Population Growth: Characteristics, Factors, and Growth Types
Chapter 5
Section 1
How Populations
Grow
• List the characteristics used to describe a population
• Identify factors that affect population size
• Differentiate between exponential and logistic growth
Introduction 5-1 Activity
December 2, 2013
Write these questions and your answers on a sheet of paper.
• How many people are in this classroom?
(include me because I am a person)
• What is the room’s area?
(there are 39.37 inches per meter)(area is length x width)
• How many people are there in the room per square meter?
(divide the number of people by the room’s area)
Population density = # of individuals/unit area
• Suppose there are 150 bullfrogs living in a pond that covers an area of 3 square kilometers. What is the density of the bullfrog population?
List the characteristics used to describe a population.
• Three important characteristics of a population are its geographic distribution, density, growth rate, and population age structure.
– Density – the number of individuals per unit area.
This can vary greatly depending on the species and its ecosystem.
– Geographic distribution – also called the range, the area inhabited by a population. This can vary greatly.
List the characteristics used to describe a population - continued
– Growth rate – the rate at which the size of a population changes
– Population age structure – the age distribution of the individuals in that population
Population growth – Three factors can affect population size:
- The number of births (if you have more births than deaths the population size grows)
- The number of deaths (if you have more deaths than births the population size shrinks)
- The number of individuals that enter or leave a population
- Immigration is the movement of individuals into an area
- Emigration is the movement of individuals out of an area
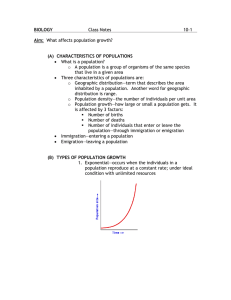
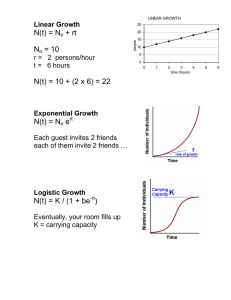
Differentiate between exponential and logistic growth.
Logistic Growth
• This occurs when a population slows or stops following a period of exponential growth
• As resources become less available, the growth of a population slows or stops.
• This ususally appears as a
“S-shaped” curve on a line graph.
Exponential Growth
• This occurs when a population grows at a constant rate
• Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially.
• This usually appears as a “Jshaped” curve on a line graph.
Post Notes Assignment
• Write questions numbered 1-6 on page 123 and answer them.
• Then write the definitions for the vocabulary terms found only in section 1
1. population density
2. immigration
3. emigration
4. exponential growth
5. logistic growth
6. carrying capacity