Levels of Organization
advertisement

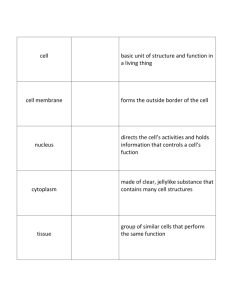
Levels of Organization ATOMS • Smallest part of matter • NON-living Molecules • 2 or more bonded atoms • Form compounds • NON-living Macromolecule • Very large molecules • Proteins, fats, carbohydrates, nucleic acids • NON-living Organelles • “Tiny organs” • Made of macromolecules Cell • Made of organelles • Basic unit of structure & function • LIVING Tissue • The same kind cell working together • Living Organs • Tissues that work together • Living Systems • Organs that work together • Living Organism • Entire living things (organisms) • Usually made of systems • May be a single cell • Living Population • Same type of organism living together Community • Several populations living together • Population interact Ecosystem • A biotic (living) community plus the abiotic (nonliving) features Biome • Similar ecosystems on earth together Biosphere • Whole living layer around the globe • Includes abiotic features http://people.hofstra.edu/geotrans/eng/ch8en/conc8en/envisys.html Atom Molecule Macromolecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ System Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biome Biosphere Body Organization and Structure HOMEOSTASIS The human body’s maintenance of a stable internal environment. My Beloved Cells I will miss you! If homeostasis is interrupted, cells suffer and sometimes die. THE WORK OF CELLS On a baseball team, every player has his job. Cells have their own positions (or jobs) in the body! RED BLOOD CELLS Groups of cells working together form a TISSUE There are 4 types of tissues: • • • • Epithelial Tissue Nervous Tissue Muscle Tissue Connective Tissue EPITHELIAL TISSUE Covers and protects underlying tissue. When you look at the surface of your skin, you see epithelial tissue NERVOUS TISSUE Sends electrical signals through the body. It is found in the brain, nerves and sense organs. MUSCLE TISSUE Made up of cells that can contract and relax to produce movement CONNECTIVE TISSUE Joins, supports, protects, insulates, nourishes, and cushions organs. It also keeps organs from falling apart. TISSUE + TISSUE= ORGAN Two or more tissues working together, form an organ. One type of tissue alone cannot do all of the things that several types working together can do. ORGAN + ORGAN = ORGAN SYSTEM Organs working together make up an organ system. The failure of any part can affect the entire system 11 MAJOR ORGAN SYSTEMS • Integumentary system • Reproductive system. • Muscular system • Nervous system • Skeletal system • Cardiovascular system • Respiratory system • Urinary system • Lymphatic system • Digestive system • Endocrine system Integumentary System Includes skin, hair, nails and their underlying tissues It’s Function is to: Protect us from germs Excrete waste Controls moisture Contains nerve ending Regulates body temp Muscular System Three types of muscles: 1. Smooth Muscle 2. Cardiac Muscle 3. Skeletal muscle Plus tendons & ligaments Function: Is movement and protection . Skeletal System Bones & cartilage Frame & support, protect, store minerals, make blood cells Cardiovascular System Heart, Veins, Arteries capillaries Function: To transport oxygen & nutrients throughout the body Respiratory System Lungs, trachea and alveoli Lungs absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Urinary System Removes wastes from the blood and regulates body fluids. Reproductive System Uterus, Ovaries Function: Offspring Testes, Penis Function: Offspring Nervous System Includes: Brain, Spinal Cord & Nerves Receives and sends electrical messages. Lymphatic System Lymph Nodes & Vessels Function: Returns leaked fluids to blood vessels and fights germs & Disease Digestive System Stomach & intestines Function: Breaks down food into nutrients . Endocrine System Glands regulate body functions by sending out chemical messages. ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANS TISSUES CELLS DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Explain the relationship between cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. 2. Compare the four kinds of tissues found in the human body. 3. Describe a time when homeostasis was disrupted in your body. Which body systems do you think were effected? T/F QUICK QUIZ 1. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment. 2. Epithelial tissue sends electrical signals throughout the body. 3. Blood is a type of connective tissue. 4. The endocrine system consists of skin, hair, nails and their underlying tissue. 5. The lymphatic system returns leaked fluids to blood vessels.