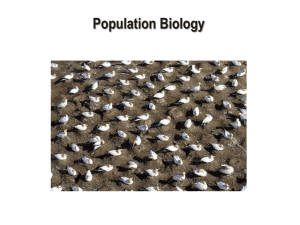
population ecology

Justin ray m guce
2008
HOW DO WE DEFINE
POPULATION???
TERMS TO REMEBER
• Population
– group of organisms that belong to the same species and live in a given area
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION
• Describes the area inhabited by a population
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• POPULATION DENSITY
• Number of individuals per unit area
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• POPULATION DISPERSION
– clumped
– uniform
– random
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• GROWTH RATE
– Factors affecting population size
• # of births
• # of deaths
• Immigration and emigration
• ARMM- 3.86%
• Region IV- 3.72
• NCR- 1.06%
WHAT DOES this picture SHOW US???
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• Types of GROWTH
– Exponential
– Logistic
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• Exponential
• J-shaped curve
• reproduction at constant rate
• ideal conditions
CHARACTERISTICS OF A POPULATION
• Logistic
• S- shaped curve
• Growth stops after an exponential growth
CHARACTERISTICS OF A
POPULATION
• AGE STRUCTURE
– growth depend on the age of the population
– age structure diagrams
CHARACTERISTICS OF A
POPULATION
• DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION
– Dramatic change in birth and death rates
– Birth rate falls to meet the death rate
LIMITS TO GROWTH
• Limiting factors
– Causes population to decline
– Insufficient supply of nutrients
• 2 types of FACTORS
– DENSITY DENPENDENT
– DENSITY INDEPENDENT
DENSITY DEPENDENT FACTORS
• depends on population size
• becomes limiting when…
– POPULATION REACHES A CERTAIN LEVEL
• large and dense population size
DENSITY DEPENDENT FACTORS
• INCLUDES
– Competition
– Predation
– Parasitism
– Disease
Competition
Competition: overcrowding
Predation
Parasitism
Disease
DENSITY INDEPENDENT FACTORS
• affects all population in similar ways
• REGARDLESS of its POPULATION SIZE
• Characteristic crash in population size
DENSITY INDEPENDENT FACTORS
• INCLUDES
– UNSUAL WEATHER
– SEASONAL CYCLES
– NATURAL DISASTERS
– HUMAN ACTIVITIES