Notes - Protists What does this mean?
advertisement

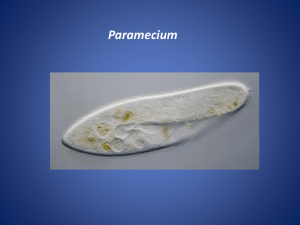
Notes - Protists We have already said that bacteria are prokaryotes or prokaryotic. What does this mean? No nucleus Protists are also __single-celled__ organisms but they are eukaryotes or eukaryotic. This means that they have a _nucleus_. Protists are neither plants nor animals, but are were classified under their own kingdom called _Protista_. (No longer exists as a kingdom) Protists are: 1. Eukaryotes 2. Most are Unicellular Protists can exist as either: 1.) Heterotrophs (these are _animal_ - like) 2.) Autotrophs (these are _plant_-like) 3.) Decomposers (these are _fungus_-like) I. Protozoans (animal-like) These: o Eukaryotic o Unicellular o Heterotrophs – Eat things for energy o Most move Protozoans are classified by _how they move_. 1. Sarcodinians – move around by extending _cytoplasm_ or a “false foot” referred to as a _pseudopod__. Example: Amoeba 2. Zooflagellates – use whip-like extensions called _flagella__ to propel themselves around. Example: __Trichonympha__ (lives in the guts of termites and helps to digest cellulose in wood). _Trypandsoma__ (lives in tsetse fly and causes African Sleeping Sickness). 3. Ciliaphorans – Also called __Ciliates__. The largest group of protozoans. Their bodies are covered by tiny hair-like projections called _cilia_. Example: Paramecium 4. Sporozoans – These do not move; they are spore-forming _parasite __ protozoans. They live by being parasites on or in animals. Can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Examples: _plasmodium__ (causes malaria) Immature sporozoans are called sporozoites and can be transmitted through fluids from one host to another. Protozoans are part of the classification of (plankton) and an integral part of the food chain. In addition to being a food source (plankton) they also feed on bacteria, yeasts, and algae. Anatomy of a Paramecium: Pellicle – the outer __layer__ or __skin__. (covering) Cilia – used for _locomotion_ and __food_ gathering. Attached to pellicle. Trichocyst – toxic _darts__ just inside of the pellicle used to capture __prey__. Oral Groove – the _mouth_; food is swept in here Food Vacuoles – when food enters the oral groove, it is surrounded and pinches to form a food vacuole. This is where _digestion__ occurs. Anal Pore – Once __nutrients__ have been extracted from the food source, the waste is ejected from here. Contractile Vacuole – Responsible for getting rid of excess __water_. They need to keep a balance of water within their system. All protozoans have contractile vacuoles. Macronucleus – Controls the ongoing __functions_ of the cell and any asexual reproduction. Micronucleus – Involved in _genetic_ exchange during sexual reproduction. During sexual reproduction, the organisms line up next to each other and exchange a pair of micronuclei through their oral grooves. Each macronucleus disintegrates and the micronuclei from each organism divides several times and forms a new __Macronucleus___. Euglena – Have a flagella, carry out photosynthesis & they can eat things for energy. Autotrophs – make their own energy Heterotrophs – eat things for energy