Literary Terms!
advertisement

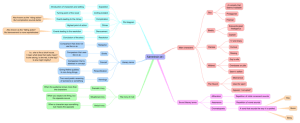
Literary Terms! PLOT • The sequence of events in a story. Think of the Parts of a Story like a Peak… Climax Rising Action Falling Action Inciting Incident Exposition Denouement The Parts of a Story… 1. Exposition – learn background information 2. Inciting Incident – when conflict is introduced Parts of a Story Continued 3. Rising Action – all events leading to the story’s climax 4. Climax – turning point of the plot where the conflict is resolved 5. Falling Action – events resulting from the climax. 6. Denouement – Aftermath of the story, where we see how things are once the conflict is resolved Activity 1) In your notes, recreate the plot diagram. With a partner, fill in the elements as they apply to Raymond’s Run. Conflict – Struggle between opposing forces Types of Conflict… • Internal Conflict – person vs. self • External Conflict – person vs. person, person vs. nature, person vs. society, man/woman vs. machine, man/woman vs. supernatural. Setting 1. Place 2. Time 3. Mood 4. Circumstance Name that setting… • Describe the four elements of setting for well-known movies… – Time – Place – Mood – Circumstance Theme – the central idea or main point of a story. Characters 1. Static (stay the same) vs. Dynamic (change) 2. Flat (one-sided) vs. Round (manysided) 3. Major/Minor/functional Protagonist – main character Antagonist – in conflict with/opposes protagonist Characterization •The act of creating or developing a character. Two Types of Characterization… 1. Direct – author states directly what a character is like. 2. Indirect – learn what characters are like through description, what they say, do and think, and how other characters treat them. Point of View •Through whose eyes and mind the story is told. Point of View Continued… 1. First Person – told by a character in the story (uses “I”). 2. Third Person – told by a narrator in the story (uses he/she/they) a. Omniscient – all knowing (thoughts of two or more characters) b. Limited – only gets in the mind of one character (or no characters’ thoughts at all) Symbol An object, character, or event which represents something else. Tone Attitude the author is trying to convey about the subject. Ways to Create Tone: • Tone can be achieved through what one says: EX: The baby whimpered softly, as warm tears pooled around eyes that began to search desperately for his mother. Vs. The baby wailed endlessly, as salty tears jetted from eyes that began to search demandingly for his mother. • Or how one says it: EX: Students, will you take your seats please? -Caring, Angry, Amused, Confused Irony 1. Verbal – say one thing and mean another 2. Dramatic – we know something the characters don’t know 3. Situational – what we expect to happen doesn’t happen Huh??? • Verbal Irony (say one thing and mean another): – A guy shows up for a date in ripped jeans and a t-shirt. His date says, “Oh how nice of you to dress up for our date.” – A mother scolds her son, saying “You stop being so smart with me!” and the son replies, “If I’m so smart, why don’t you let me make my own decisions!” – You try! Huh??? • Dramatic Irony (we know something the character doesn’t): – Pretty much every scene in a horror movie – Talk shows when the guest doesn’t know that his ex-girl friend or long lost mother is waiting for him, but the audience does – You Try! Huh??? • Situational Irony (what we would expect to happen doesn’t): – An Olympic swimmer drowns. – You stay up studying all night for a test. When you get to class, you realize the test is the next day. – You Try! Suspense – a feeling of growing curiosity or anxious uncertainty about the outcome of an event. Foreshadowing – hints at what may happen in a story. Flashback – reverting to an earlier time to relate an event. Character Motivation -- the reason for a character’s actions and decisions. Personification – giving human qualities to non-human objects. EX: The tree branch tapped angrily against the window.