Protists
advertisement

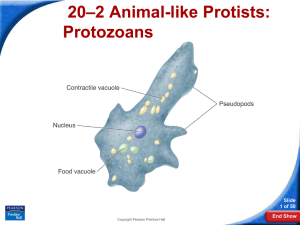
Protists Characteristics • live in water • eukaryotic • most are unicellular, some are multicellular (algae) • some are autotrophic (can make own food); some are heterotrophic (cannot make own food) Characteristics (cont.) • all can reproduce asexually (by mitosis or binary fission); some are capable of sexual reproduction (by conjugation) Characteristics (cont.) - some have cells with contractile vacuoles that help maintain homeostasis (can hold and expel fluid) Can be … 1. animal-like (protozoa) – absorb or gather/capture food * flagellates – move by flagella examples: ones that live in termite’s intestine, ones that cause African sleeping sickness More animal-like protists … • sarcodines – uses pseudopods to move and capture prey example: amoeba http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/moviegallery/pondscum/protozoa/amoeba/index.html More animal-like protists … • ciliates – move/eat by cilia, has oral groove and anal pore example: paramecium http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/movieg allery/pondscum/protozoa/parameci um/index.html Still more animal-like protists … • sporozoans – parasitic, reproduces by spores example: Plasmodium (malaria) Can be … 2. plant-like (algae) – contain chlorophyll and are photosynthetic * Euglena – can make and consume food http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/moviegallery/pondscum/pro tozoa/euglena/rostrifera/index.html More plant-like protists … • diatoms – various shapes, cell walls of silicon are used in toothpaste and scouring products More plant-like protists … * dinoflagellates – have flagella; one example causes red tide Still more plant-like protists … * multicellular algae – green, brown, red Can be … 3. fungus-like – cell walls, absorb nutrients, reproduce by spores * slime molds More fungus-like protists … * water molds – ex. Phytophthora infestans – cause of Irish potato famine (1845 – 1852)