Cell structure and function
advertisement

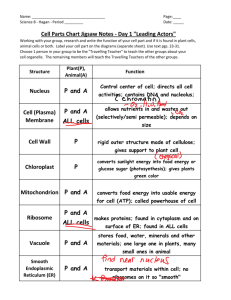
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Cell Theory 1) Every organism is composed of one or more cells 2) Cell is smallest unit having properties of life 3) Continuity of life arises from growth and division of single cells Structure of Cells All start out life with: Two types: – Plasma membrane – Prokaryotic – Region where DNA is stored – Eukaryotic – Cytoplasm – Know figure 4:7 – Know table 4.3 Animal Cell Features • • • • • • • • Plasma membrane Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Vesicles Mitochondria Cytoskeleton nuclear enevelope nucleolus NUCLEUS DNA + nucleoplasm microfilaments vesicle microtubules lysosome components of cytoskeleton rough ER ribosomes (attached to rough ER and free in cytoplasm) smooth ER plasma membrane vesicle Golgi body mitochondrion pair of centrioles Fig. 4.8b, p. 57 Lipid Bilayer • Main component of cell membranes • Gives the membrane its fluid properties • Two layers of phospholipids Membrane Proteins • Transport proteins • Receptor proteins • Recognition proteins • Adhesion proteins oligosaccharide cholesterol groups phospholipid EXTRACELLULAR ENVIRONMENT (cytoskeletal proteins beneatch ADHESION the plasma PROTEIN membrane) open gated channel channel protein proten (open) gated channel proten (closed) (area of enlargment) TRANSPORT PROTEINS active transport protein RECEPTOR PROTEIN LIPID BILAYER RECOGNITION PROTEIN CYTOPLASM PLASMA MEMBRANE Fig. 4.4, p. 53 Functions of Nucleus • Keeps the DNA molecules of eukaryotic cells separated from metabolic machinery of cytoplasm • Makes it easier to organize DNA and to copy it before parent cells divide into daughter cells Components of Nucleus nuclear envelope nucleoplasm chromatin (DNA + proteins) Nucleolus cytoplasm nucleus plasma membrane nuclear envelope nucleoplasm chromatin (DNA + proteins) nucleus Fig. 4.11, p. 62 Nuclear Envelope • Two outer membranes (lipid bilayers) • Innermost surface has DNA attachment sites • Pores span bilayer Chromatin • Cell’s collection of DNA and associated proteins • Chromosome is one DNA molecule and its associated proteins • Appearance changes as cell divides Nucleolus • Dense mass of material in nucleus • Area of intense transcription of rRNA • Materials from which ribosomal subunits are built • Genes that encode Ribosome's are located in this area Components of Cytomembrane System Golgi bodies Vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum • In animal cells, continuous with nuclear membrane • Extends throughout cytoplasm • Two regions - rough and smooth Rough ER • Ribosomes on surface give it a rough appearance. • ER is the site of protein synthesis. • Some polypeptide chains enter rough ER and are folded and modified Smooth ER • No ribosomes on surface • Lipids assembled inside tubules • Synthesizes steroids, such as estrogen and testosterone. • inactivates wastes, toxic chemicals and drugs Golgi Bodies • Put finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER • Package finished material for shipment to final destinations outside the cell. • Material arrives and leaves in vesicles Vesicles • Membranous sacs that move through the cytoplasm • Lysosomes – Digests, recycles materials Mitochondria • ATP-producing powerhouses • Double-membrane system • These reactions require oxygen Cytoskeleton • Present in all eukaryotic cells • Basis for cell shape and internal organization • Allows organelle movement within cells and, in some cases, cell motility Cytoskeletal Elements intermediate filament microtubule microfilament Cilia and Flagella • Cilia and Flagella are made up of microtubules – Cilia functions to move microorganism or the movement of substances in the body • Example: Protozoa move through water by beating their cilia as small ores • Example: Cilia found in the body moves mucus out of the lungs and oocytes down the oviduct – Flagella functions in the transport of cells Cilia and Flagella • Length of microtubules or microfilaments can change • Parallel rows of microtubules or microfilaments actively slide in a specific direction • As one side lengthens and the other side contracts it causes the flagella or cilia to bend.