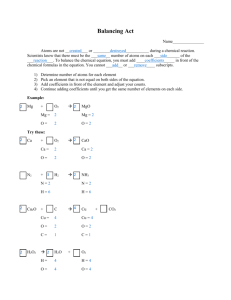
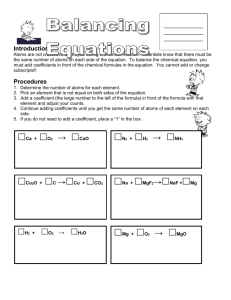
Reactions in Chemistry
advertisement

Reactions in Chemistry Conservation of Mass Chemical Equations • Chemical equations are supposed to accurately reflect the reaction taking place. • Remember that in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. • What does this mean when writing chemical reactions? ▫ It means that the same elements must be present both before and after reaction, and that the number of atoms of each element should remain constant during the reaction. Chemical Equations • To ensure that this is the case requires counting the number of each type of atom on the reactants side and on the products side. These two counts should be identical. • In order to do this, begin by understanding the role of subscripts in formulas as well as coefficients in balanced chemical equations. The role of subscripts • Remember that subscripts in a formula can tell us the number of atoms of a particular element in one unit of the substance: NaCl AgNO 3 NaNO3 AgCl NaCl: Na – Cl – AgNO3 Ag – N– O– The role of subscripts • What happens when there are parentheses in the formula, followed by a subscript? FeSO4 Ba(NO3 ) 2 BaSO 4 Fe(NO3 ) 2 • The number outside the parentheses tells you how many units of what is in parentheses there are in one unit of the substance: (NO3 ) 2 means NO3 NO3 N–2 O-6 The role of subscripts • This count can be arrived at by taking the subscript outside parentheses times the subscript of each element in parentheses (NO3 ) 2 N: 2(1) = 2 O: 2(3) = 6 Counting reactants • Looking at just the reactants in this reaction: FeSO4 Ba(NO3 ) 2 BaSO 4 Fe(NO3 ) 2 FeSO4: Fe – S– O– Ba(NO3)2 Ba – N– O– Counting atoms • Sometimes the same element shows up more than once in a particular formula, such as in the formula for ethanol in the following combustion reaction: C2 H5OH 3O2 2CO2 3H 2O C2H5OH: C– H– O– www.personal.psu.edu upload.wikimedia.org The impact of coefficients • This reaction also contains coefficients. Coefficients are whole numbers that tell how many units there are of a substance in a reaction. C2 H5OH 3O2 2CO2 3H 2O • Understanding that 3O2 means there are 3 molecules of oxygen: O O O O O O 3O 2 means O 2 O 2 O 2 so there are 6 oxygen atoms The impact of coefficients • This means that if you know the number of atoms in one unit of the substance, all you need to do is multiply that number by the coefficient of the formula to find the total number represented: 3O2 means there are 3 2 6 O atoms 2CO2 means there are 2 1 2 C atoms 2 2 4 O atoms Putting it all together • Count the number of each type of atom indicated by each of the following: 4H2O 2P2O5 3Ba(NO3)2 Challenge: 2CH3COOH Resources • http://www.personal.psu.edu/amd16/images/Et hanol.gif • http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commo ns/0/04/Ethanol-displayed.png