Lecture 2 Slide Show

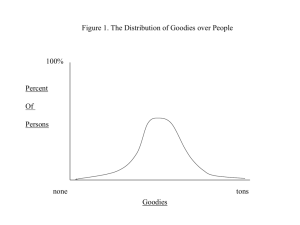
Percent
Of
Persons
100%
Figure 1. The Distribution of Goodies over People none tons
Goodies
Figure 2. Distribution of U.S. Households by Income, in
Thousands of U.S. Dollars, 2005 (from Kerbo, p. 21)
20
15
10
5
0
<$5 <10 <15 <25 <35 <50 <75 <100 $100+ percent 3.3
5 6.4
12.4
11.4
14.9
18.4
11.1
17.2
Figure 3. Black U.S. Households by Income in Thousands of
U.S. Dollars, 2005 (from Kerbo, p. 21)
20
15
10
5
0
<$5 <10 <15 <25 <35 <50 <75 <100 $100+ percent 6.8
10.3
8.9
16.1
12.6
15.1
15.1
7.3
7.8
Figure 4. Percentage of Aggregate U.S. Household Income By Lowest to Highest
Earning Fifths, 2005 (from Kerbo, p. 22)
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Percent low fifth 2nd 5th 3rd 5th
3.4
8.6
14.6
4th 5th
23
5th 5th
50.4
Figure 5. Annual Wages in U.S. Dollars by Occupational Category for U.S. Males and
Females in 2005
70,000
60,000
50,000
40,000
30,000
20,000
10,000
0
Exec
Prof
Service
Sale/Off
Nat Res
Prod/Tran
Male Female
U.S. Census, Table PINC-06, "Occupation of Longest Held Job in 2005
Figure 6. Gender Gap (Percent Female/MaleWage) in Annual Wages for U.S. Workers in 2005 (Computed from Figure 5)
80%
75%
70%
65%
60% percent
Admin
71%
Prof
69%
Service
78%
Sale/Off Nat Res Prod/Tran
73% 73% 66%
Figure 7. Median Income in U.S. Dollars by Education for U.S. Men and Women, 2005
(from Kerbo, p. 23)
80,000
60,000
40,000
20,000
0
<HS HS Coll BA MA+
Men 22,138 31,683 39,601 53,693 71,918
Women 13,076 20,176 25,736 36,250 47,319
Figure 8. Gender Gap (Percent Female/MaleWage) in Annual Wages for U.S. Workers by Education in 2005 (Computed from Figure 7)
68%
66%
64%
62%
60%
58%
56% percent
<hs
60% hs
64% college
65% bachelor
68% master+
66%
Figure 9. Percent Income Gains and Losses, 1980-1989, for Lowest to Highest Earning
U.S. Households (in Fifths, plus Top 10% and Top 1%, from Kerbo, p. 27)
80
60
40
20
0
-20
Low
5th
2nd
5th
3rd
5th
4th
5th top
5th top
10th top
1% percent -4.6
-4.1
-0.8
4.6
9.1
15.6
62.9
Figure 10. Income Gains and Losses, 1967-2000, for Lowest to Highest U.S. Earners
(in Fifths, from Kerbo, p. 28)
15
10
5
0
-5
-10
-15
-20
Low 5th 2nd 5th 3rd 5th 4th 5th Top 5th percent -10 -17.6
-13.9
-5 13.5
Figure 11. Median U.S. Household Net Worth by Race, 1991 and 2004 (from Kerbo, p.
33) and Percent of White Wealth for Black Households (Calculated from Kerbo, p. 33)
$150,000
$100,000
$50,000
$0
1991
White $44,408
Black $4,604
2004
118,300
$11,800
% of W 1991 %of W 2004
10% 10%
Figure 12. Median Income and Net Worth for White Families and Other Families in
2001(From The Wealth Inequality Reader, p. 14)
$150,000
$100,000
$50,000
$0
Income Net Worth
White $45,200 $120,900
Other $25,700 $17,900
%White
Income
% White
Net Worth
57% 15%
Figure 13. Median Net Worth and Net Financial Assets for U.S. Households: All,
Married, Single Male Head and Single Female Head in 2001 (From The Wealth
Inequality Reader, p. 16)
150,000
100,000
50,000
0
All Married Male Female
Net Worth 86,100 $140,000 46,990 $27,850
Financial Assets $21,900 $39,770 13,940 $5,600
Figure 14. Average Pre-Retirement Employment Earnings (From Longest Held Job:
“Income”), Social Security, Pension, and Asset Earnings for New (1980-1981) Social Security
Old Age Pension Recipients Interviewed in the New Beneficiary Survey of 1982 (From
Hogan and Perrucci 1998)
$50,000
$45,000
$40,000
$35,000
$30,000
$25,000
$20,000
$15,000
$10,000
$5,000
$0
Income Social
Security
Pension Assets
White Males
White Females
Black Males
Black Females
Figure 15. Race and Gender Gaps (Percent of White Male Income) for White Women and
Black Men and Women in Pre-Retirement Employment Earnings (From Longest Held Job:
“Income”), Social Security, Pension, and Asset Earnings for New (1980-1981) Social Security
Old Age Pension Recipients Interviewed in the New Beneficiary Survey of 1982 (From
Hogan and Perrucci 1998)
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
40%
30%
20%
10%
0%
Income Social
Security
Pension Assets
White Females
Black Males
Black Females