Plant Parts, Structures, and Functions PowerPoint
advertisement

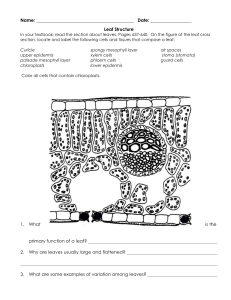
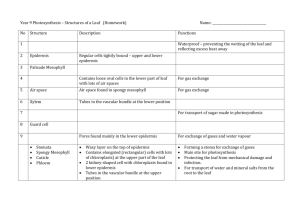
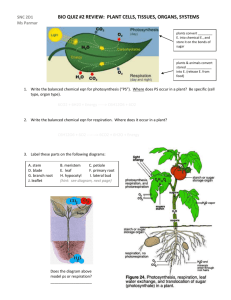
Unit: Plant Growth & Development Advanced Plant Sciences Mr. Dieckhoff 1. ID the parts of a plant cell… A. Chloroplast – holds chlorophyll B. Plasma Membrane – Controls entrance & exits C. Cell Wall – 3 layers D. Cytoplasm – Liquid in cell E. Vacuole – Store water F. Mitochondrion – Respiration G. Nucleus - Genetics **Four elements of the cell structure: A. B. C. D. Cell wall Plasma membrane Cytoplasma Nucleus Cell Wall Structure Too little water in vacuole….. Tobacco flower losing pigment because lack of mitochondria proteins 2. What are 2 function of PM? a) Control entrance & exit into and out of cell b) Relays environmental information about condition 3. What are 3 organelles…… 1) Mitochondria – Control Chemical Reactions, site of respiration 2) Plastids – Contain Chloroplasts; contain chromoplasts (red, yellow, brown pigments) 3) Vacuoles – store water, dissolve minerals 4. What are 3 func. of nucleus.. A. Control Physiological Characteristics B. Control Appearance of Plant C. Passes Characteristics to Offspring 5. What are 2 types tissue…. 1) Meristem 2) Permanent 6. What are differences…… Meristem actively divides to form new growth where permanent does not actively divide 7. What are 3 types meristems.. 1) Apical – plant length 2) Cambium – plant diameter 3) Intercalary Zone – stem height **Cambium Meristem View Video Intercalary Zone Meristem 8. What two types permanent… 1) Epidermis – outside covering 2) Vascular System – transportation system of plant a) Xylem - Up b) Phloem - Down • • • • **Five basic parts of a plant: A. Seeds B. Roots C. Stems D. Leaves E. Flowers 9. What are three parts mono… 1) Seed Coat – Protect embryo 2) Embryo – Miniature plant 3) Endosperm - Nourishment 10. **Which is found only mono…Endosperm 11. What are 4 parts embryo? 1) Cotyledon 2) Epicotyl 3) Hypocotyl 4) Radicle 12. **What another term seed leaf Cotyledon 13. What type of Plant…. A) Has one leaf – Monocot B) Has two leaves - Dicot **Stems…. Stolon **Crown Thick, compressed stem whose leaves and flower buds grow just above ground Example in CCC Greenhouse: fern Rhizome 14. **What are 3 func. Roots…. A) Synthesize hormones for plant growth B) Store carbohydrates C) Provide aerial support D) Anchor plant E) Absorb Water and Nutrients Application of Rooting Hormone Don’t cut alfalfa in October Wait Until November Or Next Year will Look Like…. 15. What are 5 types roots…. A) Taproot B) Fibrous C) Aerial D) Adventitious E) Aquatic Adventitious Roots Tap Root Aerial Roots Aquatic Roots 16. What is pith? Parenchyma cells 17. What is hyposophylls? Floral bracts – protect buds during development Dogwood 18. ID interior parts of leaf…. A) B) C) D) E) F) View Video Phloem Xylem Cuticle Upper epidermis Chloroplast Lower epidermis G) Cuticle H) Stomata I) Guard Cell J) Spongy mesophyll K) Palisade mesophyll **The 3 structures of a leaf: A. Epidermis B. Mesophyll layer C. Vascular bundles View Guard Cells & Stomata of Wandering Jew 19. What are 2 func. Leaves? A) Manufacture food through photosynthesis B) Protect vegetative and floral buds 20. What do not have stomata? Submerged plants (aquatic) 21. What are char. xeromorphic Thick-walled epidermis covered with waxy cuticle (holds water in stems) 22. What type modified leaf…. Sac 23. What is corolla…. Petals – protect stamen and pistil in bud stage; attract pollinating insects 24. Gynoecium refers to… Female reproductive parts 25. What do head, spike, umbel Types of inflorescence flowers 26. What are 3 char perfect… A) Contain male and female parts B) All four parts of flower are present C) Usually self-pollinating **KNOW **Monoecious (different places) vs. Dioecious (same place) Cross Pollinating Self Pollinating