File
advertisement

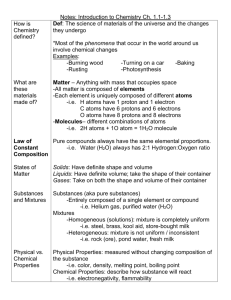
Chemistry - Science 10 REVIEW Classification of Matter MATTER MIXTURES SUSPENSIONS Particles of one of the substances remain partly clumped together Ex/Orange Juice PURE SUBSTANCES SOLUTIONS Particles of the different substances are completely mixed together. Ex/ Coffee with sugar MECHANICAL Particles of the different substances remain clumped together. Ex/ cereal, nuts,bolts,pepper ELEMENTS COMPOUNDS Contain only a single type of atom Contain 2 or more types of atoms, joined together. Ex/ Gold-Au or Calcium-Ca Ex/ Ethanol CH3CH2OH Two Types of Mixtures Heterogeneous Different from place to place Not evenly mixed Included suspensions and mechanical mixtures Chocolate chip cookie, gravel, soil HomogeneousThe same throughout Evenly mixed solutions Kool-aid, sea water, air Pure Substance Elements- Simplest kind of matter Can’t be broken down further All one kind of atom About 120 kinds of elements Each has a 1 or 2 letter symbol Each behaves differently Everything else is made up of them Pure Substances Compounds- Made of two or more elements chemically combined Atoms combine together to make molecules All molecules of a compound are the same They mix in the same ratio Compounds behave completely differently from the elements that make them Ex. Water H2O–liquid puts out fire: hydrogen burns, oxygen supports combustion Physical vs. Chemical Changes Physical Changes: No new substance has been formed.(ex/ ice cube melting, or crumpling a piece of paper. All the molecules stay the same Might look a little different Keeps original properties Changing phases Making a mixture Cutting Grinding Dissolving Chemical Changes: If one or more substances have been produced, substances with properties different from the starting materials, then a chemical change has taken place. Products are not at all like the reactants Makes new odor, color, etc. Completely new properties Clues to tell you a “Chemical Change” has taken place: A new colour may appear. Heat or light may be given off. Bubbles of gas may be formed. Solid material may form in a liquid. The change may be difficult to reverse. Chemical Reactions Chemical Reaction is another term for chemical change. (ex. Fast- fireworks, or slow- rust) Starting materials are called reactants. (Found on the left of the arrow in a chemical equation) Any substance produced in the reaction is a product. (on the right of the arrow). Word Equations Word equations tell us the names of the reactants and products in a reaction. Reactants on the left,(of the arrow) products on the right. Note: It does not tell us the amounts of the atoms/elements required to make the reaction go! Ex/ SodiumChlorine-----Sodium Chloride Mass and Chemical Change The Law of Conservation of Mass: In a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants is always equal to the total mass of the products Chemical Formulas Tell the element and number of atoms in a molecule Symbols identifies the element Subscripts tell the number of atoms Don’t write one as a subscript Chemical Formulas H2O subscript 2 Hydrogen atoms 1 Oxygen atom Chemical Formulas C12H22O11 12 Carbon atoms 11 Oxygen atoms 22 Hydrogen atoms Chemical Properties Used to describe how substance reacts How it changes By combining with other substances Or breaking apart Reactivity how a substance combines with other substances Things like flammability, rusting, etc. Physical Properties Can be observed or measured without changing the composition Melting point , boiling point, hardness, odor, ability to conduct electricity and heat Density – how heavy something is for its size Ratio of mass to volume If the density of substance is less than its surroundings, it floats Density Found by dividing the mass by volume D= m V Units of g/mL or g/cm3 Water has a density of 1 g/mL Law of Conservation of Energy In all chemical changes, energy cannot be created or destroyed All the energy you put in, you get out It might be hard to count KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY •All matter is made up of extremely small particles that are always moving (atoms and molecules) with spaces between them •The particles are close together and slowest moving in solids, and farthest apart and fastest in gases •Heat makes the particles move faster Changes of State of Matter GAS condensation sublimation evaporation LIQUID sublimation melting solidification SOLID