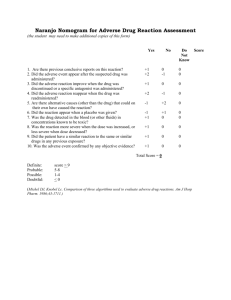
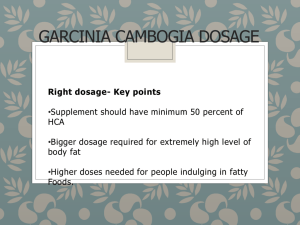
fda approved drugs 2014
advertisement

FDA APPROVED DRUGS YEAR 2014 AKYNZEO MECHANISM OF ACTION Netupitant is a selective antagonist of human substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors Palonosetron is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist with a strong binding affinity for this receptor and little or no affinity for other receptors 5-HT3 receptors are located on the nerve terminals of the vagus in the periphery and centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the area postrema. Chemotherapeutic agents produce nausea and vomiting by stimulating the release of serotonin from the enterochromaffin cells of the small intestine. Serotonin then activates 5-HT3 receptors located on vagal afferents to initiate the vomiting reflex. The development of acute emesis is known to depend on serotonin and its 5-HT3 receptors have been demonstrated to selectively stimulate the emetic response. STRUCTURE Netupitant exists as a single isomer and has the following structural formula: Netupitant is chemically described: 2-[3,5bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N, 2 dimethyl-N-[4-(2-methylphenyl)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1yl)pyridin-3-yl] propanamide. The empirical formula is C30H32F6N4O, with a molecular weight of 578.61. Netupitant exists as a single isomer and has the following structural formula: Palonosetron hydrochloride is chemically described: (3aS)-2-[(S)-1-Azabicyclo [2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3,3a,4,5,6-hexahydro-1-oxo-1Hbenz[de]isoquinoline hydrochloride. The empirical formula is C19H24N2O.HCl, with a molecular weight of 332.87. Palonosetron hydrochloride exists as a single isomer and has the following structural formula. INDICATIONS AND USAGE AKYNZEO is a fixed combination of netupitant, a substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, and palonosetron, a serotonin-3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist indicated for the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of cancer chemotherapy, including, but not limited to, highly emetogenic chemotherapy. Oral palonosetron prevents nausea and vomiting during the acute phase and netupitant prevents nausea and vomiting during both the acute and delayed phase after cancer chemotherapy. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION One AKYNZEO capsule administered approximately 1 hour prior to the start of chemotherapy. AKYNZEO can be taken with or without food. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Capsule: 300 mg netupitant/0.5 mg palonosetron CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in patients receiving palonosetron with or without known hypersensitivity to other 5-HT3 receptor antagonists . Serotonin syndrome has been reported with 5-HT3 receptor antagonists alone but particularly with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common adverse reactions (incidence ~3% and greater than palonosetron) are headache, asthenia, dyspepsia, fatigue, constipation and erythema. DRUG INTERACTIONS • CYP3A4 Substrates: inhibition of CYP3A4 by netupitant can result in increased plasma concentrations of the concomitant drug that can last at least 4 days and may last longer after single dosage administration of AKYNZEO; use with caution. • CYP3A4 Inducers (e.g., rifampin): decreased plasma concentrations of netupitant; avoid use. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment • Renal Impairment: Avoid use in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease BELEODAQ (belinostat) Beleodaq is indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). Beleodaq is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor. HDACs catalyze the removal of acetyl groups from the lysine residues of histones and some non-histone proteins. In vitro, belinostat caused the accumulation of acetylated histones and other proteins, inducing cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis of some transformed cells. Belinostat shows preferential cytotoxicity towards tumor cells compared to normal cells. INDICATIONS AND USAGE Beleodaq is a histone deacetylase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and duration of response. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2 Recommended dosage of Beleodaq is 1,000 mg/m administered over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion once daily on days 1-5 of a 21-day cycle. Cycles can be repeated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Treatment discontinuation or interruption with or without dosage reductions by 25% may be needed to manage adverse reactions. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS For injection: 500 mg, lyophilized powder in single-use vial for reconstitution CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia (neutropenia and lymphopenia), and anemia: Monitor blood counts and modify dosage for hematologic toxicities. Infection: Serious and fatal infections (e.g., pneumonia and sepsis) Hepatotoxicity: Beleodaq may cause hepatic toxicity and liver function test abnormalities. Monitor liver function tests and omit or modify dosage for hepatic toxicities. Tumor lysis syndrome: Monitor patients with advanced stage disease and/or high tumor burden and take appropriate precautions Embryo-fetal toxicity: Beleodaq may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise women of potential harm to the fetus and to avoid pregnancy while receiving Beleodaq ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (>25%) are nausea, fatigue, pyrexia, anemia, and vomiting. BELSOMRA (suvorexant) BELSOMRA is an orexin receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of insomnia, characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or sleep maintenance . MECHANISM OF ACTION The mechanism by which suvorexant exerts its therapeutic effect in insomnia is presumed to be throughantagonism of orexin receptors. The orexin neuropeptide signaling system is a central promoter of wakefulness. Blocking the binding of wake-promoting neuropeptides orexin A and orexin B to receptors OX1R and OX2R is thought to suppress wake drive. Antagonism of orexin receptors may also underlie potential adverse effects such as signs of narcolepsy/cataplexy. Genetic mutations in the orexin system in animals result in hereditary narcolepsy; loss of orexin neurons has been reported in humans with narcolepsy. BELSOMRA tablets contain suvorexant, a highly selective antagonist for orexin receptors OX1R and OX2R. INDICATIONS AND USAGE BELSOMRA is an orexin receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of insomnia, characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or sleep maintenance. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Use the lowest dose effective for the patient. Recommended dose is 10 mg, no more than once per night taken. Within 30 minutes of going to bed, with at least 7 hours remaining. Before the planned time of awakening. If the 10 mg dose is well tolerated but not effective, the dose can be increased, not to exceed 20 mg once daily Time to effect may be delayed if taken with or soon after a meal DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets, 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg CONTRAINDICATIONS Do not use in patients with narcolepsy WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Daytime somnolence: Risk of impaired alertness and motor coordination, including impaired driving; risk increases with dose; caution patients taking 20 mg against next-day driving and other activities requiring complete mental alertness. Need to evaluate for co-morbid diagnoses: Reevaluate if insomnia persists after 7 to 10 days of treatment. Nighttime “sleep-driving” and other complex behaviors while out of bed and not fully awake. Risk increases with dose, with use of CNS depressants, and with alcohol. Depression: Worsening of depression or suicidal thinking may occur. Risk increases with dose. Immediately evaluate any new behavioral changes Compromised respiratory function: Effect on respiratory function should be considered Sleep paralysis, hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations, and cataplexy-like symptoms: Risk increases with dose. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reaction (reported in 5% or more of patients treated with BELSOMRA and at least twice the placebo rate) with BELSOMRA was somnolence. DRUG INTERACTIONS CYP3A inhibitors: Recommended dose is 5 mg when used with moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Dose can be increased to 10 mg once daily if the 5 mg dose is not effective. Not recommended for use in patients taking strong CYP3A inhibitors. Strong CYP3A inducers: Efficacy may be reduce. Digoxin: Monitor digoxin concentrations. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm Patients with severe hepatic impairment: Not recommended BLINCYTO MECHANISM OF ACTION Blinatumomab is a bispecific CD19-directed CD3 T-cell engager that binds to CD19 expressed on the surface of cells of B-lineage origin and CD3 expressed on the surface of T cells. It activates endogenous T cells by connecting CD3 in the T-cell receptor (TCR) complex with CD19 on benign and malignant B cells. Blinatumomab mediates the formation of a synapse between the T cell and the tumor cell, upregulation of cell adhesion molecules, production of cytolytic proteins, release of inflammatory cytokines, and proliferation of T cells, which result in redirected lysis of CD19+ cells. INDICATIONS AND USAGE BLINCYTO is a bispecific CD19-directed CD3 T-cell engager indicated for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-negative relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Dosage -Hospitalization is recommended for the first 9 days of the first cycle and the first 2 days of the second cycle. (2) A single cycle of treatment consists of 4 weeks of continuous intravenous infusion followed by a 2-week treatment-free interval. For patients at least 45 kg in weight, in Cycle 1, administer BLINCYTO at 9 mcg/day on Days 1–7 and at 28 mcg/day on Days 8–28. For subsequent cycles, administer BLINCYTO at 28 mcg/day on Days 1–28. (2.1) Administration Premedicate with dexamethasone 20 mg intravenously 1 hour prior to the first dose of BLINCYTO of each cycle, prior to a step dose (such as Cycle 1 day 8), or when restarting an infusion after an interruption of 4 or more hours. Administer as a continuous intravenous infusion at a constant flow rate using an infusion pump. The IV bag should be infused over 24 hours or 48 hours. BLINCYTO should be infused through a dedicated lumen. Preparation -IV Solution Stabilizer is provided and is used to coat the prefilled IV bag prior to addition of reconstituted BLINCYTO. Reconstitute BLINCYTO with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, only. Aseptic technique must be strictly observed when preparing the solution for infusion since BLINCYTO does not contain antimicrobial preservatives. Use the specific volumes described in the admixing instructions. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • For injection: 35 mcg of lyophilized powder in a single-use vial for reconstitution. CONTRAINDICATIONS • Known hypersensitivity to blinatumomab or to any component of the product formulation. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Infections: Monitor patients for signs or symptoms and treat appropriately. • Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines: Advise patients to refrain from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities such as operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery while BLINCYTO is being administered. • Preparation and Administration Errors: Strictly follow instructions for preparation (including admixing) and administration. ADVERSE REACTIONS • The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were pyrexia, headache, peripheral edema, febrile neutropenia, nausea, hypokalemia, tremor, rash, and constipation. WARNING CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME and NEUROLOGICAL TOXICITIES • Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), which may be life-threatening or fatal, occurred in patients receiving BLINCYTO. Interrupt or discontinue BLINCYTO as recommended. • Neurological toxicities, which may be severe, life-threatening, or fatal, occurred in patients receiving BLINCYTO. Interrupt or discontinue BLINCYTO as recommended. CERDELGA CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1). MECHANISM OF ACTION Gaucher disease is caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme acid β-glucosidase. Acid β-glucosidase catalyzes the conversion of the sphingolipid glucocerebroside intoglucose and ceramide. The enzymatic deficiency causes an accumulation of glucosylceramide (GL-1) primarily in the lysosomal compartment of macrophages, giving rise to foam cells or "Gaucher cells". CERDELGA is a specific inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase (IC50 = 10 ng/mL), and acts as a substrate reduction therapyfor GD1. In clinical trials CERDELGA reduced spleen and liver size, and improvedanemia and thrombocytopenia. In this lysosomal storage disorder (LSD), clinical features are reflective of the accumulation of Gaucher cells in the liver, spleen, bone marrow, and other organs. The accumulation of Gaucher cells in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow leads to organomegaly and skeletal disease. Presence of Gaucher cells in the bone marrow and spleen lead to clinically significant anemia and thrombocytopenia. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Select patients using an FDA-cleared test for determining CYP2D6genotype. • CYP2D6 EMs or IMs: 84 mg orally twice daily. • CYP2D6 PMs: 84 mg orally once daily. • Swallow capsules whole, do not crush, dissolve or open capsules. • Avoid eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice. • 84 mg capsules DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS • CYP2D6 EMs and IMs taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor. • CYP2D6 IMs and PMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • ECG Changes and Potential for Cardiac Arrhythmias: Not recommended in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, and concomitant use of Class IA and Class III antiarrhythmics ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) are: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain. DRUG INTERACTIONS • Eliglustat is a CYP2D6 and CYP3A substrate. Co-administration of CERDELGA with drugs that inhibit CYP2D6 and CYP3A may significantly increase the exposure to eliglustat and result in prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval, which could result in cardiac arrhythmias. Consider potential drug interactions prior to and during therapy. • CYP2D6 IMs and PMs taking moderate CYP3A inhibitors: not recommended • CYP2D6 PMs taking weak CYP3A inhibitors: not recommended • CYP2D6 EMs and IMs taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors and CYP2D6 EMs taking strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors: reduce the dosage to 84 mg once daily. • Eliglustat is an inhibitor of P-gp and CYP2D6. Co-administration with drugs that are substrates for P-gp or CYP2D6 may result in increased concentrations of the other drug. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Pregnancy: Only administer if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. • Nursing mothers: Discontinue drug or nursing based on importance of drug to mother. • Renal impairment: Not recommended in moderate to severe impairment. • Hepatic impairment: Not recommended. CYRAMZA (ramucirumab) CYRAMZATM is a human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) antagonist indicated for the treatment of Gastric Cancer. MECHANISM OF ACTION Ramucirumab is a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) antagonist that specifically binds VEGF Receptor 2 and blocks binding of VEGFR ligands, VEGF-A, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D. As a result, ramucirumab inhibits ligand-stimulated activation of VEGF Receptor 2, thereby inhibiting ligand-induced proliferation, and migration of human endothelial cells. Ramucirumab inhibited angiogenesis in an in vivo animal model. INDICATIONS AND USAGE CYRAMZATM is a human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) antagonist indicated for the treatment of: Gastric Cancer. • Advanced gastric cancer or gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinoma, as a single-agent after prior fluoropyrimidine- or platinum-containing chemotherapy. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Administer 8 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks. • For intravenous infusion only. Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg per mL) solution, single-dose vial • 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg per mL) solution, single-dose vial CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Arterial Thromboembolic Events (ATEs): Serious, sometimes fatal ATEs have been reported in clinical trials. Discontinue CYRAMZA for severe ATEs. • Hypertension: Monitor blood pressure and treat hypertension. Temporarily suspend CYRAMZA for severe hypertension. Discontinue CYRAMZA for hypertension that cannot be medically controlled. • Infusion Related Reactions: Monitor for signs and symptoms during infusion. • Gastrointestinal perforation: Discontinue CYRAMZA. • Impaired Wound Healing: Withhold CYRAMZA prior to surgery. • Clinical Deterioration in Patients with Cirrhosis: New onset or worsening encephalopathy, ascites, or hepatorenal syndrome can occur in patients with Child-Pugh B or C cirrhosis. • Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome: Discontinue CYRAMZA. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions observed in CYRAMZA-treated patients at a rate of ≥10% and ≥2% higher than placebo were hypertension and diarrhea. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Pregnancy: Based on its mechanism of action, CYRAMZA may cause fetal harm. • Nursing Mothers: Discontinue nursing or discontinue CYRAMZA. WARNING: HEMORRHAGE CYRAMZA increased the risk of hemorrhage, including severe and sometimes fatal hemorrhagic events. Permanently discontinue CYRAMZA in patients who experience severe bleeding. DALVANCE (dalbavancin) MECHANISM OF ACTION Dalbavancin, a semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide, interferes with cell wall synthesis by binding to the D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of the stem pentapeptide in nascent cell wall peptidoglycan, thus preventing cross-linking. Dalbavancin is bactericidal in vitro against Staphylococcus aureusand Streptococcus pyogenes at concentrations similar to those sustained throughout treatment in humans treated according to the recommended dosage regimen. INDICATIONS AND USAGE DALVANCE is indicated for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by designated susceptible strains of Gram-positive microorganisms. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of DALVANCE and other antibacterial drugs, DALVANCE should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Two-dose regimen: 1000 mg followed one week later by 500 mg. Dosage adjustment for patients with creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min and not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis. 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg. Administer by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS For injection: 500 mg of lyophilized powder in a single-use vial for reconstitution. Hypersensitivity to dalbavancin CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) and skin reactions have been reported with glycopeptide antibacterial agents, including DALVANCE; exercise caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to glycopeptides. Rapid intravenous infusion of glycopeptide antibacterial agents can cause reactions. ALT elevations with DALVANCE treatment were reported in clinical trials Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including DALVANCE. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with DALVANCE were nausea (5.5%), headache (4.7%), and diarrhea (4.4%). USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Dosage adjustment is required in patients whose creatinine clearance is less than 30 mL/min and who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis. ENTYVIO (vedolizumab) MECHANISM OF ACTION Vedolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the α4β7 integrin and blocks the interaction of α4β7 integrin with mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) and inhibits the migration of memory T-lymphocytes across the endothelium into inflamed gastrointestinal parenchymal tissue. Vedolizumab does not bind to or inhibit function of the α4β1 and αEβ7 integrins and does not antagonize the interaction of α4 integrins with vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). The α4β7 integrin is expressed on the surface of a discrete subset of memory Tlymphocytes that preferentially migrate into the gastrointestinal tract. MAdCAM-1 is mainly expressed on gut endothelial cells and plays a critical role in the homing of Tlymphocytes to gut lymph tissue. The interaction of the α4β7 integrin with MAdCAM-1 has been implicated as an important contributor to the chronic inflammation that is a hallmark of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. INDICATIONS AND USAGE ENTYVIO is an integrin receptor antagonist indicated for: Adult Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Adult patients with moderately to severely active UC who have had an inadequate response with, lost response to, or were intolerant to a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker or immunomodulator; or had an inadequate response with, were intolerant to, or demonstrated dependence on corticosteroids: inducing and maintaining clinical response inducing and maintaining clinical remission improving endoscopic appearance of the mucosa achieving corticosteroid-free remission Adult Crohn's Disease (CD) • Adult patients with moderately to severely active CD who have had an inadequate response with, lost response to, or were intolerant to a TNF blocker or immunomodulator; or had an inadequate response with, were intolerant to, or demonstrated dependence on corticosteroids: • achieving clinical response • achieving clinical remission • achieving corticosteroid-free remission DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Recommended dosage in UC and CD: 300 mg infused intravenously over approximately 30 minutes at zero, two and six weeks, then every eight weeks thereafter. (2.3) Discontinue ENTYVIO in patients who do not show evidence of therapeutic benefit by Week 14. Must reconstitute ENTYVIO lyophilized powder with Sterile Water for injection and must dilute in 250 mL of sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride injection prior to administration Administer infusion solution within four hours of reconstitution and dilution. Bring patients up to date with all immunizations (according to current immunization guidelines) before initiating treatment with ENTYVIO. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS For injection: 300 mg of lyophilized vedolizumab in a single-use 20 mL vial. CONTRAINDICATIONS Patients who have had a known serious or severe hypersensitivity reaction to ENTYVIO or any of its excipients. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Hypersensitivity Reactions (including anaphylaxis): Discontinue ENTYVIO if anaphylaxis or other serious allergic reactions occur. Infections: Treatment with ENTYVIO is not recommended in patients with active, severe infections until the infections are controlled. Consider withholding ENTYVIO in patients who develop a severe infection while on treatment with ENTYVIO. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy: Although no cases have been observed in ENTYVIO clinical trials, JCV infection resulting in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) and death has occurred in patients treated with another integrin receptor antagonist. A risk of PML cannot be ruled out. Monitor patients for any new or worsening neurological signs or symptoms. ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥3% and ≥1% higher than placebo): nasopharyngitis, headache, arthralgia, nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, bronchitis, influenza, back pain, rash, pruritus, sinusitis, oropharyngeal pain, and pain in extremities. HARVONI (ledipasvir and sofosbuvir) MECHANISM OF ACTION Ledipasvir is an inhibitor of the HCV NS5A protein, which is required for viral replication. Resistance selection in cell culture and cross-resistance studies indicate ledipasvir targets NS5A as its mode of action. Sofosbuvir is an inhibitor of the HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which is required for viral replication. Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide prodrug that undergoes intracellular metabolism to form the pharmacologically active uridine analog triphosphate (GS-461203), which can be incorporated into HCV RNA by the NS5B polymerase and acts as a chain terminator. In a biochemical assay, GS-461203 inhibited the polymerase activity of the recombinant NS5B from HCV genotypes 1b, 2a, 3a and 4a with IC50 values ranging from 0.7 to 2.6 µM. GS-461203 is neither an inhibitor of human DNA and RNA polymerases nor an inhibitor of mitochondrial RNA polymerase. INDICATIONS AND USAGE HARVONI is a fixed-dose combination of ledipasvir, a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitor, and sofosbuvir, an HCV nucleotide analog NS5B polymerase inhibitor, and is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) genotype 1 infection in adults. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Recommended dosage: One tablet (90 mg of ledipasvir and 400 mg of sofosbuvir) taken orally once daily with or without food Recommended treatment duration Treatment-naïve with or without cirrhosis: 12 weeks Treatment-experienced without cirrhosis: 12 weeks Treatment-experienced with cirrhosis: 24 weeks A dose recommendation cannot be made for patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets: 90 mg ledipasvir and 400 mg sofosbuvir None CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Bradycardia with amiodarone coadministration: Serious symptomatic bradycardia may occur in patients taking amiodarone, particularly in patients also receiving beta blockers, or those with underlying cardiac comorbidities and/or advanced liver disease. Coadministration of amiodarone with HARVONI is not recommended. In patients without alternative, viable treatment options, cardiac monitoring is recommended. Use with other drugs containing sofosbuvir, including SOVALDI, is not recommended . ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, all grades) observed with treatment with HARVONI for 8, 12, or 24 weeks are fatigue and headache DRUG INTERACTIONS Coadministration with amiodarone may result in serious symptomatic bradycardia. Use of HARVONI with amiodarone is not recommended. P-gp inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John’s wort): May alter concentrations of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir. Use of HARVONI with P-gp inducers is not recommended. HETLIOZ (tasimelteon) MECHANISM OF ACTION The precise mechanism by which tasimelteon exerts its therapeutic effect in patients with Non-24 is not known. Tasimelteon is an agonist at melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. These receptors are thought to be involved in the control of circadian rhythms. INDICATIONS AND USAGE HETLIOZ is a melatonin receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of Non-24-Hour SleepWake Disorder (Non-24) • • DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 20 mg prior to bedtime, at same time every night Take without food Capsules: 20 mg (3) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS May cause somnolence: After taking HETLIOZ, patients should limit their activity to preparing for going to bed, because HETLIOZ can impair the performance of activities requiring complete mental alertness ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (incidence >5% and at least twice as high on HETLIOZ than on placebo) were headache, increased alanine aminotransferase, nightmares or unusual dreams, and upper respiratory or urinary tract infection. DRUG INTERACTIONS Strong CYP1A2 inhibitors (e.g., fluvoxamine): Avoid use of HETLIOZ in combination with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors because of increased exposure (7.1, 12.3) Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin): Avoid use of HETLIOZ in combination with rifampin or other CYP3A4 inducers, because of decreased exposure USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. • Hepatic impairment: HETLIOZ has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment and is not recommended in these patients ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ IMPAVIDO (miltefosine) MECHANISM OF ACTION The specific mode of action of miltefosine against Leishmania species is unknown. The mechanism of action of miltefosine is likely to involve interaction with lipids (phospholipids and sterols), including membrane lipids, inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase (mitochondrial function), and apoptosis-like cell death. INDICATIONS AND USAGE IMPAVIDO is an antileishmanial drug indicated in adults and adolescents≥12 years of age weighing ≥30 kg (66 lbs) for treatment of: • Visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani (1). • Cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis, Leishmania guyanensis, and Leishmania panamensis (1). • Mucosal leishmaniasis due to Leishmania braziliensis (1). Limitations of use: Leishmania species evaluated in clinical trials were based on epidemiologic data. There may be geographic variation in the response of the same Leishmania species to IMPAVIDO (1, 14). The efficacy of IMPAVIDO in the treatment of other Leishmania species has not been evaluated. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer with food to ameliorate gastrointestinal adverse reactions. • 30 to 44 kg: one 50 mg capsule twice daily for 28 consecutive days (2). • 45 kg or greater: one 50 mg capsule three times daily for 28 consecutive Days. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Each IMPAVIDO capsule for oral use contains 50 mg miltefosine CONTRAINDICATIONS • Pregnancy • Sjögren-Larsson-Syndrome • Hypersensitivity to miltefosine or any of its excipients WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Embryo-Fetal Toxicity. Do not use in pregnant women. Obtain a urine or serum pregnancy test prior to initiation of therapy. Advise use of effective contraception in females of reproductive potential (BoxedWarning). • Reproductive effects. Miltefosine caused testicular atrophy and impaired fertility in male rats and impaired fertility in female rats. Advise patients of reproductive toxicities in animal studies and that the potential effects on human fertility have not been adequately evaluated. • Renal Effects. Monitor serum creatinine during therapy and for 4 weeks after end of therapy. • Hepatic Effects. Monitor transaminases and bilirubin during therapy. • Gastrointestinal Effects. Encourage fluid intake. • Thrombocytopenia. Monitor platelet count during therapy for visceral leishmaniasis. • Absorption of Oral Contraceptives. Advise use of alternative method of contraception if vomiting and/or diarrhea occur. • Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Discontinue IMPAVIDO. ADVERSE REACTIONS Adverse reactions occurring in ≥2% of patients include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, decreased appetite, dizziness, abdominal pain, pruritus, somnolence, elevated transaminases, and elevated creatinine. DRUG INTERACTIONS • IMPAVIDO did not inhibit human cytochrome P450 enzymes in vitro. • IMPAVIDO did not induce cytochrome 3A activity in rats. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Pregnancy: IMPAVIDO should not be used during pregnancy. Obtain a urine or serum pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to prescribing. • Nursing Mothers: Discontinue drug or nursing depending on importance of drug to mother. Avoid breastfeeding for 5 months after IMPAVIDO therapy. • Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise females to use effective contraception during therapy and for 5 months after therapy. Advise patients of reproductive toxicities in animals, and that the potential for impaired fertility in humans has not been adequately evaluated. JARDIANCE (empagliflozin) MECHANISM OF ACTION Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) is the predominant transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. Empagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2. By inhibiting SGLT2, empagliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion. INDICATIONS AND USAGE JARDIANCE is a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Limitation of Use: Not for the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus or diabetic ketoacidosis. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The recommended dose of JARDIANCE is 10 mg once daily, taken in the morning, with or without food. Dose may be increased to 25 mg once daily. Assess renal function before initiating JARDIANCE. Do not initiate JARDIANCE if eGFR is below 45mL/min/1.73 m2. Discontinue JARDIANCE if eGFR falls persistently below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHs Tablets: 10 mg, 25 mg • • • • • • CONTRAINDICATIONS History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to JARDIANCE. Severe renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, or dialysis. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Hypotension: Before initiating JARDIANCE assess and correct volume status in patients with renal impairment, the elderly, in patients with low systolic blood pressure, and in patients on diuretics. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy. Impairment in renal function: Monitor renal function during therapy. More frequent monitoring is recommended in patients with eGFR below 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (5.2) Hypoglycemia: Consider lowering the dose of insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when initiating JARDIANCE Genital mycotic infections: Monitor and treat as appropriate Urinary tract infections: Monitor and treat as appropriate Increased LDL-C: Monitor and treat as appropriate Macrovascular outcomes: There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with JARDIANCE. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions associated with JARDIANCE (5% or greater incidence) were urinary tract infections and female genital mycotic infections. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: No adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Use during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Nursing mothers: Discontinue JARDIANCE or discontinue nursing. Geriatric patients: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to volume depletion and reduced renal function . Patients with renal impairment: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced renal function. JUBLIA(efinaconazole) MECHANISM OF ACTION Efinaconazole is an azole antifungal. Efinaconazole inhibits fungal lanosterol 14αdemethylase involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a constituent of fungal cell membranes. INDICATIONS AND USAGE JUBLIA is an azole antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenails due to Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. • • • • DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Apply JUBLIA to affected toenails once daily for 48 weeks using the integrated flowthrough brush applicator. When applying JUBLIA, ensure the toenail, the toenail folds, toenail bed, hyponychium, and the undersurface of the toenail plate, are completely covered. For topical use only. Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. CONTRAINDICATIONS None ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (incidence >1%) were ingrown toenails, application site dermatitis, application site vesicles, and application site pain. KERYDIN (tavaborole) MECHANISM OF ACTION The mechanism of action of tavaborole is inhibition of fungal protein synthesis. Tavaborole inhibits protein synthesis by inhibition of an aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) synthetase (AARS). INDICATIONS AND USAGE KERYDIN is an oxaborole antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenails due to Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton mentagrophytes. • • • • DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Apply KERYDIN to affected toenails once daily for 48 weeks. KERYDIN should be applied to the entire toenail surface and under the tip of each toenail being treated. For topical use only. Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. Solution, 5%. None. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE REACTIONS Common adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% in subjects treated with KERYDIN included application site exfoliation, ingrown toenail, application site erythema, and application site dermatitis. KEYTRUDA(pembrolizumab) • • • • • • • MECHANISM OF ACTION Binding of the PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, to the PD-1 receptor found on T cells, inhibits T cellproliferation and cytokine production. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors and signalingthrough this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumors. Pembrolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, releasing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response, including the anti-tumor immune response. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD-1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth. INDICATIONS AND USAGE KEYTRUDA is a human programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)-blocking antibody indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab and, if BRAF V600 mutation positive, a BRAF inhibitor. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response. An improvement in survival or disease-related symptoms has not yet been established. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer 2 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks. Dilute prior to intravenous infusion. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • • • For injection: 50 mg lyophilized powder in single-use vial for reconstitution (3) Injection: 100 mg/4 mL (25 mg/mL) solution in a single-use vial. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Immune-mediated adverse reactions: Administer corticosteroids based on the severity of the reaction. Immune-mediated pneumonitis: Withhold for moderate, and permanently discontinue for severe or life-threatening pneumonitis. Immune-mediated colitis: Withhold for moderate or severe, and permanently discontinue for life-threatening colitis. Immune-mediated hepatitis: Monitor for changes in hepatic function. Based on severity of liver enzyme elevations, withhold or discontinue. Immune-mediated hypophysitis: Withhold for moderate, withhold or discontinue for severe, and permanently discontinue for life-threatening hypophysitis. Immune-mediated nephritis: Monitor for changes in renal function. Withhold for moderate, and permanently discontinue for severe or life-threatening nephritis. Immune-mediated hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism: Monitor for changes in thyroid function. Withhold for severe and permanently discontinue for life-threatening hyperthyroidism. Embryofetal Toxicity: KEYTRUDA may cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥20% of patients) included fatigue, cough, nausea, pruritus, rash, decreased appetite, constipation, arthralgia, and diarrhea. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Nursing mothers: Discontinue nursing or discontinue KEYTRUDA. LYNPARZA (olaparib) MECHANISM OF ACTION Lynparza is an inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) enzymes, including PARP1, PARP2, and PARP3. PARP enzymes are involved in normal cellular homeostasis, such as DNA transcription, cell cycle regulation, and DNA repair. Olaparib has been shown to inhibit growth of select tumor cell lines in vitro and decrease tumor growth in mouse xenograft models of human cancer both as monotherapy or following platinum-based chemotherapy. Increased cytotoxicity and anti-tumor activity following treatment with olaparib were noted in cell lines and mouse tumor models with deficiencies in BRCA. In vitro studies have shown that olaparib-induced cytotoxicity may involve inhibition of PARP enzymatic activity and increased formation of PARP-DNA complex, resulting in disruption of cellular homeostasis and cell death. Olaparib is an inhibitor of the mammalian polyadenosine 5’-diphosphoribose polymerase (PARP) enzyme. INDICATIONS AND USAGE • • • • Lynparza is a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor indicated as monotherapy in patients with deleterious or suspected deleterious germline BRCA mutated (as detected by an FDA-approved test) advanced ovarian cancer who have been treated with three or more prior lines of chemotherapy. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Recommended dose is 400 mg taken twice daily. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. For adverse reactions, consider dose interruption of treatment or dose reduction. • Capsules: 50 mg DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Myelodysplastic syndrome/Acute Myeloid Leukemia: (MDS/AML) occurred in patients exposed to Lynparza, and some cases were fatal. Monitor patients for hematological toxicity at baseline and monthly thereafter. Discontinue if MDS/AML is confirmed. • Pneumonitis: occurred in patients exposed to Lynparza, and some cases were fatal. Interrupt treatment if pneumonitis is suspected. Discontinue if pneumonitis is confirmed. • Embryo-Fetal toxicity: Lynparza can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to avoid pregnancy. ADVERSE REACTIONS • Most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in clinical trials were anemia, nausea, fatigue (including asthenia), vomiting, diarrhea, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, headache, decreased appetite, nasopharyngitis/pharyngitis/URI, cough, arthralgia/musculoskeletalPain, myalgia, back pain, dermatitis/rash and abdominal pain/discomfort. • Most common laboratory abnormalities (≥25%) were increase in creatinine, mean corpuscular volume elevation, decrease in hemoglobin, decrease in lymphocytes, decrease in absolute neutrophil count, and decrease in platelets. DRUG INTERACTIONS • CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If the inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the dose. • CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inducers. If a moderate CYP3A inducer cannot be avoided, be aware of a potential for decreased efficacy. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS •Nursing Mothers: Discontinue treatment or discontinue nursing. MYALEPT Mechanism of Action Adipocytes store lipids to meet the fuel requirements of non-adipose tissues during fasting. In patients with generalized lipodystrophy, the deficiency of adipose tissue leads to hypertriglyceridemia and ectopic deposition of fat in non-adipose tissues such as liver and muscle, contributing to metabolic abnormalities including insulin resistance. Native leptin is a hormone predominantly secreted by adipose tissue that informs the central nervous system of the status of energy stores in the body. In patients with generalized lipodystrophy, leptin deficiency, resulting from the loss of adipose tissue, contributes to excess caloric intake, which exacerbates the metabolic abnormalities. MYALEPT (metreleptin for injection) exerts its function by binding to and activating the human leptin receptor (ObR), which belongs to the Class I cytokine family of receptors that signals through the JAK/STAT transduction pathway. INDICATIONS AND USAGE MYALEPT is a leptin analog indicated as an adjunct to diet as replacement therapy to treat the complications of leptin deficiency in patients with congenital or acquired generalized lipodystrophy. LIMITATIONS OF USE • The safety and effectiveness of MYALEPT for the treatment of complications of partial lipodystrophy have not been established. (1) • The safety and effectiveness of MYALEPT for the treatment of liver disease, including nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), have not been established. (1) • MYALEPT is not indicated for use in patients with HIV-related lipodystrophy. (1) • MYALEPT is not indicated for use in patients with metabolic disease, without concurrent evidence of generalized lipodystrophy. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer as a subcutaneous injection once daily after the lyophilized cake is reconstituted with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection (BWFI) or preservative-free sterile Water for Injection (WFI). The recommended daily dosages in milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight are: • Body weight 40 kg or less: starting dose 0.06 mg/kg/day, increase or decrease by 0.02 mg/kg to a maximum daily dose of 0.13 mg/kg. Males greater than 40 kg body weight: starting dose 2.5 mg/day, increase or decrease by 1.25 mg to 2.5 mg/day to a maximum dose of 10 mg/day. (2.1) Females greater than 40 kg body weight: starting dose 5 mg/day, increase or decrease by 1.25 mg to 2.5 mg/day to a maximum dose of 10 mg/day. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS MYALEPT is supplied as a sterile, white, solid, lyophilized cake of 11.3 mg metreleptin per vial to deliver 5 mg per mL when reconstituted in 2.2 mL of BWFI or WFI. CONTRAINDICATIONS • General obesity not associated with congenital leptin deficiency. • Hypersensitivity to metreleptin. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Anti-metreleptin antibodies with neutralizing activity: Could inhibit endogenous leptin action and/or result in loss of MYALEPT efficacy. Test for neutralizing antibodies in patients with severe infections or loss of efficacy during MYALEPT treatment. • T-cell lymphoma: Carefully consider benefits and risks of treatment with MYALEPT in patients with significant hematologic abnormalities and/or acquired generalized lipodystrophy. • Hypoglycemia: A dose adjustment, including possible large reductions, of insulin or insulin secretagogue may be necessary. Closely monitor blood glucose in patients on concomitant insulin or insulin secretagogue therapy. • Autoimmunity: Autoimmune disorder progression has been observed in patients treated with MYALEPT. Carefully consider benefits and risks of MYALEPT treatment in patients with autoimmune disease. • Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria or generalized rash) have been reported. Patient should promptly seek medical advice regarding suspected reactions. • Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity: Preservative-free sterile WFI recommended for neonates and infants. ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common in clinical trials (≥10%): headache, hypoglycemia, decreased weight, abdominal pain. NEURACEQ MECHANISM OF ACTION Florbetaben F18 is a F18-labeled stilbene derivative, which binds to β-amyloid plaques in the brain. The F 18 isotope produces a positron signal that is detected by a PET scanner. 3 Florbetaben F 18 does not bind to tau or α-synuclein in tissue from patients with AD. Neither Neuraceq nor non-radioactive florbetaben F 19 bind to AT8 positive tau deposits in brain tissue from patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), using autoradiography and immunohistochemistry, respectively. H-florbetaben in vitro binding experiments reveal two binding sites (Kd of 16 nM and 135 nM) in frontal cortex homogenates from patients with AD. Binding of florbetaben F18 to β-amyloid plaques in post-mortem brain sections from patients with AD using autoradiography correlates with both immunohistochemical and Bielschowsky silver stains. INDICATIONS AND USAGE Neuraceq™ is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the brain to estimate β-amyloid neuritic plaque density in adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and other causes of cognitive decline. A negative Neuraceq scan indicates sparse to no neuritic plaques and is inconsistent with a neuropathological diagnosis of AD at the time of image acquisition; a negative scan result reduces the likelihood that a patient’s cognitive impairment is due to AD. A positive Neuraceq scan indicates moderate to frequent amyloid neuritic plaques; neuropathological examination has shown this amount of amyloid neuritic plaque is present in patients with AD, but may also be present in patients with other types of neurologic conditions as well as older people with normal cognition. Neuraceq is an adjunct to other diagnostic evaluations. LIMITATIONS OF USE A positive Neuraceq scan does not establish the diagnosis of AD or any other cognitive disorder Safety and effectiveness of Neuraceq have not been established for: • Predicting development of dementia or other neurologic conditions. • Monitoring responses to therapies DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Use appropriate radiation handling measures (2.1). • Administer 300 MBq (8.1 mCi) as a slow single intravenous bolus (6 sec/mL) in a total volume of up to 10 mL. • Obtain 15-20 minute PET images starting from 45 to 130 minutes after intravenous administration. • Image interpretation: refer to full prescribing information • The radiation absorbed dose from a 300 MBq (8.1 mCi) dose of Neuraceq is 5.8 mSv in an adult DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 30 mL multi-dose vials containing a clear injectable solution at a strength of 50 to 5000 MBq/mL (1.4 to135 mCi/mL) florbetaben F18 at End Of Synthesis (EOS). At time of administration 300 MBq (8.1 mCi) are contained in up to 10 mL solution for injection (3) None CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Image interpretation errors (especially false positives) have been observed. • Neuraceq, like all radiopharmaceuticals, contributes to a patient’s long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Ensure safe handling to protect patients and health care workers from unintentional radiation exposure . • ADVERSE REACTIONS The most commonly reported adverse reactions were: injection site reaction consisting of erythema (1.7 %), irritation (1.2 %), and pain. NORTHERA (droxidopa) MECHANISM OF ACTION The exact mechanism of action of NORTHERA in the treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is unknown. NORTHERA is a synthetic amino acid analog that is directly metabolized to norepinephrine by dopa-decarboxylase, which is extensively distributed throughout the body. NORTHERA is believed to exert its pharmacological effects through norepinephrine and not through the parent molecule or other metabolites. Norepinephrine increases blood pressure by inducing peripheral arterial and venous vasoconstriction. NORTHERA in humans induces small and transient rises in plasma norepinephrine. INDICATIONS AND USAGE NORTHERA is indicated for the treatment of orthostatic dizziness, lightheadedness, or the “feeling that you are about to black out” in adult patients with symptomatic neurogenic orthostatic hypotension caused by primary autonomic failure (Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, and pure autonomic failure), dopamine beta-hydroxylase deficiency, and nondiabetic autonomic neuropathy. Effectiveness beyond 2 weeks of treatment has not been demonstrated. The continued effectiveness of NORTHERA should be assessed periodically. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Starting dose is 100 mg three times during the day. • Titrate by 100 mg three times daily, up to a maximum dose of 600 mg three times daily. • Take consistently with or without food. • To reduce the potential for supine hypertension, elevate the head of the bed and give the last dose at least 3 hours prior to bedtime. • Take NORTHERA capsule whole DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • 100 mg , 200 mg and 300 mg capsules • None CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • NORTHERA can cause supine hypertension and may increase cardiovascular risk if supine hypertension is not well-managed. • Hyperpyrexia and confusion. • May exacerbate symptoms in patients with existing ischemic heart disease, arrhythmias, and congestive heart failure. • Allergic reactions ADVERSE REACTIONS Headache, dizziness, nausea, hypertension, and fatigue (greater than 5%). DRUG INTERACTIONS • Use of DOPA decarboxylase inhibitors may require dose adjustments for NORTHERA. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Nursing Mothers: Choose nursing or NORTHERA • Patients with Renal Impairment: Dosing recommendations cannot be provided for patients with GFR less than 30 mL/min WARNING: SUPINE HYPERTENSION Monitor supine blood pressure prior to and during treatment and more frequently when increasing doses. Elevating the head of the bed lessens the risk of supine hypertension, and blood pressure should be measured in this position. If supine hypertension cannot be managed by elevation of the head of the bed, reduce or discontinue NORTHERA. OFEV (nintedanib) MECHANISM OF ACTION • • • • Nintedanib is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and non-receptor tyrosine kinases (nRTKs). Nintedanib inhibits the following RTKs: platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) α and β, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 1-3, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 1-3, and Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3). Among them, FGFR, PDGFR, and VEGFR have been implicated in IPF pathogenesis. Nintedanib binds competitively to the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding pocket of these receptors and blocks the intracellular signaling which is crucial for the proliferation, migration, and transformation of fibroblasts representing essential mechanisms of the IPF pathology. In addition, nintedanib inhibits the following nRTKs: Lck, Lyn and Src kinases. The contribution of FLT3 and nRTK inhibition to IPF efficacy is unknown. INDICATIONS AND USAGE OFEV is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Recommended dosage: 150 mg twice daily approximately 12 hours apart taken with food. • Consider temporary dose reduction to 100 mg, treatment interruption, or discontinuation for management of adverse reactions. • Prior to treatment, conduct liver function tests. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • Capsules: 150 mg and 100 mg CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Elevated liver enzymes: ALT, AST, and bilirubin elevations have occurred with OFEV. Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin before and during treatment. Temporary dosage reductions or discontinuations may be required. • • • Gastrointestinal disorders: Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting have occurred with OFEV. Treat patients at first signs with adequate hydration and antidiarrheal medicine (e.g., loperamide) or anti-emetics. Discontinue OFEV if severe diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting persists despite symptomatic treatment. Embryofetal toxicity: Women of childbearing potential should be advised of the potential hazard to the fetus and to avoid becoming pregnant. Arterial thromboembolic events have been reported. Use caution when treating patients at higher cardiovascular risk including known coronary artery disease. Bleeding events have been reported. Use OFEV in patients with known bleeding risk only if anticipated benefit outweighs the potential risk. Gastrointestinal perforation has been reported. Use OFEV with caution when treating patients with recent abdominal surgery. Discontinue OFEV in patients who develop gastrointestinal perforation. Only use OFEV in patients with known risk of gastrointestinal perforation if the anticipated benefit outweighs the potential risk. ADVERSE REACTIONS • Most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are: diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, liver enzyme elevation, decreased appetite, headache, weight decreased, and hypertension. DRUG INTERACTIONS • Coadministration of P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase nintedanib exposure. Monitor patients closely for tolerability of OFEV. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • • • • Nursing mothers: Discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. Hepatic impairment: Monitor for adverse reactions and consider dose modification or discontinuation of OFEV as needed for patients with mild hepatic impairment. OFEV is not recommended for use in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. Renal impairment: The safety and efficacy of OFEV have not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment and end-stage renal disease. Smokers: Decreased exposure has been noted in smokers which may alter the efficacy profile of OFEV. OPDIVO (nivolumab) MECHANISM OF ACTION • • • • • • • • Binding of the PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, to the PD-1 receptor found on T cells, inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors and signaling through this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumors. Nivolumab is a human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, releasing PD-1 pathwaymediated inhibition of the immune response, including the anti-tumor immune response. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD-1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth. INDICATIONS AND USAGE OPDIVO is a human programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab and, if BRAF V600 mutation positive, a BRAF inhibitor. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in the confirmatory trials. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer 3 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 2 weeks. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • Injection: 40 mg/4 mL and 100 mg/10 mL solution in a single-use vial. • None. CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • • • • • • Immune-mediated adverse reactions: Administer corticosteroids based on the severity of the reaction. Immune-mediated pneumonitis: Withhold for moderate and permanently discontinue for severe or life-threatening pneumonitis. (5.1) -mediated colitis: Withhold for moderate or severe and permanently discontinue for life-threatening colitis. (5.2) Immune-mediated hepatitis: Monitor for changes in liver function. Withhold for moderate and permanently discontinue for severe or life-threatening transaminase or total bilirubin elevation. Immune-mediated nephritis and renal dysfunction: Monitor for changes in renal function. Withhold for moderate and permanently discontinue for severe or life-threatening serum creatinine elevation. Immune-mediated hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism: Monitor for changes in thyroid function. Initiate thyroid hormone replacement as needed. Embryofetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise of potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. ADVERSE REACTIONS • Most common adverse reaction (≥20%) was rash. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Lactation: Discontinue breastfeeding. ORBACTIV (oritavancin) • • • • MECHANISM OF ACTION Oritavancin has three mechanisms of action: (i) inhibition of the transglycosylation (polymerization) step of cell wall biosynthesis by binding to the stem peptide of peptidoglycan precursors; (ii) inhibition of the transpeptidation (crosslinking) step of cell wall biosynthesis by binding to the peptide bridging segments of the cell wall; (iii) disruption of bacterial membrane integrity, leading to depolarization, permeabilization, and cell death. These multiple mechanisms contribute to the concentration-dependent bactericidal activity of oritavancin. INDICATIONS AND USAGE ORBACTIV is a lipoglycopeptide antibacterial drug indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections caused or suspected to be caused by susceptible isolates of designated Gram-positive microorganisms. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of ORBACTIV and other antibacterial drugs, ORBACTIV should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION A 1200 mg single dose is administered by intravenous infusion over 3 hours. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • For injection: 400 mg of lyophilized powder in a single-use vial for reconstitution. • CONTRAINDICATIONS Use of intravenous unfractionated heparin sodium is contraindicated for 48 hours after ORBACTIV administration. • Known hypersensitivity to ORBACTIV • • • • • • WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Concomitant warfarin use: Co-administration of ORBACTIV and warfarin may result in higher exposure of warfarin, which may increase the risk of bleeding. Use ORBACTIV in patients on chronic warfarin therapy only when the benefits can be expected to outweigh the risk of bleeding. Coagulation test interference: ORBACTIV has been shown to artificially prolong aPTT for up to 48 hours, and may prolong PT and INR for up to 24 hours. Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with the use of antibacterial agents including ORBACTIV. Discontinue infusion if signs of acute hypersensitivity occur. Monitor closely patients with known hypersensitivity to glycopeptides. Infusion-related reactions have been reported. Slow the rate or interrupt infusion if infusion reaction develops. Clostridium difficile-associated colitis: Evaluate patients if diarrhea occurs. Osteomyelitis: Institute appropriate alternate antibacterial therapy in patients with confirmed or suspected osteomyelitis. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (≥ 3%) in patients treated with ORBACTIV were headache, nausea, vomiting, limb and subcutaneous abscesses, and diarrhea. OTEZLA (apremilast) • • • • • • • • • • • MECHANISM OF ACTION Apremilast is an oral small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) specific for cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). PDE4 inhibition results in increased intracellular cAMP levels. The specific mechanism(s) by which apremilast exerts its therapeutic action in psoriatic arthritis patients and psoriasis patients is not well defined INDICATIONS AND USAGE OTEZLA, an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4), is indicated for the treatment of: Adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. Patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION To reduce risk of gastrointestinal symptoms, titrate to recommended dose of 30 mg twice daily according to the following schedule. Day 1: 10 mg in morning Day 2: 10 mg in morning and 10 mg in evening Day 3: 10 mg in morning and 20 mg in evening Day 4: 20 mg in morning and 20 mg in evening Day 5: 20 mg in morning and 30 mg in evening Day 6 and thereafter: 30 mg twice daily Dosage in Severe Renal Impairment: Recommended dose is 30 mg once daily. CONTRAINDICATIONS Known hypersensitivity to apremilast or any excipients in formulation WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Depression: Advise patients, their caregivers, and families to be alert for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or other mood changes and if such changes occur to contact their healthcare provider Carefully weigh risks and benefits of treatment with OTEZLA in patients with a history of depression and/or suicidal thoughts or behavior. Weight Decrease: Monitor weight regularly. If unexplained or clinically significant weight loss occurs, evaluate weight loss and consider discontinuation of OTEZLA Drug Interactions: Use with strong cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin) is not recommended because loss of efficacy may occur ADVERSE REACTIONS Psoriatic Arthritis: The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are diarrhea, nausea, and headache. Psoriasis: The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are diarrhea, nausea, upper respiratory tract infection, and headache, including tension headache. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Severe Renal Impairment: Increased systemic exposure of OTEZLA has been observed, reduction in dose to 30 mg once daily is recommended PLEGRIDY (peginterferon beta-1a) MECHANISM OF ACTION The mechanism by which PLEGRIDY exerts its effects in patients with multiple sclerosis is unknown. INDICATIONS AND USAGE PLEGRIDY is an interferon beta indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION For subcutaneous use only. Recommended dose: 125 micrograms every 14 days. PLEGRIDY dose should be titrated, starting with 63 micrograms on day 1, 94 micrograms on day 15, and 125 micrograms (full dose) on day 29. A healthcare professional should train patients in the proper technique for selfadministering subcutaneous injections using the prefilled pen or syringe. Analgesics and/or antipyretics on treatment days may help ameliorate flu-like symptoms DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Injection: 125 micrograms per 0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled pen Injection Starter Pack: 63 micrograms per 0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled pen and 94 micrograms per 0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled pen Injection: 125 micrograms per 0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe Injection Starter Pack: 63 micrograms per 0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe and 94 micrograms per 0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe CONTRAINDICATIONS History of hypersensitivity to natural or recombinant interferon beta or peginterferon, or any other component of the formulation. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Hepatic injury: monitor liver function tests; monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hepatic injury; consider discontinuation of PLEGRIDY if hepatic injury occurs Depression and suicide: advise patients to report immediately any symptom of depression or suicidal ideation to their healthcare provider; consider discontinuation of PLEGRIDY if depression occurs Seizure: Seizures are associated with the use of interferon beta. Exercise caution when administering PLEGRIDY to patients with a seizure disorder Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions: serious allergic reactions have been reported as a rare complication of treatment with interferon beta. Discontinue PLEGRIDY if a serious allergic reaction occurs Injection site reactions: change injection site or consider discontinuation of PLEGRIDY if there is necrosis Congestive heart failure: monitor patients with pre-existing significant cardiac disease for worsening of cardiac symptoms Decreased peripheral blood counts: monitor complete blood counts Autoimmune disorders: consider discontinuation of PLEGRIDY if a new autoimmune disorder occurs ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10% and at least 2% more frequent on PLEGRIDY than on placebo) were injection site erythema, influenza-like illness, pyrexia, headache, myalgia, chills, injection site pain, asthenia, injection site pruritus, and arthralgia. RAPIVAB (peramivir injection) MECHANISM OF ACTION Peramivir is an inhibitor of influenza virus neuraminidase, an enzyme that releases viral particles from the plasma membrane of infected cells. The median neuraminidase inhibitory activity (IC50 values) of peramivir in biochemical assays against influenza A/H1N1 virus, influenza A/H3N2 virus, and influenza B virus clinical isolates were 0.16 nM (n=44; range 0.01-1.77 nM), 0.13 nM (n=32; range 0.05-11 nM), and 0.99 nM (n=39; range 0.04-54.2 nM), respectively, in a neuraminidase assay with a fluorescently labeled MUNANA substrate. INDICATIONS AND USAGE RAPIVAB is an influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in patients 18 years and older who have been symptomatic for no more than two days. LIMITATIONS OF USE • Efficacy based on clinical trials in which the predominant influenza virus type was influenza A; a limited number of subjects infected with influenza B virus were enrolled. • Consider available information on influenza drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use. • Efficacy could not be established in patients with serious influenza requiring hospitalization. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Administer as a single dose within 2 days of onset of influenza symptoms. • Recommended dose is 600 mg, administered by intravenous infusion for a minimum of 15 minutes. • Renal Impairment: Recommended dose for patients with creatinine clearance 30-49 mL/min is 200 mg and the recommended dose for patients with creatinine clearance 10-29 mL/min is 100 mg. • Hemodialysis: Administer after dialysis. • RAPIVAB must be diluted prior to administration. • See the Full Prescribing Information for drug compatibility information. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Injection: 200 mg in 20 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-use vial. None CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Serious skin/hypersensitivity reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme have occurred with RAPIVAB. • Neuropsychiatric events: Patients with influenza may be at an increased risk of hallucinations, delirium and abnormal behavior early in their illness. Monitor for signs of abnormal behavior. ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common adverse reaction (incidence >2%) is diarrhea. DRUG INTERACTIONS Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV), intranasal: Avoid use of LAIV within 2 weeks before or 48 hours after administration of RAPIVAB, unless medically indicated USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Pregnancy: Use if benefit outweighs risk • Nursing mothers: Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman. SIVEXTRO (tedizolid phosphate) MECHANISM OF ACTION The antibacterial activity of tedizolid is mediated by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome resulting in inhibition of protein synthesis. Tedizolid inhibits bacterial protein synthesis through a mechanism of action different from that of other non-oxazolidinone class antibacterial drugs; therefore, cross-resistance between tedizolid and other classes of antibacterial drugs is unlikely. The results of in vitro time-kill studies show that tedizolid is bacteriostatic against enterococci, staphylococci, and streptococci. INDICATIONS AND USAGE SIVEXTRO is an oxazolidinone-class antibacterial drug indicated in adults for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by designated susceptible bacteria. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of SIVEXTRO and other antibacterial drugs, SIVEXTRO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 200 mg administered once daily orally or as an intravenous (IV) infusion over 1 hour for six (6) days. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS For injection: 200 mg, sterile, lyophilized powder in single-use vial for reconstitution for intravenous infusion; Tablet: 200 mg (3) None CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Patients with neutropenia: The safety and efficacy of SIVEXTRO in patients with neutropenia (neutrophil counts <1000 cells/mm3) have not been adequately evaluated. In an animal model of infection, the antibacterial activity of SIVEXTRO was reduced in the absence of granulocytes. Consider alternative therapies in neutropenic patients. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (>2%) are nausea, headache, diarrhea, vomiting, and dizziness. STRIVERDI/RESPIMAT(olodaterol) MECHANISM OF ACTION Olodaterol is a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA). The compound exerts its pharmacological effects by binding and activation of beta2adrenoceptors after topical administration by inhalation. Activation of these receptors in the airways results in a stimulation of intracellular adenyl cyclase, an enzyme that mediates the synthesis of cyclic-3’, 5’ adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Elevated levels of cAMP induce bronchodilation by relaxation of airway smooth muscle cells. In vitro studies have shown that olodaterol has 241-fold greater agonist activity at beta2-adrenoceptors compared to beta1-adrenoceptors and 2,299-fold greater agonist activity compared to beta3-adrenoceptors. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Beta-adrenoceptors are divided into three subtypes: beta1-adrenoceptors predominantly expressed on cardiac smooth muscle, beta2adrenoceptors predominantly expressed on airway smooth muscle, and beta3-adrenoceptors predominantly expressed on adipose tissue. Beta2-agonists cause bronchodilation. Although the beta2-adrenoceptor is the predominant adrenergic receptor in the airway smooth muscle, it is also present on the surface of a variety of other cells, including lung epithelial and endothelial cells and in the heart. The precise function of beta2-receptors in the heart is not known, but their presence raises the possibility that even highly selective beta2-agonists may have cardiac effects. INDICATIONS AND USAGE STRIVERDI RESPIMAT Inhalation Spray is a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist indicated for: The long-term, once-daily maintenance bronchodilator treatment of airflow obstruction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema. Important limitations: STRIVERDI RESPIMAT is NOT indicated to treat acute deterioration of COPD . STRIVERDI RESPIMAT is NOT indicated to treat asthma . DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • For oral inhalation only. • Two inhalations of STRIVERDI RESPIMAT once-daily at the same time of day. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Inhalation spray: Each actuation from the mouthpiece contains 2.7 mcg olodaterol hydrochloride, equivalent to 2.5 mcg olodaterol. Two actuations equal one dose CONTRAINDICATIONS All LABA are contraindicated in patients with asthma without use of a long-term asthma control medication. (4) STRIVERDI RESPIMAT is not indicated for the treatment of asthma. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Do not initiate STRIVERDI RESPIMAT in acutely deteriorating COPD patients Do not use for relief of acute symptoms. Concomitant short-acting beta2agonists can be used as needed for acute relief. Do not exceed the recommended dose. Excessive use of STRIVERDI RESPIMAT, or use in conjunction with other medications containing LABA can result in clinically significant cardiovascular effects and may be fatal. Life-threatening paradoxical bronchospasm can occur. Discontinue STRIVERDI RESPIMAT immediately. Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular or convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis or sensitivity to sympathomimetic drugs ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common adverse reactions (incidence >2% and more than placebo) are nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, urinary tract infection, cough, dizziness, rash, diarrhea, back pain and arthralgia. DRUG INTERACTIONS Other adrenergic drugs may potentiate effect. Use with caution. Xanthine derivatives, steroids, diuretics or non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate hypokalemia or ECG changes. Use with caution. MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and drugs that prolong QTc interval may potentiate effect on cardiovascular system. Use with extreme caution. Beta-blockers may decrease effectiveness. Use with caution and only when medically necessary. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ SYLVANT (siltuximab) MECHANISM OF ACTION Siltuximab binds human IL-6 and prevents the binding of IL-6 to both soluble and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors. IL-6 has been shown to be involved in diverse normal physiologic processes such as induction of immunoglobulin secretion. Overproduction of IL-6 has been linked to systemic manifestations in patients with MCD. INDICATIONS AND USAGE SYLVANT is an interleukin-6 (IL-6) antagonist indicated for the treatment of patients with multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD) who are human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) negative and human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) negative. LIMITATION OF USE SYLVANT was not studied in patients with MCD who are HIV positive or HHV-8 positive because SYLVANT did not bind to virally produced IL-6 in a nonclinical study. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION For intravenous infusion only. Administer as an 11 mg/kg dose given over 1 hour by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS • 100 mg of lyophilized powder in a single-use vial. • 400 mg of lyophilized powder in a single-use vial. CONTRAINDICATIONS Severe hypersensitivity reaction to siltuximab or any of the excipients in SYLVANT WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Concurrent Active Severe Infections 1. Do not administer SYLVANT to patients with severe infections until the infection resolves. 2. Monitor patients receiving SYLVANT closely for infections. Institute prompt anti-infective therapy and do not administer SYLVANT until the infection resolves. Vaccinations: Do not administer live vaccines because IL-6 inhibition may interfere with the normal immune response to new antigens. Infusion Related Reactions: Administer SYLVANT in a setting that provides resuscitation equipment, medication, and personnel trained to provide resuscitation. Gastrointestinal (GI) perforation: Use with caution in patients who may be at increased risk. Promptly evaluate patients presenting with symptoms that may be associated or suggestive of GI perforation. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (>10% compared to placebo) during treatment with SYLVANT in the MCD clinical trial were pruritus, increased weight, rash, hyperuricemia, and upper respiratory tract infection. TANZEUM (albiglutide) INDICATIONS AND USAGE TANZEUM is a GLP-1 receptor agonist indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. LIMITATIONS OF USE • Not recommended as first-line therapy for patients inadequately controlled on diet and exercise. • Has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis. Consider other antidiabetic therapies in patients with a history of pancreatitis. • Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus or diabetic ketoacidosis. • Not for patients with pre-existing severe gastrointestinal disease. • Has not been studied in combination with prandial insulin. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Administer once weekly at any time of day, without regard to meals. • Inject subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. • Initiate at 30 mg subcutaneously once weekly. Dose can be increased to 50 mg once weekly in patients requiring additional glycemic control. • If a dose is missed, administer within 3 days of missed dose. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS For injection: 30 mg or 50 mg in a single-dose Pen. CONTRAINDICATIONS • TANZEUM is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2. • TANZEUM is contraindicated in patients with a prior serious hypersensitivity reaction to albiglutide or any of the product components. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Thyroid C-cell Tumors: See Boxed Warning. • Pancreatitis: Discontinue promptly if suspected. Do not restart if confirmed. Consider other antidiabetic therapies in patients with a history of pancreatitis. • Hypoglycemia: Can occur when used in combination with insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylureas) or insulin. Consider lowering sulfonylurea or insulin dosage when starting TANZEUM. • Hypersensitivity Reactions: Discontinue TANZEUM if suspected. Monitor and treat promptly per standard of care until signs and symptoms resolve. • Renal Impairment: Monitor renal function in patients with renal impairment reporting severe adverse gastrointestinal reactions. • Macrovascular Outcomes: There have been no clinical trials establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with TANZEUM or any other antidiabetic drug. ADVERSE REACTIONS Adverse reactions, reported in ≥10% of patients treated with TANZEUM and more frequently than in patients on placebo, were upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, nausea, and injection site reaction. DRUG INTERACTIONS TANZEUM delays gastric emptying. May impact absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS • Pregnancy: TANZEUM may cause fetal harm; only use if potential benefit justifies potential risk to fetus. • Nursing Mothers: Discontinue nursing or discontinue TANZEUM. • Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment recommended. Monitor renal function in patients with renal impairment reporting severe adverse gastrointestinal reactions. VIEKIRA PAK (ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir tablets; dasabuvir tablets) MECHANISM OF ACTION VIEKIRA PAK combines three direct-acting antiviral agents with distinct mechanisms of action and non-overlapping resistance profiles to target HCV at multiple steps in the viral lifecycle. INDICATIONS AND USAGE VIEKIRA PAK with or without ribavirin is indicated for the treatment of patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection including those with compensated cirrhosis. VIEKIRA PAK includes ombitasvir, a hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitor, paritaprevir, a hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor, ritonavir, a CYP3A inhibitor and dasabuvir, a hepatitis C virus non-nucleoside NS5B palm polymerase inhibitor. LIMITATION OF USE VIEKIRA PAK is not recommended for use in patients with decompensated liver disease. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Recommended dosage: Two ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir 12.5/75/50 mg tablets once daily (in the morning) and one dasabuvir 250 mg tablet twice daily (morning and evening) with a meal without regard to fat or calorie content. HCV/HIV-1 co-infection: For patients with HCV/HIV-1 co-infection, follow the dosage recommendations in the table above. Liver Transplant Recipients: In liver transplant recipients with normal hepatic function and mild fibrosis (Metavir fibrosis score ≤2), the recommended duration of VIEKIRA PAK with ribavirin is 24 weeks. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets: • Ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir: 12.5/75/50 mg • Dasabuvir: 250 mg CONTRAINDICATIONS • If VIEKIRA PAK is administered with ribavirin, the contraindications to ribavirin also apply to this combination regimen. • Patients with severe hepatic impairment. • Co-administration with drugs that are: highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance; strong inducers of CYP3A and CYP2C8; and strong inhibitors of CYP2C8. • Known hypersensitivity to ritonavir (e.g. toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome). WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • ALT Elevations: Discontinue ethinyl estradiol-containing medications prior to starting VIEKIRA PAK (alternative contraceptive methods are recommended). Perform hepatic laboratory testing on all patients during the first 4 weeks of treatment. For ALT elevations on VIEKIRA PAK, monitor closely and follow recommendations in full prescribing information. (5.1) • Risks Associated With Ribavirin Combination Treatment: If VIEKIRA PAK is administered with ribavirin, the warnings and precautions for ribavirin also apply to this combination regimen. • Drug Interactions: The concomitant use of VIEKIRA PAK and certain other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to loss of therapeutic effect of VIEKIRA PAK. ADVERSE REACTIONS In subjects receiving VIEKIRA PAK with ribavirin, the most commonly reported adverse reactions (greater than 10% of subjects) were fatigue, nausea, pruritus, other skin reactions, insomnia and asthenia. In subjects receiving VIEKIRA PAK without ribavirin, the most commonly reported adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 5% of subjects) were nausea, pruritus and insomnia. VIMIZIM (elosulfase alfa) MECHANISM OF ACTION Mucopolysaccharidoses comprise a group of lysosomal storage disorders caused by the deficiency of specific lysosomal enzymes required for the catabolism of glycosaminoglycans (GAG). Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA (MPS IVA, Morquio A Syndrome) is characterized by the absence or marked reduction in N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase activity. The sulfatase activity deficiency results in the accumulation of the GAG substrates, KS and C6S, in the lysosomal compartment of cells throughout the body. The accumulation leads to widespread cellular, tissue, and organ dysfunction. Vimizim is intended to provide the exogenous enzyme N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase that will be taken up into the lysosomes and increase the catabolism of the GAGs KS and C6S. Elosulfase alfa uptake by cells into lysosomes is mediated by the binding of mannose6-phosphate-terminated oligosaccharide chains of elosulfase alfa to mannose-6-phosphate receptors. In the absence of an animal disease model that recapitulates the human disease phenotype, elosulfase alfa pharmacological activity was evaluated using human primary chondrocytes from two MPS IVA patients. Treatment of MPS IVA chondrocytes with elosulfase alfa induced clearance of KS lysosomal storage from the chondrocytes. INDICATIONS AND USAGE Vimizim is a hydrolytic lysosomal glycosaminoglycan (GAG)-specific enzyme indicated for patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA (MPS IVA; Morquio A syndrome). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2 mg per kg body weight administered once every week as an intravenous infusion over a minimum of 3.5 to 4.5 hours, based on infusion volume . DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Injection: 5 mg/5 mL (1 mg/mL) in single-use vials (3). CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity Reactions: Life-threatening anaphylaxis and hypersensitivity reactions have been observed in some patients during treatment with Vimizim. If anaphylaxis or severe hypersensitivity reactions occur, immediately stop the infusion and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Pre-treatment with antihistamines with or without antipyretics is recommended prior to the start of infusion. • Risk of Acute Respiratory Complications: Patients with acute febrile or respiratory illness may be at higher risk of life-threatening complications from hypersensitivity reactions. Careful consideration should be given to the patient's clinical status prior to administration of Vimizim and consider delaying the Vimizim infusion. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (≥10% in Vimizim patients and occurring at a higher incidence than placebo-treated patients) were pyrexia, vomiting, headache, nausea, abdominal pain, chills, and fatigue USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of Vimizim have not been established in pediatric patients less than 5 years of age. XTORO (finafloxacin otic suspension) MECHANISM OF ACTION Finafloxacinbelongs to the fluoroquinolone class of antibacterials which involves the inhibition of bacterial type II topoisomerase enzymes, DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination. Finafloxacin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria, both in vitro and clinical studies as described in the INDICATIONS and USAGE section of the package insert for XTORO 1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa 2. Staphylococcus aureus. INDICATIONS AND USAGE XTORO* is a quinolone antimicrobial indicated for the treatment of acute otitis externa (AOE) caused by susceptible strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Instill four drops in the affected ear(s) twice daily for seven days. For patients requiring use of an otowick, the initial dose can be doubled (to 8 drops), followed by 4 drops instilled into the affected ear twice daily for seven days. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 5 mL of finafloxacin otic suspension, 0.3% in 8 mL bottle. CONTRAINDICATIONS None. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Prolonged use of this product may lead to overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Discontinue use if this occurs. Allergic reactions may occur in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to finafloxacin, to other quinolones, or to any of the components in this medication. Discontinue use if this occurs. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions occurring in 1% of patients with XTORO were ear pruritus and nausea. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ZERBAXA (ceftolozane/tazobactam) MECHANISM OF ACTION Ceftolozane belongs to the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs. The bactericidal action of ceftolozane results from inhibition of cell wall biosynthesis, and is mediated through binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Ceftolozane is an inhibitor of PBPs of P. aeruginosa (e.g., PBP1b, PBP1c, and PBP3) and E. coli (e.g., PBP3). Tazobactam sodium has little clinically relevant in vitro activity against bacteria due to its reduced affinity to penicillin-binding proteins. It is an irreversible inhibitor of some beta-lactamases (e.g., certain penicillinases and cephalosporinases), and can bind covalently to some chromosomal and plasmid-mediated bacterial beta-lactamases. INDICATIONS AND USAGE ZERBAXA (ceftolozane/tazobactam) is a combination product consisting of a cephalosporin-class antibacterial drug and a beta-lactamase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by designated susceptible microorganisms: Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections, used in combination with metronidazole. Complicated Urinary Tract Infections, including Pyelonephritis . To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of ZERBAXA and other antibacterial drugs, ZERBAXA should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ZERBAXA (ceftolozane/tazobactam) for Injection, 1.5 g (1 g/0.5 g) every 8 hours by intravenous infusion administered over 1 hour for patients 18 years or older with creatinine clearance (CrCl) greater than 50 mL/min. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS ZERBAXA for Injection (ceftolozane/tazobactam) 1 g/0.5 g powder for reconstitution in single-dose vials containing 1 g ceftolozane (equivalent to 1.147 g ceftolozane sulfate) and 0.5 g tazobactam (equivalent to 0.537 g tazobactam sodium) CONTRAINDICATIONS ZERBAXA is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity to ceftolozane/tazobactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, or other members of the beta-lactam class. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Decreased efficacy in patients with baseline CrCl of 30 to ≤50 mL/min. Monitor CrCl at least daily in patients with changing renal function and adjust the dose of ZERBAXA accordingly. (5.1) Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported with beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. Exercise caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to betalactam antibacterial drugs. (5.2) Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including ZERBAXA. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (≥ 5% in either indication) are nausea, diarrhea, headache and pyrexia. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Dosage adjustment is required in patients with moderately or severely impaired renal function and in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis (HD). Higher incidence of adverse reactions was observed in patients age 65 years and older. In complicated intra-abdominal infections, cure rates were lower in patients age 65 years and older. ZERBAXA has not been studied in pediatric patients. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ZONTIVITY (vorapaxar) MECHANISM OF ACTION Vorapaxar is a reversible antagonist of the protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) expressed onplatelets, but its long half-life makes it effectively irreversible. Vorapaxar inhibits thrombin-induced andthrombin receptor agonist peptide (TRAP)induced platelet aggregation in in vitro studies. Vorapaxar doesnot inhibit platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate (ADP), collagen or a thromboxane mimetic and does not affect coagulation parameters ex vivo. PAR-1 receptors are also expressed in a wide variety of cell types, including endothelial cells, neurons, and smooth muscle cells, but the pharmacodynamic effects of vorapaxar in these cell types have not been assessed. INDICATIONS AND USAGE ZONTIVITY is a protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) antagonistindicated for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events inpatients with a history of myocardial infarction (MI) or with peripheralarterial disease (PAD). ZONTIVITY has been shown to reduce the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, and urgent coronary revascularization. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION One tablet of ZONTIVITY orally once daily. Use with aspirin and/or clopidogrel according to their indications or standard of care. There is limited clinical experience with other antiplatelet drugs and none with ZONTIVITY as the only antiplatelet agent. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets: 2.08 mg vorapaxar. History of stroke, TIA, or ICH. Active pathologic bleeding. CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Like other antiplatelet agents, ZONTIVITY increases the risk of bleeding. Avoid use with strong CYP3A inhibitors or inducers. ADVERSE REACTIONS Bleeding, including life-threatening and fatal bleeding, is the most commonly reported adverse reaction. ZYDELIG(idelalisib) MECHANISM OF ACTION Idelalisib is an inhibitor of PI3Kδ kinase, which is expressed in normal and malignant Bcells. Idelalisib induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in cell lines derived from malignant B-cells and in primary tumor cells. Idelalisib inhibits several cell signaling pathways, including B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and the CXCR4 and CXCR5 signaling, which are involved in trafficking and homing of B-cells to the lymph nodes and bone marrow. Treatment of lymphoma cells with idelalisib resulted in inhibition of chemotaxis and adhesion, and reduced cell viability. STRUCTURE Idelalisib is an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PI3Kδ. The chemical name for idelalisib is 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1S)-1-(9H-purin-6ylamino)propyl]quinazolin-4(3H)-one. It has a molecular formula of C22H18FN7O and a molecular weight of 415.42 g/mol. Idelalisib has the following structural formula. INDICATIONS AND USAGE Zydelig is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with: Relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), in combination with rituximab, in patients for whom rituximab alone would be considered appropriate therapy due to other comorbidities. Relapsed follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (FL) in patients who have received at least two prior systemic therapies. Relapsed small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in patients who have received at least two prior systemic therapies. Accelerated approval was granted for FL and SLL based on overall response rate. Improvement in patient survival or disease related symptoms has not been established. Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Recommended starting dose: 150 mg orally, twice daily. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets: 150 mg, 100 mg. CONTRAINDICATIONS History of serious allergic reactions including anaphylaxis and toxic epidermal necrolysis. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Severe cutaneous reactions: Monitor patients for the development of severe cutaneous reactions and discontinue Zydelig. Anaphylaxis: Monitor patients for anaphylaxis and discontinue Zydelig. Neutropenia: monitor blood counts. Embryo-fetal toxicity: may cause fetal harm. Advise women of potential risk to a fetus and to avoid pregnancy while taking Zydelig. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥20%) are diarrhea, pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, cough, pneumonia, abdominal pain, chills, and rash. The most common laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥30%) are neutropenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, ALT elevations, and AST elevation. DRUG INTERACTIONS • • CYP3A inducers: Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A inducers with Zydelig. CYP3A substrates: Avoid coadministration of CYP3A substrates with Zydelig. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Nursing mothers: Discontinue drug or nursing. WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: HEPATIC, SEVERE DIARRHEA, COLITIS, PNEUMONITIS, and INTESTINAL PERFORATION Fatal and/or serious hepatotoxicity occurred in 14% of Zydeligtreated patients. Monitor hepatic function prior to and during treatment. Interrupt and then reduce or discontinue Zydelig. Fatal and/or serious and severe diarrhea or colitis occurred in 14% of Zydeligtreated patients. Monitor for the developmentof severe diarrhea or colitis. Interrupt and then reduce or discontinue Zydelig. Fatal and serious pneumonitis can occur in Zydelig-treatedpatients. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms and bilateralinterstitial infiltrates. Interrupt or discontinue Zydelig. Fatal and serious intestinal perforation can occur in Zydeligtreated patients across clinical trials. Discontinue Zydelig if intestinal perforation is suspected. ZYKADIA(ceritinib) MECHANISM OF ACTION Ceritinib is a kinase inhibitor. Targets of ceritinib inhibition identified in either biochemical or cellular assays at clinically relevant concentrations include ALK, insulinlike growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), insulin receptor (InsR), and ROS1. Among these, ceritinib is most active against ALK. Ceritinib inhibited autophosphorylation of ALK, ALK-mediated phosphorylation of the downstream signaling protein STAT3, and proliferation of ALK-dependent cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo assays. Ceritinib inhibited the in vitro proliferation of cell lines expressing EML4-ALK and NPMALK fusion proteins and demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of EML4-ALK-positive NSCLC xenograft growth in mice and rats. Ceritinib exhibited dose-dependent anti-tumor activity in mice bearing EML4-ALKpositive NSCLC xenografts with demonstrated resistance to crizotinib, at concentrations within a clinically relevant range. STRUCTURE ZYKADIA (ceritinib) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for oral administration. The molecular formula for ceritinib is C28H36N5O3ClS. The molecular weight is 558.14 g/mole. Ceritinib is described chemically as 5-Chloro-N4-[2-[(1methylethyl)sulfonyl]phenyl]-N2-[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethoxy)-4-(4-piperidinyl)phenyl]-2,4pyrimidinediamine. INDICATIONS AND USAGE ZYKADIA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have progressed on or are intolerant to crizotinib. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and duration of response. An improvement in survival or disease-related symptoms has not been established. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 750 mg orally once daily. Administer ZYKADIA on an empty stomach (i.e., do not administer within 2 hours of a meal). (2.1) Capsules: 150 mg DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS None WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Severe or Persistent Gastrointestinal Toxicity: Dose modification due to diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain occurred in 38% of patients. Withhold if not responsive to anti-emetics or anti-diarrheals, then dose reduce ZYKADIA. Hepatotoxicity: ZYKADIA can cause hepatotoxicity. Monitor liver laboratory tests at least monthly. Withhold then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis: Occurred in 4% of patients. Permanently discontinue ZYKADIA in patients diagnosed with treatment-related ILD/pneumonitis. QT Interval Prolongation: ZYKADIA can cause QTc interval prolongation. Monitor electrocardiograms and electrolytes in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, electrolyte abnormalities, or those who are taking medications that are known to prolong the QTc interval. Withhold then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. Hyperglycemia: ZYKADIA can cause hyperglycemia. Monitor glucose and initiate or optimize anti-hyperglycemic medications as indicated. Withhold then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. Bradycardia: ZYKADIA can cause bradycardia. Monitor heart rate and blood pressure regularly. Withhold then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. Embryofetal Toxicity: ZYKADIA may cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions (incidence of at least 25%) are diarrhea, nausea, elevated transaminases, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, decreased appetite, and constipation. DRUG INTERACTIONS CYP3A Inhibitors and Inducers: Avoid concurrent use of ZYKADIA with strong CYP3A inhibitors or inducers. If concurrent use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce the dose of ZYKADIA. CYP3A and CYP2C9 Substrates: Avoid concurrent use of ZYKADIA with CYP3A or CYP2C9 substrates with narrow therapeutic indices. A HEARTLY THANKS TO FDA AND ALL THE CONTRIBUTORS FOR THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HEREIN. Dr. JAYESH RAJGOPAL MD PHARMACOLOGY