Semester 2 Revision 3
advertisement

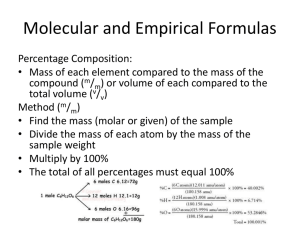
1 C2A2B Semester 2 Revision 1 Hart Semester 2 Revision 3 Use your Chemistry Data Sheet 1. Given an example of each of the following, indicating your example by a chemical formula. a. b. c. d. an alkyl group an amphoteric oxide a network solid a saturated alkane 2. How is it possible to overcome the problem of hardness in water? 3. Explain the meaning by giving an example of each of the following chemical reactions. a. b. c. d. homogeneous reaction precipitation reaction ionisation reaction redox reaction 4. An iron bar is exposed to the atmosphere for an extended period of time. What will happen? Why? 5. Explain why metals are malleable while ionic solids are not. 6. A gaseous organic compound is found by analysis to consist of 41.0% C, 13.4% H and the remainder N. a. What is the empirical formula of the compound? b. A flask of volume 435 mL was evacuated and weighed. It was then filled the above compound and reweighed. The experimental figures were; i. ii. Mass of empty flask 102.792 g Mass of flask and vapour 103.970 g Pressure of the vapour 740 mm Hg Temperature of the vapour 263 K What is the molecular mass of the vapour? What is the molecular formula of the compound? 7. Under what conditions can a gas be collected by the downward displacement of water? 8. 170.0 g of H2O2 was decomposed by the addition of MnO2 and the resulting gas collected over water at 753 mm Hg and 25.0 ˚C. Given the vapour pressure of water was 33.0 mm Hg at 25 ˚C, what was the volume of dry oxygen produced at these conditions? 2 C2A2B Semester 2 Revision 1 Hart 9. Describe sublimation and give an example of a substance that sublimes. 10. Hydrogen chloride reacts with water to produce an acidic solution. It is soluble in water and reacts with alkalis to form salts and water. Hydrogen chloride is colurless and denser than air. It reacts with ammonia to produce white clouds of ammonia chloride (NH4Cl). Hydrogen chloride has an irritating smell, poisonous and not reactive with oxygen. Classify these properties of hydrogen chloride into physical and chemical properties. 11. What is meant by an isomer? Sketch the structural formula of trans-2-butene and cis-2butene. 12. Write down the electron configuration of; Species Electron Configuration a Neon atom a chloride ion a Ba2+ ion a Fe atom 13. Draw structural formula for; i. ii. iii. iv. 2,4,6-octa-tri-ene 1,3-difluoro-4-iodo-2-methylnonane 2,3-dichloro-3-ethyl-4-methyldecane 3-fluoro cyclopentene 14. Why does a burning match light a candle? 15. Explain why an explosion is possible whenever a large amount of dry, combustible material is distributed as dust sized particles. 16. The explosive TNT, when exploded, decomoses according to the equation; 2C7 H 5 (NO2 )3(s) 12CO(g) 2C(s) 3H 2(g) 3N 2(g) A 2.50 x 102 g charge of TNT is detonated in an evacuated 60.0 L container. Calculate: i. the mass of carbon deposited ii. the final pressure of the system if the final temperature reaches 245 ˚C. iii. the partial pressure of the nitrogen under these conditions. 3 C2A2B Semester 2 Revision 1 Hart 17. Which type of reaction, endothermic or exothermic, would result in product molecules having the greater energy. Why? 18. A white crystalline compound containing only C, H and O was analysed. 2.76 g of the compound when burned in excess oxygen produced 1.93 g CO2 and 1.18 g H2O. a. What was the empirical formula of the compound? b. Given that the relative molecular mass of the compound was 126.0 g, what is the molecular formula of the compound? c. Given that the compound is a dihydrate, rewrite the molecular formula to indicate this. 19. Explain why photography can be viewed as a redox process. 20. Why is energy needed to remove an electron from an atom even if the atom would tend to form a positive ion? 21. What is wrong with the electron configurations shown below? a. b. c. d. B: Be: Mg: Zn: 1s2 2s3 1s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p8 1s2 2s2 2p6 2d10 3s2 3p6 4s2 22. If an ion X- acquire a 2- charge, has it been oxidised or reduced? Explain your answer and write a general equation for the reaction. 23. Name the alkanes, alkenes and alkynes that incorporate five carbon atoms. 24. What reason can you give for the generally low melting points of molecular solids? 25. What tests might a chemistry student perform to determine whether a substance is ionically bonded. 26. Analysis shows a hydrocarbon to be composed of 80.0% C and 20.0% H. What is its empirical formula? Its gas density is 1.34 g per litre at STP. What is its molecular weight? What is its molecular formula? 27. Briefly outline four (4) ways in which steel could be protected from corrosion. 28. 120.0 L of a gas mixture known to contain butane and nitrogen gas was mixed with excess oxygen and ignited. The products were cooled to 25.0 ˚C and dried. The volume of the products was 77.0 L. The products were then passed through a solution of KOH to absorb the CO2, (to make KHCO3) and the remaining gases dried. The volume of this final mixture was found to be 37.0 L. All gas measurements were carried out at 25.0 ˚C and 101.3 kPa. 4 C2A2B Semester 2 Revision 1 a. b. c. d. Hart Write the equation for the combustion of butane. Determine the volume of butane in the original sample. Determine the volume of oxygen gas mixed with the original sample. Calculate the percentage by mass of butane in the original sample. 29. The density of mercury is 13.6 g cm-3. On average, how far apart are mercury atoms? 30. Why does a chemist set up an hypothesis or proposal in an experiment. 31. What must be done to a 2s electron in order to make it a 3s electron? What happens when the 3s electron falls back to form a 2s electron? 32. Why does the attainment of the inert gas structure cause chemical stability to electrons? 33. In general, what conditions cause 2 atoms to combine to form an ionic bond? 34. A compound X with the molecular formula C4H10O2 was reacted with phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) to form 1,2-dichlorobutane. Which of the structures below is most likely to represent the structure of X? 35. What mass of KCl is required to make 225 mL of 0.0500 mol L-1 solution? 36. Name the following compounds. a. b. c. d. e. CH3CH2CH=CH2 CH3CHCFCH2CH3 CH3CH2CH=CClHCH2Br CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH2Cl CH3CH=C(C2H5)CH3 37. Pool chlorine (NaOCl) is an oxidising agent. Explain the meaning of an oxidising agent. 38. Write down the oxidation mumbers of chlorine in; ClO4 39. OCl ClO3 KClO4 Draw all the isomers of C5H12. Cl2 HCl 5 C2A2B Semester 2 Revision 1 Hart 40. What effect does a catalyst have on the activation energy of a reaction? Illustrate your answer with a diagram. 41. Graphically depict the effect of increasing temperature on the volume of a gas (at constant pressure) 42. Why are cycloalkanes that have a small number of carbon atoms in the chain unusual? 43. What is an homologous series? In your answer give three examples of homologous series. 44. Explain the factors that determine the rate of reaction of a chemical reaction. 45. Upon what characteristics are the elements of the periodic table classified? 46. Why do atoms of the same element have similar physical properties? 47. Two glass flasks of equal volume were evacuated. One flask filled with gas A and the remaining flask filled with gas B. Conditions of temperature and pressure were the same. Gas A, hydrogen, was found to have a mass of 0.400 g. Determine the molar mass of gas B, which was determined to have a mass of 6.00 g. 48. Explain the meanings of each of the following terms. 49. a. covalent bond b. addition reaction c. reduction d. ductile e. valence electrons f. anion g. pH h. distillation i. dissociation j. entropy Write down the species which are acting as acids and species acting as bases in the following equation. HCO3(aq) H 2O(l ) H 2CO3(aq) OH(l )