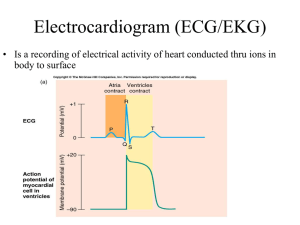
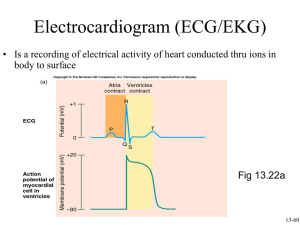
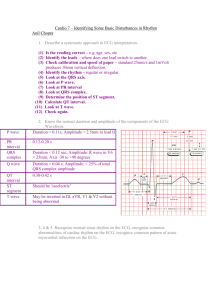
ECG
advertisement

Heart Anatomy + ECG Aaqid Akram MBChB (2013) Clinical Education Fellow L Subclavian Artery Brachiocephalic Trunk L Common Carotid Artery Superior Vena Cava Arch of the Aorta Pulmonary Artery L Atrium L Pulmonary Vein R Atrium Aortic Valve (Semilunar) Fossa Ovalis Mitral Valve (Bicuspid) Chordae Tendinae L Ventricle Papillary Muscle Pulmonary Valve Tricuspid Valve Endocardium Inferior Vena Cava R Ventricle Myocardium Septum Ligamentum Arteriosum Circumflex Artery L Anterior Descending Artery R Coronary Artery Cardiac Cycle Introduction • • • • • • Wash Hands Introduce yourself Confirm patient + ALLERGY STATUS Explain investigation to patient Gain verbal consent Offer chaperone (Chest will be exposed) – If opposite sex you require a chaperone for your own safety The ECG Machine • • • • • • Power (plugged/battery) Demographics Paper All leads intact Stickers available Scale – vertical axis (0.1mV = 1mm = 1 small square) Placing Stickers There’s only 10 leads…. How can it be a 12 lead ECG? Interpreting an ECG • • • • • • • Demographics Obvious abnormality Rate Rhythm Axis P wave PR Interval • • • • QRS Complex ST segment T wave Summary Rate • 1500 small squares (0.04 seconds) = 60s • No of small squares between R-R = x • 1500/x = ventricular rate per minute • If normal calibration rhythm strip = 50 large squares (0.2seconds) = 10 seconds • Count QRS complexes on rhythm strip • Multiply by 6 = ventricular rate per minute Rhythm • Sinus = p wave before every QRS Complex • Regular = QRS complexes equidistant – Mark 3 R-R points on the edge of a paper – Move to next three complexes – Do the marks on the paper correlate to the R waves? Axis P Wave T Wave P wave • • • • • • • Atrial depolarisation (Sino Atrial Node) 2-3 mm high 0.06 – 0.12 seconds duration Usually positive deflection throughout ECG Peaked/enlarged = atrial hypertrophy Inverted = retrograde/reverse conduction Absent = conduction by route other than SA PR Interval • Impulse from atria to AV Node, Bundle of His, bundle branches • 0.12 – 0.2 seconds duration • Short = impulse did not originate from SA • Long = AV Block 1st Degree Heart Block 1st Degree: – QRS complex after every P wave – Prolonged PR Interval – No Rx necessary unless symptomatic 2nd Degree Heart Block Mobitz Type 1 (Wenckebach): – Each successive impulse from SA node delayed slightly longer than previous impulse – A QRS complex is dropped – Cycle repeats 2nd Degree Heart Block Mobitz Type 2: – Occasional SA impulses fail to cause ventricular depolarisation – Regular P waves, but some dropped QRS complexes x x x x x x 2:1 Heart block 3rd Degree Heart Block • Complete Heart Block: – Impulses from atria cannot pass the AV node – Atria depolarise independently to ventricles – Life threatening QRS Complex • Deep wide Q waves may suggest old infarct • Total duration <0.12 seconds • >0.12 seconds = ventricular conduction delay Bundle Branch Block • • • • Bundle branch fails to conduct impulses Ventricles contract at slightly different times Block further down the bundle = hemiblock Cell-cell conduction slower than via specialised pathway therefore prolonged depolarisation • New Left Bundle Branch Block = ACS QT Interval • Time from ventricular depolarisation to ventricular repolarisation • Varies according to heart rate • QTc = corrected QT interval to 60bpm • Males <450 ms / Females <470 ms • Prolonged QT interval increases risk of life threatening arrhythmias Torsades de Pointes Drugs affecting QT Interval Drug Type Amiodarone Antiarrhytmic Amitriptylline Antidepressant Chlorpromazine Antipsychotic/antiemetic Clarithromycin Antibiotic Droperidol Sedative/antiemetic Erythromycin Antibiotic Fluoxetine Antidepressant Haloperidol Antipsychotic Ketoconazole Antifungal Levofloxacin Antibiotic Methadone Opiate agonist Quinidine Antiarrhythmic Sertraline Antidepressant Sotalol Antiarrhythmic Sumatriptan Anti migraine ST Segment • Segment affected if acute ischaemia/infarction • Elevation = >1mm • Depression = >0.5mm T Wave • Ventricular repolarisation • Usually upright deflection • Tented T waves = hyperkalaemia/myocardial injury • Inverted T wave = ischaemia • Camel Hump = hidden P/U wave Summary • Present all positive findings and important negative findings. • Advise on urgency of management. Supraventricular Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Any Questions? Thank You