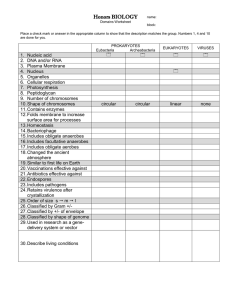
I. Prokaryotes A. General Characteristics – smaller than eukaryotic
advertisement

I. Prokaryotes A. General Characteristics – smaller than eukaryotic cells, no membrane bound organelles, circular DNA and plasmids as genetic material, have cell walls, rapid reproduction by binary fission, they can also be classified/categorized by the following characteristics 1. Body Shapes – cocci (coccus) are spherical; bacilli (bacillus) are club or rod-shaped; spiral can range from commalike to long coils 2. Type of Cell walls which are made up of peptidoglycan (eukaryotes have cellulose or chitin) a. Gram-positive – simple cell wall with large amount of peptidoglycan b. Gram-negative – cell wall with less peptidoglycan, more complex, and have an outer membrane 3. Modes of Nutrition a. Autotrophs make their own organic needs i. Photoautotrophs use photosynthesis and light as the energy source ii. Chemoautotrophs perform chemosynthesis using inorganic chemicals as energy source b. Heterotrophs need to consume their organic needs i. Parasites feed on their hosts, Saprophytes feed on dead or dying organisms, Decomposers break down organic material and absorb it 4. Relationship to oxygen a. Obligate aerobes – require oxygen for cellular respiration b. Obligate anaerobes – poisoned by oxygen; uses fermentation c. Facultative anaerobes – can use either depending on presence/absence of oxygen B. Domain Archaea contain extremophiles that live in extreme conditions 1. Extreme thermo(acido)philes live in hot and acid environments (thermal vents, geysers, etc.) 2. Extreme halophiles live in areas of high salt concentrations 3. Methanogens are anaerobes that produce methane as a waste product and live in mud, swamps or guts of other organisms I. Prokaryotes A. General Characteristics – smaller than eukaryotic cells, no membrane bound organelles, circular DNA and plasmids as genetic material, have cell walls, rapid reproduction by binary fission, they can also be classified/categorized by the following characteristics 1. Body Shapes – cocci (coccus) are spherical; bacilli (bacillus) are club or rod-shaped; spiral can range from commalike to long coils 2. Type of Cell walls which are made up of peptidoglycan (eukaryotes have cellulose or chitin) a. Gram-positive – simple cell wall with large amount of peptidoglycan b. Gram-negative – cell wall with less peptidoglycan, more complex, and have an outer membrane 3. Modes of Nutrition a. Autotrophs make their own organic needs i. Photoautotrophs use photosynthesis and light as the energy source ii. Chemoautotrophs perform chemosynthesis using inorganic chemicals as energy source b. Heterotrophs need to consume their organic needs i. Parasites feed on their hosts, Saprophytes feed on dead or dying organisms, Decomposers break down organic material and absorb it 4. Relationship to oxygen a. Obligate aerobes – require oxygen for cellular respiration b. Obligate anaerobes – poisoned by oxygen; uses fermentation c. Facultative anaerobes – can use either depending on presence/absence of oxygen B. Domain Archaea contain extremophiles that live in extreme conditions 1. Extreme thermo(acido)philes live in hot and acid environments (thermal vents, geysers, etc.) 2. Extreme halophiles live in areas of high salt concentrations 3. Methanogens are anaerobes that produce methane as a waste product and live in mud, swamps or guts of other organisms