Animal Systems
advertisement

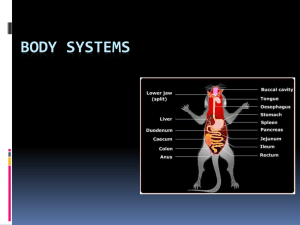
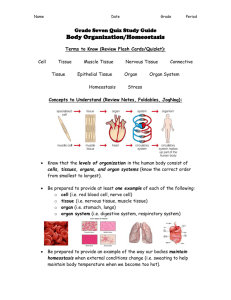
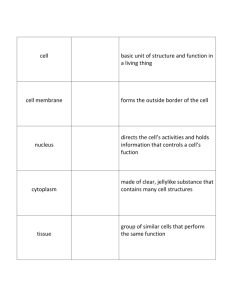
Animal Systems Organization and Homeostasis Which of these is the correct sequence of levels of organization? 1. Organs -> cells -> tissues -> organs 2. Cells -> organs -> organ systems -> tissues 3. Cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 W O R K • Of all human body systems, which do you think is most important. Discuss. Try to explain your answer. T O G E T H E R Organization in Living Things • Cells are organized into tissues • Tissues are organized into organs • Organs are organized into systems • Systems form an organism Four tissue types • Epithelial • Connective • Nervous • Muscular Epithelial tissue • Epithelial cells form the outer covering, line the internal cavities, and make up the glands. • Examples: Skin, mucous membranes. Connective tissue • Consists of living cells in a secreted matrix. • Examples: bone, cartilage, blood. Muscular tissue • Specialized protein fibers allow these cells to contract. • Examples: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle. Nervous tissue • Neurons have the ability to pass an “electrical” signal from one cell to another, or to target cells (muscles, glands, organs). Tissues form organs • The skin is an example of an organ made up of multiple tissues: epithelial, muscular, nervous, and connective tissues. A group of cells that perform a similar function is know as: 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% Tissue Organ Organ system Organism 1 2 3 4 One cell type that must undergo continual loss and replacement is: 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue 1 2 3 4 Which tissue type is in direct contact with the environment? 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 25% Epithelial Muscle Nervous Connective 1 2 3 4 Homeostasis • Homeostasis is the act of keeping the internal environment of a living organism within an acceptable range of conditions. • Homeostasis controls temperature, pH, blood volume, oxygen levels, blood sugar levels, and other conditions. • Negative feedback maintains homeostasis. Negative Feedback • Negative feedback keeps conditions within an ideal range. • As conditions exceed the limits of the ideal range, chemical signals (hormones) regulate conditions. Most often this is controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain. Positive Feedback • Positive feedback takes a condition out of the normal range, often to some end point. • During labor, oxytocin increases contractions, which stimulate more oxytocin production, until birth occurs. Maintaining Temperature • Ectotherms are animals that derive body heat from the environment. Their body temperature may vary widely. • Endotherms rely on metabolic reactions and physiological systems to maintain a steady body temperature. Maintaining Temperature Blood Glucose Regulation Body systems maintain homeostasis through: 33% 33% 33% 1. Positive feedback systems. 2. Negative feedback systems. 3. Uncontrolled feedback systems. 1 2 3 True or false: “cold blooded” animals always have a lower body temperature than “warmblooded” animals. 50% 50% 1. True 2. False 1 2 • Why is positive feedback not a good way to maintain homeostasis? • What are some other examples of positive feedback loops in the human body? • Why do young animals often have more body fat than adults? How does this maintain homeostasis? W O R K T O G E T H E R • Draw a negative feedback loop for blood calcium regulation. • Falling calcium level signals release of parathyroid hormone from the parathyroid glands. Calcium is released from bones, increased uptake by digestive system. • Rising calcium level signals release of calcitonin from the thyroid. Blood calcium is taken up into bone tissue. W O R K T O G E T H E R