Key Questions from Toxicology Review w answers
advertisement

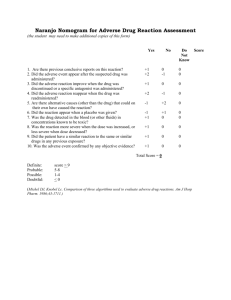
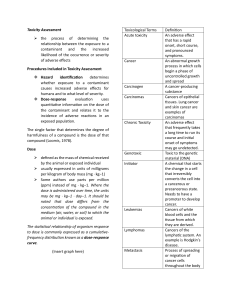
Key Questions from Toxicology Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. All substances are poisons: there is none shich is not a poison. The right dose differentiates a poison from a remedy. a. True b. False Haber’s Rule holds in that C*t = K for a substance at all combinations of concentration and time. a. True b. False Determining an Occupational Exposure Limit from animal toxicity data may be based on which of the following general approaches: a. Dose-response model extrapolation b. Benchmark dose c. Lowest Observed Adverse Effect d. No Observed Adverse Effect Level e. Adjustment factors (e.g., Lewis, Lynch, Nikiforov method) f. All the above g. None of the above Nephrotoxicity involves adverse effects on: a. Nerves b. Kidneys c. Liver d. None of the above Metabolism of a toxin always reduces its toxicity. a. True b. False For aerosols, the thoracic faction of the size distribution deposits primarily in a. The nose and throat b. The alveolar spaces c. The upper tracheal/bronchial system Antagonistic effects in a toxicological context means the toxin makes the exposed person unusually prone to anger a. True b. False The classic additive Effects Model for OEL/TLV® interpretation of mixed exposures is: 1≤ 𝐶1 𝐶2 𝐶𝑛 + + … 𝑇𝐿𝑉1 𝑇𝐿𝑉2 𝑇𝐿𝑉𝑛 a. True b. False 9. Possible route of exposure, depending on the toxic agent and use situation include: a. Inhalation b. Injection c. Dermal absorption d. Ingestion e. All the above f. a and c only 10. Teratogens belong to a general category that can also be called reproductive toxins a. True b. False