Case Study of John D. Rockefeller: Business Pioneer or Robber
advertisement

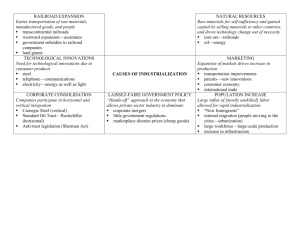
Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Name ____________________________ Period _____ Essential Question: How can rapid industrial and technological development be a blessing and a curse? 1 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Railroads and Industry Aim: Do Now: Growth of Railroads The period from 1865 to 1900 was the great age of railroad building. Coast-to-coast rail service, in particular, helped tie the nation together. How did the railroads improve? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ What impact did the railroad networks have on those that would ship goods? How was Railroad travel improved? _______________________________designed and sold an air brake that allowed a locomotive engineer to stop all railroad cars at once. Before this invention each car had its own break and break operator and if they did not stop at the same time there would be serious accidents. ________________________________designed a railroad sleeping car which made long distance travel more comfortable. _______________________________, or combining, of Railroads. Large railroads bought smaller railroads. If you were a railroad owner and you bought all of the other railroads would that be good or bad for you? Explain ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Important People ____________________________was a very tough businessman who believed in consolidation. He bought lines in NY first and then continued to buy more and more. He was a ruthless businessman. 2 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis _____________________________ built the Great Northern Railroad. He did so with no help from the Government rather he worked with the farmers and people moving west. What was the most important invention for the railroad? Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Document 1: GROSS EARNINGS OF THE RAILROADS $600,000,000 $550,000,000 $500,000,000 $450,000,000 $400,000,000 $350,000,000 $300,000,000 $250,000,000 $200,000,000 $150,000,000 $100,000,000 $529,012,999 $403,329,208 $130,000,000 1861 Use the graph above to answer the following questions. 1871 1879 1. How much money was earned in 1861? 1879? 1861_______________________ 1879____________________________ 2. What is the difference between 1861 and 1879? 3. What do you think is the reason for this? 4. How did the railroad effect industrialization? 3 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Mark Twain wrote about his experiences living and working out West in his book Roughing It, published in 1872. 4 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Describe the differences that Twain wrote about between his travel on the mail coach and the accounts from the railroad travel. Reducing Competition Define rebates: _______________________________________________________________ Define pools: ________________________________________________________________ Why were pools created? Railroads and Farmers How did rebates and pools affect farmers? How did the farmers attempt to address the problem? 5 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis “With Rail lines in place, the United States was ready to become the greatest Industrial Nation the world had ever seen.” Why? ________________________________________________________________________ Positives of the Railroad Negatives of the Railroad Directions: You are to create your own political cartoon about the Railroad. You can portray either the negatives or the positives of the railroad. Rise of Big Business Aim: Do Now: 6 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis How would having a single company produce all of the video and computer games affect the variety, quality and pricing? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Why did the steel industry become important? What was the Bessemer process and why was it important? What new ways of doing business did Americans develop? What are the pros and cons to Big Business? Pros Cons Andrew Carnegie Where did Carnegie build his mill? Carnegie owned every process of making steel from the mining of iron ore to shipping the steel. This ability to gain control of all steps used to change raw materials into finished product is called__________________________________________________. _______________________________ - Carnegie’s idea or belief that the rich had a responsibility to help the poor and improve society. Gave millions to charities. 7 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis John D. Rockefeller Oil is discovered in Pennsylvania, but Rockefeller believes the money is in _________________. He invests in an oil refinery at the age of 23. He believes competition is wasteful. He buys out other refineries. Why? _________________________________________________________. Creates Standard Oil in 1870. Rockefeller formed the Standard Oil trust in 1882. He had a monopoly in the oil industry. Define monopoly: _____________________________________________________________. Rockefeller= Horizontal Integration Carnegie=Vertical Integration Answer the Chart Skills Question: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Analyzing a Document 1. Who is the man in this cartoon? 2. What industry does he control? 3. What is made to look like a factory in the background? 4. What is the message of this cartoon? 5. What act was passed to try to prevent monopolies? J.P. Morgan Morgan was the most powerful banker of the late 1800s. He used his profits from the banking industry to gain control of major corporations. _____________________________________ first billion dollar corporation. Social Darwinism Definition: 9 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Rockefeller’s Standard Oil Company Cuts Prices to Kill Competition Throughout her life, muckraker Ida Tarbell was interested in the unfair competition between the small oil producers of Pennsylvania and the Standard Oil Company. In this excerpt, which is taken from Tarbell’s book The History of the Standard Oil Company, she wrote about how the Standard Oil Company dealt with competition. Her information is based on interviews with former Standard Oil Company employees. The marketing department of the Standard Oil Company is organized to cover the entire country, and aims to sell all of the oil sold in each of its divisions. To eliminate competition it had organized an elaborate secret service for locating the quantity, quality, and selling price of independent or competitor shipments. Having located an order for independent oil with a dealer, Standard Oil persuades the independent dealer, if possible, to cancel the order. If this impossible, Standard Oil threatens “predatory competition,” that is, to sell at cost (the amount spent in producing and manufacturing) or less until the rival is worn out… The sureness and promptness with which Standard Oil located their competitors’ shipments was remarkable. The ruthlessness (harshness) and persistency with which Standard Oil cut and continued to cut their prices drove small independent oil producers to despair. 1. According to Tarbell, how did Standard Oil eliminate competition? 2. If you were an independent oil producer in the late 1800s, how would you have responded to Rockefeller’s business methods? 10 Unit 2 Industrialization Form Proprietorship Partnership Corporation SS8 Mrs. Francis Forms of Business Organization Advantages *owner close to customers ad workers *has total control of management *receives all profits *more capital can be raised *risks are shared *more management perspective *increased capital through sale of shares (stocks) *losses limited to investment *increased number of managers *ownership transferable *larger growth potential *research facilities possible *risks shared Disadvantages *owner assumes all risks *limited capital available *one manager’s perspective *profits must be shared *unlimited liability for owners *ends if one partner leaves *state & federally regulated *subject to corporate taxes *management removed from customers & workers Government Response to Industrial Development and Abuses The great strides in technology made the remote geographic areas of the United States more accessible to each other. Telephone and telegraph communication and railroad transportation went beyond state borders. However, in the industrial age, the new interstate commerce required national laws. The new laws made the national government grow increasingly stronger. prices because there is no competition to deep it in line by offering the product for a lower price. The trust becomes the dictator of the market. In the 1870s, farmers of prairie and western states were at the mercy of railroad trusts. Railroad companies formed pools to eliminate competition. The group of companies conspired to control prices. Together they acted as a monopoly. Railroad pools charged high prices to get farmers produce to market. The farmers had no alternatives. The public was hurt, too. Food prices rose because it cost so much to bring crops to the market. There were no laws to stop some companies from forming mergers (combinations of several companies) so big that they dominated the market for their product. When one company eliminates all others it becomes a monopoly or a trust. Once a company controls the market, it can set the design, quality, and quantity of a product. A monopoly can charge high The farmers pressed their states to regulate such railroad abuse. However, rich and powerful railroad owners bribed legislators and prosecutors and found ways 11 Unit 2 Industrialization around the regulations. The Supreme Court of the United States said states could regulate the railroads but only within their state boundaries. In Wabash RR v. Illinois decision of 1886, the Court said Congress alone could regulate interstate commerce. SS8 Mrs. Francis regulated railroad rates. It also prohibited railroad pools. Shortly afterwards, Congress passed the Sherman Anti-trust Act (1890). It outlawed monopolies in all industries by forbidding “combinations in restraint of trade.” These acts were a weak start. Neither act was exceptionally strong, and corrupt officials worked to keep them weak. Not until the Progressive Era were strong laws passed to control monopolies. Farmers and the public turned to Congress for action. In 1887, Congress passed the Interstate Commerce Act. It Define all bold terms from the reading above in the space below: 1. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________________________ 5. ________________________________________________________________________ 6. ________________________________________________________________________ 12 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Rockefeller: Captain of Industry or Robber Baron? Directions: For each situation listed below, decide if you think Rockefeller was a Captain of Industry or a Robber Baron. Write your answer in the space provided. ______________ 1. Rockefeller cut waste in the oil industry and thus was able to lower production costs. Lower production costs led to lower prices and higher wages for workers. ______________ 2. Rockefeller forced railroads to give Standard Oil rebates, or kickbacks. In other words, owners had to pay him for using their railroads. ______________ 3. Before Rockefeller built his trust, there were dozens of small companies competing against each other in the oil industry. In this confusing situation companies could not provide the oil needed to meet the nation’s needs. ______________ 4. Rockefeller owned not only companies that refined oil, but also ships, barrels, and pipelines that carried oil. He had a complete monopoly of the oil industry. ______________ 5. Rockefeller gave $500,000,000 to charity, the largest amount of money ever given by one person. ______________ 6. During Rockefeller’s time, many people thought the United States was still a nation of small businesses. They failed to see that Americans were no long completely independent and self-sufficient. To build and manage the great empire of railroads, oil, and steel, Americans had to form large groups. In other words, they had to realize that they were becoming increasingly interdependent. ______________ 7. Rockefeller lived during a time of change. There were no laws or established business practices. He used the tools available to him as well as his own original ideas. ______________ 8. Rockefeller used the rebates he received from railroads to lower prices and destroy competitors. ______________ 9. Rockefeller was a hero of the age of industry, similar to the heroes of the age of exploration. Drake, Hawkins, Cavendish, and Cabot pursued new opportunities boldly and confidently, and some of them were good businessmen, too. ______________ 10. Rockefeller was worth $1,000,000,000 at a time when the most able factory workers made $14 to $16 a week. 13 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Case Study of John D. Rockefeller: Business Pioneer or Robber Baron? 14 Unit 2 Industrialization 15 SS8 Mrs. Francis Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Inventions Aim: Do Now: Name one invention that has had a major impact on the way people live today ______________________________________________________________________________ Between 1860 and 1890 approximately ________________ patents were issued. A __________________ is a license for an invention that allows you the rights to the invention and prevents people from copying what you have made. What is necessary to experience the Industrial Revolution? 1. 2. 3. 4. ___________________________ such as coal, iron ore, rich soil, timber, etc. ___________________________ which are needed to work and purchase goods. ___________________________ money to buy machines and pay workers. ___________________________ willing to take risks to establish new businesses. Identify two new sources of power: 1. ______________________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________________ Inventions that sped up Communication In 1844, Samuel Morse received a patent for ___________________ which improved communication in the United States. It sent _______________________ based on a code of dots and dashes. 1866- ______________________ ran an underwater cable across the Atlantic Ocean that could now connect the US to Europe. ____________________________invented the telephone “talking machine” It improved business (no longer had to go to the telegraph office, quickly get prices, or check on supplies in inventory) Thomas Edison Edison was known as the “Wizard of Menlo Park” He invented the _______________________, ______________________, and hundreds of other devices. He created the first_______________________ (1882 NYC) which gave people light. 16 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Technology Takes Over It seemed like every day there was a new invention and with the new technology, businesses became more _______________ and life became more _________________. Examples: Refrigerated Railroad Car (1880) – _________________________________ Typewriter (1868) – _____________________________________________ Lightweight Kodak camera(1888) – ________________________________ Automobiles No single person invented the automobile. Henry Ford made the first car that was affordable. In 1913, he introduced the _________________________________________. A method of production where workers stayed in one place and the product moved along. The assembly line allowed for _______________________________________________. What are two benefits to mass producing products? 1. _________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________ Airplanes __________________________________invented the first plane. At the time, people saw no use for the “flying machine.” New Technologies during Industrialization Directions: Use your textbook (page 545) and your notes to complete the following chart. Advancements in Communication Advancements in Travel 17 Advancements in Home/office Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Create an Advertisement Directions: Choose one of the inventions above and create an advertisement for it that you could see in the newspaper during the time of industrialization. Remember, you want people to want to buy your product, so your advertisement should be catchy. Letter Writing Directions: On a separate sheet of paper, you are to write a letter pretending you were a person living in 1910 to someone who is alive today. In your letter, you have to explain how the inventions from 1860-1910 changed the way people lived. Explain how advancements in transportation, communication, and home/office changed your life (you were alive between 1860-1910). The letter should be at least a page long. 18 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis 1876 Fair At the 1876 Centennial Exhibition in Philadelphia, a celebration of our nations’ one hundredth birthday, nearly 200 buildings showcased the country‘s newest technology. Examine some inventions and innovations that were changing life and work in the United States at the time; then complete the exercise that follows. The telephone invented by Alexander Graham Bell. The Corliss steam engine supplied power to more than 8,000 other machines on the fairground. An aerial view of the buildings of the 1876 Centennial Exhibition in Philadelphia, which featured the country’s newest inventions. Advertising poster for Columbia Bicycle Typewriter 19 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Factories engaged in mass production began to employ assembly lines like those later used by the Ford Motor Company. Consumers in rural areas looked forward to receiving mail order catalogues sent by large companies such as Montgomery Ward and Sears, Roebuck and Company. 20 In the 1870s, Edison tested the first successful electric light bulb. Invention of the Bessemer process for refining iron into steel made possible the construction of steel frame buildings, elevated railroads, and suspension bridges such as the Brooklyn Bridge. Unit 2 Industrialization 21 SS8 Mrs. Francis Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Factory Conditions Aim: Do Now: A New Workplace _________________ the Civil War, most factories were ____________ and ____________________. Bosses knew their workers. Most workers had skills that the factory needed, so they were able to _____________________________________________________. Working Conditions ________________________ - is a workplace where people labor ____________________ in ____________________________________________ for ____________________________. Who worked in the sweatshops? Why? What hazards could be found in the workplace? Describe what life was like for children during this time period. Who was Lewis Hine? Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire The Triangle Shirtwaist factory was located in the Asch Building in NYC. It’s workforce was made up of mainly young immigrant women, most of them Italians and Jews from Eastern Europe. Most workers earned $9 per week, with the most experienced making up to $12 per week. The younger workers, some only 13 years old, earned just $6 a week. Everybody was expected to work at least 59 hours a week. Working at the factory was unhealthy, uncomfortable, and unsafe. Managers seldom let workers leave to use the bathroom or drink from the dirty tap in the hallway. Fire hazards were everywhere. Workers stuffed leftover fabric into wooden bins where it sat for months. 22 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis 1. Describe the workers and working conditions in the Triangle Shirtwaist factory, using at least three examples. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ On March 25th 1911, a fire swept through the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory. The cause of the fire was unknown. But suddenly people on the 8th floor began to cry “fire!” Within minutes, the entire floor was a mass of flames. Escaping workers rushed to the stairs, however, they were soon ablaze. The workers on the 9th floor had no warning. Some women died immediately. Fireman later found them as “skeletons bending over sewing machines.” Those who had time to escape found themselves trapped by the locked factory door. In desperation, they rushed to the windows and began to jump. The crowd that gathered outside the Asch building watched in horror as girls began to fall out of the sky – “fire streaming back from their hair and dresses.” Their bodies hit the pavement with sickening thuds. Firefighters arrive quickly, but had trouble because bodies had fallen on the hoses and their ladders did not extend further than the 7th floor. A total of 146 women died that day. Why did so many women die in the fire? Could the fire have been prevented? 23 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Analyzing a Document 1. What type of work is shown in this picture? 2. Describe the worker. 3. Describe the working conditions. 4. What problem is shown in this picture? 24 Unit 2 Industrialization 25 SS8 Mrs. Francis Unit 2 Industrialization 26 SS8 Mrs. Francis Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Workers in the Age of Industry Aim: Do Now: HW: Changes in the Workplace Factory life: _____________________________________________________________ Hazards on the job: _______________________________________________________ Child labor: _____________________________________________________________ Knights of Labor – Goals: 1. ________________workday 2. ________________ pay for men and women 3. ______________ child labor Haymarket Square Workers at McCormick Harvester went on Strike – The Knights ____________________ McCormick hired strikebreakers, which are ____________________________________ Workers and strikebreakers clashed and the police ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Thousands gathered in Haymarket Square the next day to protest. The rally was led by ______________________. (Definition: ______________________________________) American Federation of Labor (AFL) was a union organized by _______________________. It was made up of ______________________________________. Goals: 1. 2. 3. 4. _______________________wages _______________________hours. _______________________working conditions. Collective bargaining: ____________________________________________________ 27 Unit 2 Industrialization Women at Work Why would women need to organize in response to working conditions? What union did the women join? 28 SS8 Mrs. Francis Unit 2 Industrialization Government Response How did the government respond to strikes? Read the following articles and answer the questions below. 29 SS8 Mrs. Francis Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis 1. What role did the federal government play in the industrialization of the United States? 2. How did the formation of monopolies or trusts by big railroad, oil, and steel companies affect consumers in the United States? Workers in the United States? 3. Why do you suppose the government generally adopted a “hands-off” policy during this period? 4. Why did workers strike in 1894 at the Pullman Palace Car Factory? 5. How did the federal government respond to the Pullman Worker’s strike? 6. Was the government justified in sending troops to enforce the injunction against the Pullman strike? Why or why not? 30 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Aim: How did the media portray industrialization? Do now: View scenes from Charlie Chaplin's Modern Times classic film. Answer questions while the film is shown. 1. Referring to the opening scene, what are people (going to work) compared to? 2. Describe the work done by Charlie Chaplin? 3. What were the effects of this type of work on the workers? 4. How are machines used in the film? a. b. c. 5. What is the relationship between the workers and the boss? 6. Does this film show industrialization as positive or negative? Explain. 31 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Review for Test on Industrialization Social Darwinism ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Large companies forced small companies out of business. Big Business Leaders ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Cornelius Vanderbilt – ___________________________________________________________ JP Morgan – ___________________________________________________________________ Mass Production ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Increase in demand in steel and rubber Inventors ______________________________________________________________________________ Samuel Morse – Telegraph ______________________________________________________________________________ Inventions – helped factories to improve efficiency Railroads ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Terms ______________________________________________________________________________ Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire After the fire – called for laws to regulate safety in factories Child labor ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 32 Unit 2 Industrialization SS8 Mrs. Francis Labor Unions Late 1800s – American opinion – striking workers didn’t need help Labor unions developed to ___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Labor Unions ______________________________________________________________________________ Union for skilled and unskilled – Knights of Labor ______________________________________________________________________________ Terms ______________________________________________________________________________ Blacklist – ______________________________________________________________________________ 33