooth muscle tissue ◦ Glandular epithelial tissue (tissue that forms glands) Regulates the body’s automatic/involuntary functions such as heart rate, breathing, contractions of intestinal musculature, and secretions of hormones from the glands Responsible for “fight or flight” mechanism Triggered by strong emotional situations (i.e. anger, fear, anxiety, hate, etc.) and by strenuous exercise Increases heart rate, blood pressure, sweat excretion Decreases digestion Charges you up! Opposite of sympathetic nervous system Decreases heart rate and blood pressure (Vagus nerve) Increases digestion processes Calms you down