Nervous System
advertisement

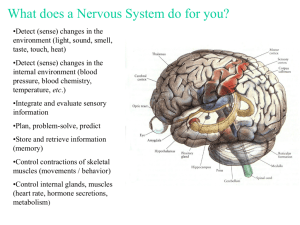
Nervous System Important Vocabulary • Neuron • Dendrite • Axon • Sensory neuron • Interneuron • motor neuron • Synapse • Central nervous system • Peripheral nervous system • Cerebrum • Cerebellum • Brain stem • reflec EXPLORE ACTIVITY pg. 677 • What did you find out about their heights? How were your eyes tricked? Response to Stimuli • Any change inside or outside your body that brings a response is called a stimulus • Stimuli • • • • Our bodies have internal control systems that maintain homeostasis • Breathing, heartbeat,digestion Neurons • Neuron: the working unit of the nervous system • A neuron is made up of a cell body and branches called dendrites • Dendrites receive messages and send them to the cell body • An axon carries messages away from the cell body • Messages carried by a neuron is called an impulse • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cUGuWh2UeM k&list=PLLEfSFm6js-_SjqVDF3bcG6lox9O43h_L Types of Neurons 1. Sensory: receive information and send impulses to the brain or spinal cord 2. Interneurons: relay impulses from the sensory to motor neurons. There are more of interneurons than any other type 3. Motor: conduct impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands throughout your body. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C4Gt322-XxI Synapse • Since neurons don’t touch each other, how does an impulse move from one another? • Synapse: small space where an impulse moves from one neuron to another. • When impulse reaches the end of the axon, a nerve transmitting chemical is released by the axon • This chemical diffuses across the synapse and starts an impulse in the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron CNS AND PNS Central Nervous System • Made up of the • Brain • Spinal cord • All body activities are coordinated • If steps on your foot, your whole body reacts The Brain • Made up of 100 billion neurons • Divided into 3 parts • Cerebrum • Cerebellum • Stem • Cerebrum: • divided into two large sections called hemispheres • Impulses from the senses are interpretted, • Memory is stored • Voluntary muscle control center The Brain • Cerebellum • Behind and under the cerebrum • Coordinates voluntary muscle movement • Maintains balance and muscle tone • Stem • Extends from the cerebrum and connects the brain to the spinal cord • Parts: midbrain, pons, medulla • Controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure Peripheral Nervous System • Brain and spinal cord are connected to the rest of your body by the peripheral nervous system • Made up of 12 pairs of cranial nerves from your brain • 31 pairs of spinal nerves from your spinal cord • These nerves link your CNS with all parts of your body • Spinal Nerves: made up of bundles of sensory and motor neurons • Somatic System and autonomic system Somatic and Autonomic System • Somatic: consists of the cranial and spinal nerves that go from the CNS to your skeletal muscles • Connect the central nervous system to the organs, muscles, and skin • It is like a passageway from the environment to the central nervous system • processing sensory information that arrives via external stimuli including hearing, touch and sight • Autonomic: controls heartbeat rate, breathing, digestions and gland functions • When salivary glands release saliva Reflex Drugs and the Nervous System Activity 25-1 p. 685