Document 9758899
advertisement

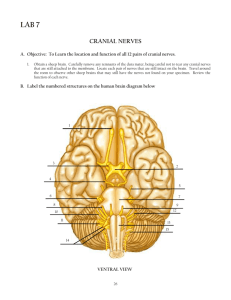
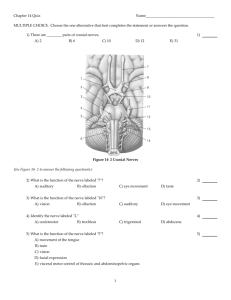
SWALLOW REFLEX LUNGS GAG REFLEX PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES OCULOMOTOR NERVE III- Pupil Constriction Pupil constriction is the automatic contraction of the pupil. It is done via the oculomotor nerve and sphincter muscle of the iris in response to stimuli such as a bright light shined onto the eye. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES OCULOMOTOR NERVE III- Pupil Accommodation Pupil accommodation is when contraction of the ciliary muscles change the eye's focal distance, making near or far images come into focus on the retina of the eye. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES FACIAL NERVE VII- Lacrimal Gland The Facial nerve innervates the Lacrimal gland into producing a moistening fluid for the surface of the eyes. This serves a double function as lubricant and protection, as tears contain lysosomes that are capable of destroying foreign bodies and bacteria. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES FACIAL NERVE VII- Corneal Reflex When the cornea is touched by a foreign object, the eye lids close. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES FACIAL NERVE VII- Olfactory Bowman's Glands Bowman's glands, otherwise known as the olfactory gland is positioned in the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. It produces mucus that moistens and lubricates the olfactory epithelium. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES FACIAL NERVE VII- Submandibular and Sublingual Glands The Submandibular and Sublingual glands control the release of saliva into the mouth. The former is responsible for producing up to 65 percent of saliva, while the latter is responsible for producing only up to 5 percent. The Facial nerve innervates both glands. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE IX- Parotid Gland The pair of Parotid glands in the human face are innervated by the Glossopharyngeal nerve, and are responsible for producing the saliva that ends up in the mouth aiding in mastication and food digestion. Swallow reflex initiates by Glossopharyngeal nerve to close the larynx when food touch the entrance of the pharynx. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES VAGUS NERVE X- Overview The Vagus nerve travels from the brain stem down to the abdomen. It is responsible for a variety of important involuntary body functions ranging from maintenance of the heart rate to food digestion. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES VAGUS NERVE X- The Heart The Vagus nerve acts to lower the heart rate through the sinoatrial or SA node. By parasympathetic innervation, the Vagus nerve causes acetylcholine to be released. PARASYMPATHETIC CRANIAL NERVES VAGUS NERVE X- From the lung to the digestive system The Vagus nerve innervates the smooth muscle of the lung, responsible for bronchoconstriction and secretion of mucus. Vagus nerve innervates the digestive system, responsible for gag reflex, increased peristalsis, glycogen synthesis in the liver. The Vagus nerve also innervates the kidneys, and thus urination. References Lundy-Ekman, L. (2007). Neuroscience: Fundamentals of Rehabilitation. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. http://www.medilifenet.com/photo/hn016 http://dc349.4shared.com/doc/wvzlE70U/preview_html_7c75c294.gif https://classconnechtion.s3.amazonaws.com/857/flashcards/527857/jpg/accomodation1305250857880.jpg http://www.daviddarling.info/images/lacrimal_gland.gif http://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesenseofsmell-110929125027-phpapp01/95/the-sense-of-smell-4?cb=1728.jpg317319214 http://img.tfd.com/MosbyMD/parotid_duct.jpg http://antranik.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/vagus-nerve-x.jpg?9f6b44 http://antranik.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/external-innervation-heart-vagus-nerve-visceral-sensory-fibersinterneurons-cardioacceleratory-center-cardioinhibitory-center.jpg http://img.tfd.com/MosbyMD/vagus_nerve.jpg http://entallergyandsinus.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/salivary_glands.jpg http://www.aliem.com/trick-of-the-trade-corneal-reflex-test/ Cranial Nerve Song King, Pamela. DJLK Production. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0lbwshg_Kj4