Extraction of metals
advertisement

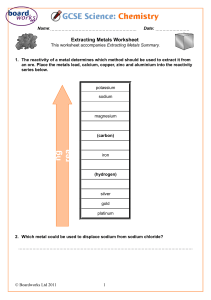
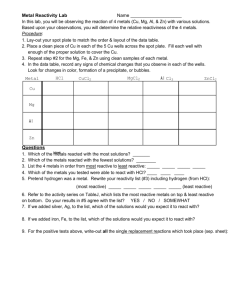
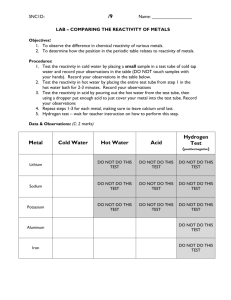
Reaction of Metals 1. Some metals react with; • Water – producing metal hydroxides and hydrogen • Acids – producing metal salts and hydrogen • Air – producing metal oxides Reactions of Metals Rusting Reactivity Series 1. In the reactivity series of metals, the most reactive metals are put at the top and the least reactive at the bottom 2. The reactivity series can be determined by looking at the relative reactivity of metals with air, water and acids Reactivity Series Reactivity Series Displacement reactions 1. A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its compound 2. Non-metal elements carbon and hydrogen can also displace less reactive metals form oxides of those compounds Displacement Reactions Reduction using carbon 1. Some unreactive metals are found in their natural state (e.g. gold) 2. Often metals are found as metal oxides 3. To extract the metal, the oxygen must be removed from the metal oxide 4. This is called reduction 5. Metals below carbon in the reactivity series can be extracted by heating with carbon Reduction using carbon Reduction using carbon The Blast Furnace 1. Iron can be extracted from iron ore in the blast furnace 2. The raw materials are iron ore, coke (carbon), and limestone 3. Hot air is used to convert carbon to carbon monoxide 4. Carbon monoxide reduces iron oxide to iron 5. Limestone reacts with impurities (e.g. sand) to produce molten slag The Blast Furnace Removing impurities The Blast Furnace Electrolysis 1. Metals above carbon in the reactivity series are extracted using electrolysis 2. Electrolysis is the process of splitting up compounds using electricity 3. Electrolysis only works if the substance is molten or dissolved (so the ions are free to move) 4. Positively charged ions (cations) move to the cathode, negatively charged ions (anions) move to the anode Electrolysis Electrolysis Purifying copper Electrolysis of Aluminium Oxide Electrolysis of Sodium Chloride 1. Sodium Chloride (common salt) is found in the sea and in underground deposits 2. Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces chlorine at the anode, hydrogen at the cathode and sodium hydroxide solutions 3. Chlorine bleaches damp litmus paper 4. Each product has important uses Electrolysis of Sodium Chloride Wordsearch Quiz