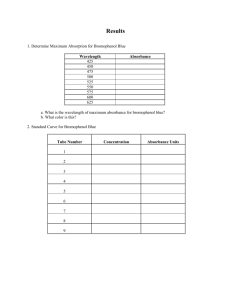
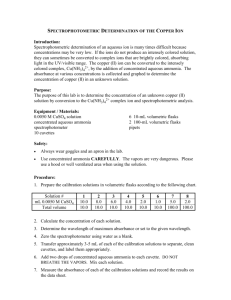
Absorption Spectroscopy Turn on Spec 20's
advertisement

Turn on Spec 20’s *** NOW! *** Absorption Spectroscopy Today’s Lab 11 :O :O !!! Lab 12 – VSEPR Lab (informal in class) Last day – NO LAB FINAL You are required to come – will clean up a certain portion of the lab (ie glassware) After clean up, I will host lecture exam studying based upon the ACS standardized exam for your lecture final your textbook, ACS books, and questions – I will stay in the lab answering questions until lab is over. Bring Unknowns Unknown Ni Co Cu Color Green Red Blue λ 395 nm 525 nm 625 nm Possible unknowns and their wavelength of maximum absorption (nm) Procedure Get unknown assignment from Lab Instructor. Fill test tube with stock solution(in back hood) of similar color, green (Ni), red (Co), or blue (Cu) Record absorbances from 400 to 700 nm at 25 nm intervals, determine the wavelength of maximum absorbance, double check with lab instructor. Finding Maximum Wavelength Procedure Set Spec 20 to appropriate wavelength Record absorbance (or %T for more significant figures) of four standard solutions: 10 mL water 3 & 7 mL diluted solutions (detailed on next slide) 10 mL stock solution Plot absorbance vs. concentration (EXCEL) Use calibration curve to ID unknown concentration! Calibration with your blank solution With empty, closed sample compartment, turn the left-hand knob to obtain a reading of 0% T. Use the mirror behind the needle to avoid parallax error. Calibration •Fill your tube ~ 1/2 to ¾ of the way with your blank solution (NaOH) •Wipe the cuvette with a dry Kimwipe to remove drops of solution or finger prints. •Insert in the compartment, and close the cover Calibration Turn the right-hand knob to obtain a reading of 100% T. Using Spectrometer To analyze your sample, insert sample cuvette and read the Absorbance value on the scale. Use the mirror behind the needle to avoid parallax error Source: http://www.dartmouth.edu/~chemlab/techniques/spectrometer.html Procedure- Calibration Curve Prepare two standard solutions with known concentrations Use graduated cylinder to deliver 3 mL and 7 mL DI H2O to separate test tubes, record actual volume Deliver 7 mL and 3 mL DI H2O, record actual volume Calculate concentrations of the two solutions Vconc M conc Vdil M dil Tables p. 47-48 SKIP PART 1 (Adjust your wavelength to the appropriate nm based on previous slide and the color of your unknown!!) Part 2 Sample Number Vol Stock Vol H2 O Diluted Vol Conc (M) Absorbance 1 (pure water 0 mL 10 mL 10 mL 2 3 mL 7 mL 10 mL CALC RECORD 3 7 mL 3 mL 10 mL THESE THESE 4 (stock soln) 10 mL 0 mL 10 mL ↑ MAKE THESE ↑ Go Home and plot Convert %T to absorbance! Convert from %T to absorbance: Absorbance = -log(%T/100) In Class Show me a rough graph of your absorption spectrum (page 40 example) and indicate where your maximum absorption you found to be. Formal Lab Data Table –raw individual data (as per page 48) Calculated data: show your slope, intercept and the unknown concentration found Graph – calibration curve of abs vs. conc based upon your own individual raw data Calibration curve (on Excel) Calibration Curve of Iron Absorbance 0.4 0.3 0.2 y = 1.5x + 0.005 R² = 0.9981 0.1 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 Concentration (M) 0.25 Calculations Calculations – show your trendline equation found from calibration curve y=mx+b Show how you determine your unknown concentration (plug in absorbance and solve for conc!) Show also your % error and how you found your dil conc Discussion – formal discussion 1-2 pages Discuss the maximum wavelength you found in part A versus the actual, and the reasoning Discuss the concentration you found Discuss the calibration curve, was it precise (r^2) Error analysis