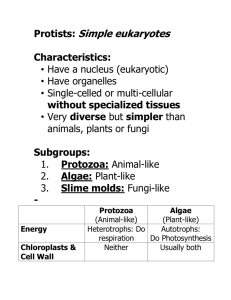
Plant-like Protista
advertisement
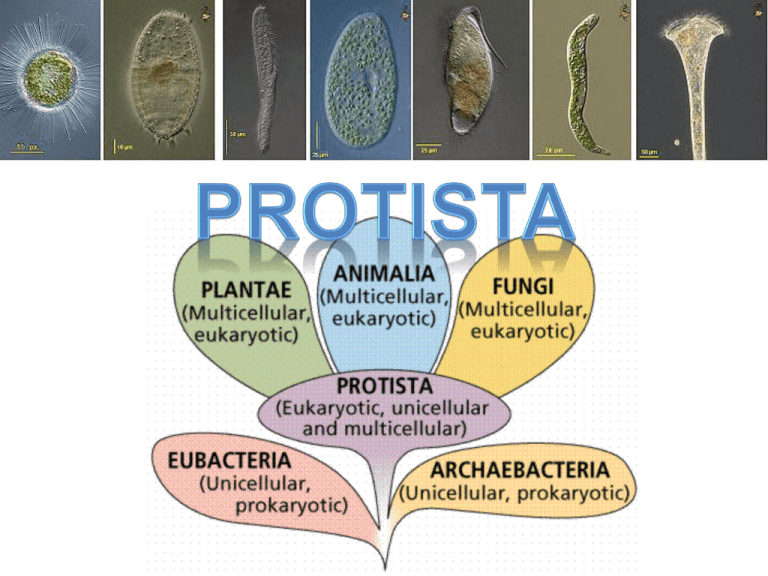
• • • • In General Mostly aquatic life Usually unicellular Always Eukaryotic Reproduction: – Some asexual, some sexual, some both Animal-like Plant-like • Feeding: – Most heterotrophic, some autotrophic • Kingdom for life that doesn’t fit in animals, plant or fungi • 3 main categories Fungi-like Analogy: Kitchen junk drawer Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas 2) Flagellates: move w/ flagella – Ex: Trypanosoma causes sleeping sickness Giardia causes Vector: tsetse fly diarrhea Trypanosoma Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas 2) Flagellates: move w/ flagella – Ex: Trypanosoma causes sleeping sickness Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas 2) Flagellates: move w/ flagella – Ex: Trypanosoma causes sleeping sickness 3) Ciliates: move w/ cilia – Ex: Paramecia Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas 2) Flagellates: move w/ flagella – Ex: Trypanosoma causes sleeping sickness 3) Ciliates: move w/ cilia – Ex: Paramecia Rotifers beat their cilia to create a current to draw water into their “mouths” Animal-Like Protista • AKA: Protozoans • Heterotrophic: pathogens, parasites, predators • Classified by how they move: 1) Pseudopods : move w/ pseudopodia (false- feet) – Engulf by phagocytosis – Ex: Amoebas 2) Flagellates: move w/ flagella – Ex: Trypanosoma causes sleeping sickness 3) Ciliates: move w/ cilia – Ex: Paramecia Amoeba (pseudopod) eating Paramecia (ciliates) The paramecia start to freak out once they start to be digested! Animal-Like Protista & Disease • Malaria – Cause: Plasmodium – Vector: mosquitoes – Effects in humans: Fever, vomiting, coma, death Plasmodium injected by mosquito bite Plasmodium develop inside your liver Plasmodium reproduce inside your RBCs Plasmodium reenters mosquito when bitten Plant-like Protista • AKA: Algae • Plant-like: Photosynthetic – No roots, no leaves, usually unicellular • Classified by their type of cell wall 1) Euglenoids (Euglena): use flagella to swim – Plant-like: photosynthetic – Animal-like: swim Plant-like Protista • AKA: Algae • Plant-like: Photosynthetic – No roots, no leaves, usually unicellular • Classified by their type of cell wall 1) Euglenoids (Euglena): use flagella to swim – Plant-like: photosynthetic – Animal-like: swim Plant-like Protista • AKA: Algae • Plant-like: Photosynthetic – No roots, no leaves, usually unicellular • Classified by their type of cell wall 1) Euglenoids – Plant-like: photosynthetic – Animal-like: swim 2) Dinoflagellates – Most plankton – Basis of aquatic food chains 3) Diatoms – Glasslike shells – Provide ~ ½ Earth’s O2 Plant-like Protista • AKA: Algae • Plant-like: Photosynthetic – No roots, no leaves, usually unicellular • Classified by their type of cell wall 1) Euglenoids – Plant-like: photosynthetic – Animal-like: swim 2) Dinoflagellates – Most plankton – Basis of aquatic food chains 3) Diatoms – Glasslike shells – Provide ~ ½ Earth’s O2 Diatom Art! Fungus-like Protista • Decomposers: recycle nutrients • Mobile at stages of life cycle – Spores can develop cilia • Slime Molds: large (~1 meter) single celled mass of cytoplasm – Fungus & animal-like Fungus-like Protista • Decomposers: recycle nutrients • Mobile at stages of life cycle – Spores can develop cilia • Slime Molds: large (~1 meter) single celled mass of cytoplasm – Fungus & animal-like Fungus-like Protista • Decomposers: recycle nutrients • Mobile at stages of life cycle – Spores can develop cilia • Slime Molds: large (~1 meter) single celled mass of cytoplasm – Fungus & animal-like • Water molds: can be parasitic – Potato blight: disease Fungus-like Protista • Decomposers: recycle nutrients • Mobile at stages of life cycle – Spores can develop cilia • Slime Molds: large (~1 meter) single celled mass of cytoplasm – Fungus & animal-like • Water molds: can be parasitic – Potato blight: disease Protista: The Origins of Multicellular Life • Some protista are… • 1) Single-celled – Live by themselves • 2) Colonial – Group of independent acting cells – No specialized cells • 3) Multicellular – Cells specialized to be specific jobs • Importance: Ancestors of multicellular life This is a colony of cells Unicellular Euglena called Volvox Multicellular Kelp Kingdom Protista Plant-like Animal-like 1. Pseudopods • Move with false feet 2. Flagellates • Move with flagella 3. Ciliates • Move with cilia 1. Diatoms • Glass-like shells 2. Dinoflagellates • Plankton 3. Euglenoids • Move like animals, autotrophs like plants Fungus-like 1. Slime molds • Move like animals, absorb food like fungi 2. Water molds • Often parasites • Responsible for Irish Potato Famine Kobe Kuiz • 1) Name the three categories of protista. • 2) Which category of protista has members that are able to move? • 3) Which category of protista has members that absorb nutrients? • 4) Which category of protista has members that are heterotrophs? • 5) Which category of protista has members that hunt? • 6) How does a pseudopod, flagella, and cilia differ? • 7) Name the 3 major categories of protozoa. • 8) Name the 3 major categories of algae. • 9) Name the 2 major categories of fungus-like protista.