File
advertisement

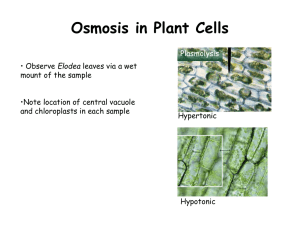
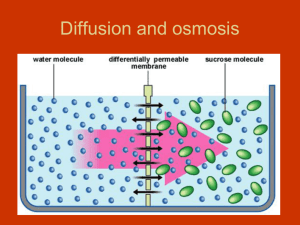
Cohesion and Adhesion The attraction of water molecules to other water molecules is called cohesion. Cohesive forces are because of the polar nature of the water molecule. The attraction of water molecules to molecules of other substances is called adhesion. water mercury Adhesive forces between the water and the walls of a test tube cause water to form a concave meniscus. In a thin capillary tube, the coloured water inches up the tube because of cohesive and adhesive forces. Root Pressure Roots take in dissolved minerals from the soil by active transport. Water then enters the root through osmosis. Root pressure plays a small part in the movement of water through the xylem when compared to transpiration pull. From Root to Leaf: Water Transport in Plants The evaporation of water through the stomata and lenticels in the process of transpiration creates a tension or transpiration pull. The Effect of Tonicity in Plant Cells A hypertonic environment has a high concentration of solutes (e.g. sea water). In a hypertonic environment, water will move out of the cell by osmosis. Plant cells will undergo plasmolysis: the cytoplasm shrinks away from the cell wall. A hypotonic environment has a low concentration of solutes (e.g. distilled water). In a hypotonic environment, water will move into the cell by osmosis. Plant cells will become turgid: the cytoplasm presses against the cell wall. Turgid Elodea cells in a hypotonic environment. Plasmolysis of Elodea cells in a hypertonic environment. From Sink to Source: Sugar Transport in Plants read pages 315 – 321 C3.4 Check and Reflect page 322 #’s 1 – 5, 8