Powerpoint protists
advertisement

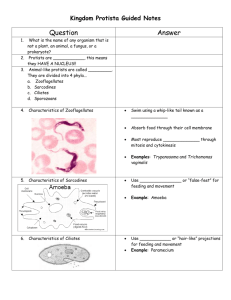
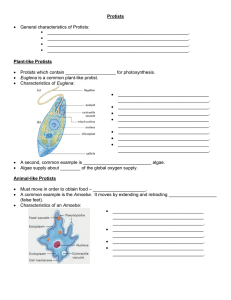
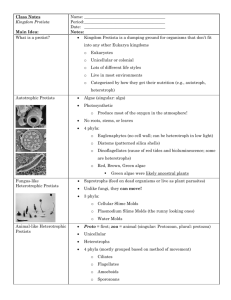
Welcome to the Exciting World of Protists… Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists SC Science Standard(s) Addressed: Standard 7-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells, cellular reproduction, and heredity. Indicator Addressed- 7-2.3 Compare the body shapes of bacteria and the body structures that protists (euglena, paramecium, amoeba) use for food gathering and locomotion. Protist Diversity 200,000 species come in different shapes, sizes, and colors All are eukaryotes – have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Protozoans Animal-like Protists Protozoans Unicellular – made up of one cell Heterotrophs – they eat other organisms or dead organic matter Classified by how they move Phyla of Protozoans Amoebas Flagellates Ciliates Sporazoans Amoebas: the blobs No cell wall Move using pseudopods – plasma extensions Engulf bits of food by flowing around and over them Flagellates: the motorboats Use a whip-like extension called a flagella to move Some cause diseases Water-borne diarrhea Giardia African Sleeping Sickness Trypanasoma (Vector: Tsetse Fly) Our Example: Euglena Ciliates: the hairy ones Tiny hairs called cilia are used for locomotion and feeding Cilia beats in a synchronized pattern to cause movement Our Example: Paramecium As an Aside… Sporazoans: the parasite Non-motile - Do not move Live inside a host One type causes malaria Plasmodium Malaria in red blood cells The End