reactivity, flammability, ability to rust (react with
advertisement

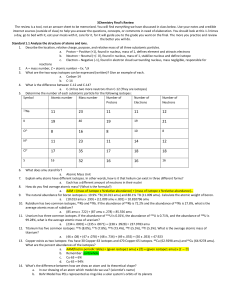
• Physical properties: mass, volume, color, hardness, melting point, boiling point • Chemical properties: reactivity, flammability, ability to rust (react with oxygen) • Physical Changes : evaporating, melting, condensing, breaking, cutting • Chemical Changes : corroding, exploding, rotting, reacting, burning Chemistry – the study of the composition of matter and the changes it undergoes How many sig fig do the following have? Round each to the number in parentheses. a. 0.0002030 (2) --> .00020 b. 99,000 (1) 100,000 c. 10.00 (2) 10. d. 50,000. (1) 50,000 e. 0.00001 (1) 0.00001 Express the following, using the correct number of sig figs: a. 2.220 x 5.00 = 11.1 b. 5.00 + 162.10 = 167.10 c. 3.20 / 6.232 = .513 d. 232 – 16.23 = 216 • Express the quantity .000075 nm in meters (109 nm = 1m) • Answer 7.5 x 10 -14 • Convert 987,000,000 micrograms to kilograms (106 mg = 1 g) (103 g = 1 kg) Answer .987 • What is the density of an object with a mass of 3.00g and a volume of 62.2cm3? • Answer .0482g/cm3 • What is the volume of 45.5g of silver if the density is 10.5 g/ml? • Answer 478ml Express the following in scientific notation: a. 0.000230 b. 430,000,000 c. .0000000000001 Compounds and Mixtures • Compounds are made up of 1 phase; mixtures more than one • Compounds can be separated by chemical means; mixtures by physical means • Mixtures are sometimes uniform in composition (homogeneous), but sometimes not (heterogeneous) Atoms - are electrically neutral, meaning the number of protons equal the number of electrons Atomic Number • Equal to the number of protons in an element Electron Configuration Potassium –1s22s22p63s23p64s1 Silver- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d9 • Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids location on the periodic table • Representative elements, transition metals, inner transition metals, noble gases location on periodic table Charges Group 1A +1 Group 2A +2 Group 3A +3 Group 4A none Group 5A -3 Group 6A -2 Group 7A -1 Group 8A none Valence Electrons • Equal to the group number for representative elements • For example, Magnesium has 2 valence electrons • Iodine has 7 valence electrons Ionic Bonds • Electrostatic force of attraction between 2 oppositely charged ions What are ionic compounds made up of? • A metal and a nonmetal, for example, magnesium and fluorine What is the formula for potassium phosphide? • K3P Unshared pairs of electrons • Pairs of electrons that do not participate in bonding When are parentheses used in ionic compound names? • When there is a transition metal that can have more than one charge What does an –ate or –ite ending indicate about an ionic compound? • It contains a polyatomic ion What is the formula for sodium sulfate? • Na2SO4 What is the correct name for FeCl2? • Iron (II) chloride How can you tell by the formula if the substance is an acid? • The cation is H Empirical Formula • The smallest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound Avogadro’s Number • The number of representative particles of a substance present in 1 mole of that substance STP • 0 degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere of pressure Mole • The SI unit used to measure amount of a substance Calculate the number of moles in 635g of NaNO2. • 9.20 moles The reaction Al + O2 Al2O3 • Combination What is a skeleton equation? • An unbalanced chemical equation (does not show relative amounts of reactants or products) What type of reaction is CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O • combustion In a chemical reaction, the mass of reactants must equal the mass of products, according to the law of conservation of mass Limiting and Excess reacants • The amount of product obtained is determined by the limiting reactant • A balanced equation is needed to determine which reactant is the limiting reactant • Some of the excess reactant is left over after the reaction is complete • The reactant that produces the least product is the limiting reactant 2CO + O2 2CO2 a. What is the ratio of moles of O2 used to moles of CO2 produced? - 1:2 b. How many moles of CO are needed to react completely with 2.23 moles of O2? - 4.46